View
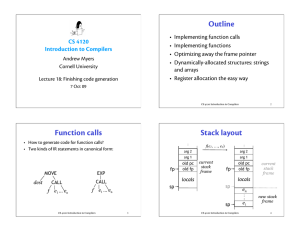
... Every time a function gets called, Python creates a new function frame, which contains the function's local variables and parameters. For a recursive function, there might be more than one frame on the stack at the same time. This figure shows a stack diagram for countdown called with n = 3: ...
... Every time a function gets called, Python creates a new function frame, which contains the function's local variables and parameters. For a recursive function, there might be more than one frame on the stack at the same time. This figure shows a stack diagram for countdown called with n = 3: ...
More Lambda Calculus
... • The debate about whether languages should be strict (CBV) or lazy (CBN) is nearly 20 years old ...
... • The debate about whether languages should be strict (CBV) or lazy (CBN) is nearly 20 years old ...
(1-4) Defining Member Functions Member functions can be defined
... cout << " Number : " << number<< "\n"; cout << " cost :" << cost <"\n"; ...
... cout << " Number : " << number<< "\n"; cout << " cost :" << cost <"\n"; ...
Control Flow - FSU Computer Science
... Selection (or alternation): a run-time condition determines the choice among two or more statements or expressions Iteration: a statement is repeated a number of times or until a run-time condition is met Procedural abstraction: subroutines encapsulate collections of statements and subroutine calls ...
... Selection (or alternation): a run-time condition determines the choice among two or more statements or expressions Iteration: a statement is repeated a number of times or until a run-time condition is met Procedural abstraction: subroutines encapsulate collections of statements and subroutine calls ...
CS 390 Unix Programming Environment
... • Parameter value is passed from calling procedure to called procedure • When the call finishes, the new parameter value overwrites the calling procedures original value • This feature is not supported by C++ • However, it holds ...
... • Parameter value is passed from calling procedure to called procedure • When the call finishes, the new parameter value overwrites the calling procedures original value • This feature is not supported by C++ • However, it holds ...
Note - CIM (McGill)
... 32 MIPS registers. These 232 bytes should not be confused with an address on a physical memory chip or a location on a disk. As we will see later in the course, MIPS Memory addresses need to be translated into physical addresses.3 You should have only a simple notion of how a MIPS computer works. Th ...
... 32 MIPS registers. These 232 bytes should not be confused with an address on a physical memory chip or a location on a disk. As we will see later in the course, MIPS Memory addresses need to be translated into physical addresses.3 You should have only a simple notion of how a MIPS computer works. Th ...
Instruction Set Principles
... General Register Machine and Instruction Formats • It is the most common choice in today’s general-purpose computers • Which register is specified by small “address” (3 to 6 bits for 8 to 64 registers) • Load and store have one long & one short address: One and half addresses • Arithmetic instructi ...
... General Register Machine and Instruction Formats • It is the most common choice in today’s general-purpose computers • Which register is specified by small “address” (3 to 6 bits for 8 to 64 registers) • Load and store have one long & one short address: One and half addresses • Arithmetic instructi ...
COS_470-Practice
... 5. Use the insert1 function created on the previous step to create a LISP function insert-sort that will recursively sort a list of numbers nums (defun insert-sort (nums) ;; define here the base case to stop the recursion: ;; if nums is empty, return an empty list ;; otherwise call insert1 appropria ...
... 5. Use the insert1 function created on the previous step to create a LISP function insert-sort that will recursively sort a list of numbers nums (defun insert-sort (nums) ;; define here the base case to stop the recursion: ;; if nums is empty, return an empty list ;; otherwise call insert1 appropria ...
Functional Programming Languages and Dataflow Principles
... Many languages: • Lisp • ML (SML, CAML, …) • Haskell ...
... Many languages: • Lisp • ML (SML, CAML, …) • Haskell ...
PL/SQL Procedures
... PL/SQL blocks executed thus far have been anonymous blocks Now we will assign a name to the block and save it in the database as a stored program unit This makes program units reusable ...
... PL/SQL blocks executed thus far have been anonymous blocks Now we will assign a name to the block and save it in the database as a stored program unit This makes program units reusable ...
Finishing code generation
... • Really no need for frame pointer register! • Idea: maintain constant offset k between frame pointer and stack pointer – Use RISC-style argument passing rather than pushing arguments on stack – All references to MEM(FP+n) translated to operand [esp+(n+k)] instead of to [ebp+n] ...
... • Really no need for frame pointer register! • Idea: maintain constant offset k between frame pointer and stack pointer – Use RISC-style argument passing rather than pushing arguments on stack – All references to MEM(FP+n) translated to operand [esp+(n+k)] instead of to [ebp+n] ...
MODULE 1 INTRODUCTION My Training Period: hours
... Both BCPL and B were typeless languages, that means the only data type is machine word and access to other kinds of objects is by special operators or function calls. In C, the fundamental data type includes characters, integers of several sizes and floating point numbers. The derived data types wer ...
... Both BCPL and B were typeless languages, that means the only data type is machine word and access to other kinds of objects is by special operators or function calls. In C, the fundamental data type includes characters, integers of several sizes and floating point numbers. The derived data types wer ...
Slide 1
... Instruction Register (IR) = Instruction being executed Accumulator (AC) = Temporary Storage ...
... Instruction Register (IR) = Instruction being executed Accumulator (AC) = Temporary Storage ...
Functions Continued
... printf (“Number:%5d\n”, num1); printf (“Number:%5.1lf\n”, num2); printf (“Number:%5.1lf\n”, num3); printf (“Number:%-5dEnd.\n”, num1); printf (“Number:%-5.1lfEnd.\n”, num2); printf (“Number:%-5.1lfEnd.\n”, num3); ...
... printf (“Number:%5d\n”, num1); printf (“Number:%5.1lf\n”, num2); printf (“Number:%5.1lf\n”, num3); printf (“Number:%-5dEnd.\n”, num1); printf (“Number:%-5.1lfEnd.\n”, num2); printf (“Number:%-5.1lfEnd.\n”, num3); ...
Introduction to Programming in Python
... - returns (or outputs) the type of the data The int, float, str conversion functions: - accept a data value as input - return the same data but as a new type Note how the output of these functions are handled in the example: • The type function output is sent back to the shell, so the shell prints t ...
... - returns (or outputs) the type of the data The int, float, str conversion functions: - accept a data value as input - return the same data but as a new type Note how the output of these functions are handled in the example: • The type function output is sent back to the shell, so the shell prints t ...
ppt
... Stack is generic to allow any type of value to be stored
Stack wordStack = new Stack();
Stack numStack = new Stack();
...
... Stack
View
... • Better understanding of the implementation of concepts • Increased ability to design new languages Slide 4 ...
... • Better understanding of the implementation of concepts • Increased ability to design new languages Slide 4 ...
Notes - Cornell Computer Science
... – What about run-time code generation and self-modification? ...
... – What about run-time code generation and self-modification? ...
Re-opening Closures
... is applied to many different input strings. Thus, the closure representation of P is surely worth optimizing in the manner described above. On the other hand, if P were just applied to one input string, then the optimization might not be cost-effective. We will introduce a new operator, reduce, into ...
... is applied to many different input strings. Thus, the closure representation of P is surely worth optimizing in the manner described above. On the other hand, if P were just applied to one input string, then the optimization might not be cost-effective. We will introduce a new operator, reduce, into ...
Working with floating point expressions
... and brackets ( ... ), we can construct arithmetic expression ...
... and brackets ( ... ), we can construct arithmetic expression ...
Functional Programming, Parametricity, Types
... theorems about this function can be reliably constructed ...
... theorems about this function can be reliably constructed ...
Programming Languages and Paradigms
... stack.h contains prototypes for push, pop stack.c contains stack code, Store and top declared static (local to stack.c) application includes stack.h Copyright 2008, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
... stack.h contains prototypes for push, pop stack.c contains stack code, Store and top declared static (local to stack.c) application includes stack.h Copyright 2008, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
Lecture 1 part a - School of Computing
... programming syntax look more like English. In the 1970s, Pascal was developed by Niklaus Wirth C was created by Dennis Ritchie while he was working at Bell Laboratories. Wirth went on to design Modula-2, and Oberon. ...
... programming syntax look more like English. In the 1970s, Pascal was developed by Niklaus Wirth C was created by Dennis Ritchie while he was working at Bell Laboratories. Wirth went on to design Modula-2, and Oberon. ...
Programming Languages and Paradigms
... stack.h contains prototypes for push, pop stack.c contains stack code, Store and top declared static (local to stack.c) application includes stack.h Copyright 2005, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
... stack.h contains prototypes for push, pop stack.c contains stack code, Store and top declared static (local to stack.c) application includes stack.h Copyright 2005, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...