Chapter 38
... this from happening again. Legislative response. Congress, fearing war after Mussolini’s invasion of Ethiopia, legislated through the Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1936 and 1937 that once the president of the US proclaims a foreign war, it would become illegal for Americans to sail on a ship of a bellige ...
... this from happening again. Legislative response. Congress, fearing war after Mussolini’s invasion of Ethiopia, legislated through the Neutrality Acts of 1935, 1936 and 1937 that once the president of the US proclaims a foreign war, it would become illegal for Americans to sail on a ship of a bellige ...
World War II Ch. 13-14 Objectives Identify and explain the causes of
... Explain the significance of the Yalta & Potsdam Conferences for Germany, Eastern Europe, Japan & the World as World War II ended. ...
... Explain the significance of the Yalta & Potsdam Conferences for Germany, Eastern Europe, Japan & the World as World War II ended. ...
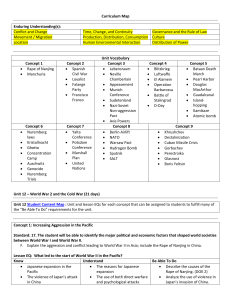
Curriculum Map Enduring Understanding(s): Conflict and Change
... C. Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Europe. D. Explain allied Post-World War II policies; include fo ...
... C. Explain the military and diplomatic negotiations between the leaders of Great Britain (Churchill), the Soviet Union (Stalin), and the United States (Roosevelt/Truman) from Tehran to Yalta and Potsdam and the impact on the nations of Europe. D. Explain allied Post-World War II policies; include fo ...
Causes of WWII - ECI Summer School 2014
... •It was clear that the organization that was set up to preserve world peace was unwilling and unable to take any action on aggressor nations. The League’s member nations were all taking isolationist approaches and would not risk starting another world war. ...
... •It was clear that the organization that was set up to preserve world peace was unwilling and unable to take any action on aggressor nations. The League’s member nations were all taking isolationist approaches and would not risk starting another world war. ...
- Kennedy HS
... Occupation zones in Germany Allowing Poland, Bulgaria, and Romania to have a representative government based on free elections A new international peace organization(United Nations) ...
... Occupation zones in Germany Allowing Poland, Bulgaria, and Romania to have a representative government based on free elections A new international peace organization(United Nations) ...
World War II, 1939–1945
... Rescue at Dunkirk After reaching the French coast, the German forces swung north again and joined with German troops in Belgium. By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille (leel). Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Al ...
... Rescue at Dunkirk After reaching the French coast, the German forces swung north again and joined with German troops in Belgium. By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille (leel). Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Al ...
Mandatory Project Guides
... Origins of Ireland and England and their relations since 1170 Reformation in England and failed effort to impose Anglican Church in Ireland Persecution of Catholics in Ireland Multiple wars of independence throughout Irish history Slow progression toward political rights in Ireland in 1800s WW I and ...
... Origins of Ireland and England and their relations since 1170 Reformation in England and failed effort to impose Anglican Church in Ireland Persecution of Catholics in Ireland Multiple wars of independence throughout Irish history Slow progression toward political rights in Ireland in 1800s WW I and ...
File - Mr. Takos` Website
... -The Non-Aggression Pact signed between Hitler and Stalin had vowed the two nations would not attack each other in a time of war -Secretly the two nations laid out plans to divide Poland between them, with the Soviets reclaiming Finland and the Baltic nations of Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia -Brita ...
... -The Non-Aggression Pact signed between Hitler and Stalin had vowed the two nations would not attack each other in a time of war -Secretly the two nations laid out plans to divide Poland between them, with the Soviets reclaiming Finland and the Baltic nations of Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia -Brita ...
Chapter 25 The World at War
... Germany’s aggression, agreeing to let Germany annex the Sudetenland—the German-speaking border areas of Czechoslovakia—in return for Hitler’s pledge to seek no more territory. Within six months, Hitler’s forces had overrun the rest of Czechoslovakia and were threatening to march into Poland. ...
... Germany’s aggression, agreeing to let Germany annex the Sudetenland—the German-speaking border areas of Czechoslovakia—in return for Hitler’s pledge to seek no more territory. Within six months, Hitler’s forces had overrun the rest of Czechoslovakia and were threatening to march into Poland. ...
World War II
... role in fighting it. How and why the U.S. foreign policy under Presidents Hoover and Roosevelt changed from disengagement to neutrality and from neutrality to total involvement? I. Herbert Hoover’s Foreign Policy Hoover concurred with the prevailing opinion of the American people that the United Sta ...
... role in fighting it. How and why the U.S. foreign policy under Presidents Hoover and Roosevelt changed from disengagement to neutrality and from neutrality to total involvement? I. Herbert Hoover’s Foreign Policy Hoover concurred with the prevailing opinion of the American people that the United Sta ...
World War II- Spring Project
... 2) DOCUMENT 1: In what year was the cartoon published? What is the main idea of this cartoon and how does it relate to the causes of World War II? 3) Why were dictators able to rise to power in Italy, Germany and the Soviet Union? 4) Who was Adolph Hitler and how did he rise to power in Germany? Wha ...
... 2) DOCUMENT 1: In what year was the cartoon published? What is the main idea of this cartoon and how does it relate to the causes of World War II? 3) Why were dictators able to rise to power in Italy, Germany and the Soviet Union? 4) Who was Adolph Hitler and how did he rise to power in Germany? Wha ...
Research Report
... à Many British at the time wanted peace. They would not support Czechoslovakia in case of a war in 1938. à Treaty of Versailles, signed at the end of World War I, proposed respect for ‘self-‐determ ...
... à Many British at the time wanted peace. They would not support Czechoslovakia in case of a war in 1938. à Treaty of Versailles, signed at the end of World War I, proposed respect for ‘self-‐determ ...
Chapter 32 - Community Unit School District 200
... Rescue at Dunkirk After reaching the French coast, the German forces swung north again and joined with German troops in Belgium. By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille (leel). Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Al ...
... Rescue at Dunkirk After reaching the French coast, the German forces swung north again and joined with German troops in Belgium. By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille (leel). Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Al ...
Introduction - Wright State University
... making large advances through Italy, it became time for the Allies to enter France. Operation Overlord, or D-Day, took place and firmly established an Allied presence in Europe. The students will study the main events, battle sites, nations involved, and major military figures involved in the D-Day ...
... making large advances through Italy, it became time for the Allies to enter France. Operation Overlord, or D-Day, took place and firmly established an Allied presence in Europe. The students will study the main events, battle sites, nations involved, and major military figures involved in the D-Day ...
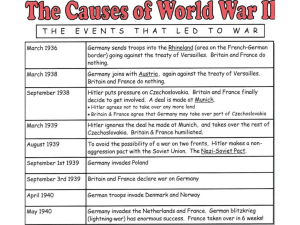
Causes of the Second World War
... Appeasement encouraged war. It made Hitler think that no one dare stop him, which encouraged him to go further and further until in the end he went too far. The Sudetenland led Stalin to make the Nazi-Soviet Pact, because he believed he could not trust Britain. ...
... Appeasement encouraged war. It made Hitler think that no one dare stop him, which encouraged him to go further and further until in the end he went too far. The Sudetenland led Stalin to make the Nazi-Soviet Pact, because he believed he could not trust Britain. ...
World War II Lecture Slides
... Hitler requested land in northern Poland (Polish Corridor) for a highway and rail line to connect Germany to East Prussia ...
... Hitler requested land in northern Poland (Polish Corridor) for a highway and rail line to connect Germany to East Prussia ...
Finals Study Guide - Get Well Kathleen Davey
... Warsaw Ghetto In the video we saw what did the Red Cross agents came to inspect the concentration camp what did they see? What was the U.S. State Department’s reaction to the Holocaust? What happened in Armenia, Cambodia, and Rwanda? 1948 Genocide Convention and Nuremeberg Trials Cold War Cold War-- ...
... Warsaw Ghetto In the video we saw what did the Red Cross agents came to inspect the concentration camp what did they see? What was the U.S. State Department’s reaction to the Holocaust? What happened in Armenia, Cambodia, and Rwanda? 1948 Genocide Convention and Nuremeberg Trials Cold War Cold War-- ...
Chapter 31: World War II & Its Aftermath
... Then, with Britain still a threat, Hitler attacked the Soviet Union Germany was seeking access to the Soviet Union’s vast mineral resources The Soviets fought back, but were defeated again and again throughout 1941 • But the fiercest winter in over a century stalled the German attack and gave the So ...
... Then, with Britain still a threat, Hitler attacked the Soviet Union Germany was seeking access to the Soviet Union’s vast mineral resources The Soviets fought back, but were defeated again and again throughout 1941 • But the fiercest winter in over a century stalled the German attack and gave the So ...
Churchill`s Southern Strategy
... Churchill’s persistence on the southern flank did not end with D-Day. In a note to his military chiefs in July 1944, Churchill said with some petulance, “Let them take their seven divisions—three American and four French. Let them monopolize all the landing craft they can reach. But at least let us ...
... Churchill’s persistence on the southern flank did not end with D-Day. In a note to his military chiefs in July 1944, Churchill said with some petulance, “Let them take their seven divisions—three American and four French. Let them monopolize all the landing craft they can reach. But at least let us ...
World War II
... 1. How did people on the home front support the war effort? 2. What government agency oversaw factory production during the war? 3. What were the WAAC and the WASP? 4. Why did A. Philip Randolph organize a march on Washington and then cancel it? 5. How did the bracero program benefit both Mexicans a ...
... 1. How did people on the home front support the war effort? 2. What government agency oversaw factory production during the war? 3. What were the WAAC and the WASP? 4. Why did A. Philip Randolph organize a march on Washington and then cancel it? 5. How did the bracero program benefit both Mexicans a ...
World War II in Europe
... Hitler wanted to own all of Europe. He planned to take Poland next. This time, both Great Britain and France told him that they would fight back if he tried. But, Hitler did not think that they would act. On September 1, 1939, he invaded Poland. This started World War II. On one side was the Axis. T ...
... Hitler wanted to own all of Europe. He planned to take Poland next. This time, both Great Britain and France told him that they would fight back if he tried. But, Hitler did not think that they would act. On September 1, 1939, he invaded Poland. This started World War II. On one side was the Axis. T ...
World History 3201: Specific Curriculum Outcomes 1.1 The student
... 3.1.5 Describe the policy of appeasement as it is related to German expansion and identify two reasons why Britain and France were prepared to follow this policy. (k) 3.1.6 Evaluate the effectiveness of appeasement in containing the territorial expansion of Nazism. (i) 3.1.7 Analyze documents to com ...
... 3.1.5 Describe the policy of appeasement as it is related to German expansion and identify two reasons why Britain and France were prepared to follow this policy. (k) 3.1.6 Evaluate the effectiveness of appeasement in containing the territorial expansion of Nazism. (i) 3.1.7 Analyze documents to com ...
Western betrayal

The concept of Western betrayal refers to the view that the United Kingdom and France failed to meet their legal, diplomatic, military and moral obligations with respect to the Czech and Polish nations of Central and Eastern Europe in the prelude to and aftermath of the Second World War.In particular, it refers to Czechoslovakia's treatment during the Munich Agreement and subsequent occupation and partition by Nazi Germany, Hungary (The First Vienna Award) and Poland (Invasion of Zaolzie), as well as the failure of the Western allies to aid Poland upon its invasion by Germany and the USSR in 1939. The same concept also refers to the concessions made by the United States and the United Kingdom to the USSR during the Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam conferences, to their stance during the Warsaw Uprising, and some other events, which allocated the region to the Soviet sphere of influence and created the Eastern Bloc.Historically, such views were intertwined with some of the most significant geopolitical events of the 20th century, including the rise and empowerment of the Third Reich (Nazi Germany), the rise of the Soviet Union (USSR) as a dominant superpower with control of large parts of Europe, and various treaties, alliances, and positions taken during and after World War II, and so on into the Cold War.