Poster
... bodies to maximize their oxygen (O2) storing potential using the protein myoglobin. Myoglobin’s structure has been known for decades, but researchers are still trying to determine just how myoglobin functions. Found in muscle tissue, myoglobin stores O2, a molecule needed to produce chemical energy. ...
... bodies to maximize their oxygen (O2) storing potential using the protein myoglobin. Myoglobin’s structure has been known for decades, but researchers are still trying to determine just how myoglobin functions. Found in muscle tissue, myoglobin stores O2, a molecule needed to produce chemical energy. ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined Stoichiometry ...
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been determined Stoichiometry ...
Chapter 5: Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Therefore, we need a conversion factor to convert atoms and molecules to grams. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Avogadro's number The name "Avogadro's Number" is just an honorary name attached to the calculated value of the number of atoms, molecules, etc. in ...
... Therefore, we need a conversion factor to convert atoms and molecules to grams. Mole is the connection or the conversion factor between atoms and grams. Avogadro's number The name "Avogadro's Number" is just an honorary name attached to the calculated value of the number of atoms, molecules, etc. in ...
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been Stoichiometry determined ...
... analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been Stoichiometry determined ...
+ 2 H2O(l Ca(OH)2 aq)
... c) Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is a nonmetal oxide that reacts with oxygen, O2, to form the higher oxide, SO3. Δ 2 SO (g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ── ...
... c) Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is a nonmetal oxide that reacts with oxygen, O2, to form the higher oxide, SO3. Δ 2 SO (g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ── ...
Answers 1998 Free Response
... Response must indicate a clear ethanol structure (Lewis diagram not necessary) 1 point The hydroxyl group forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Response must mention/indicate involvement of hydroxyl group Point earned for "Ethanol is more polar than dimethyl ether", but no point earned for "dim ...
... Response must indicate a clear ethanol structure (Lewis diagram not necessary) 1 point The hydroxyl group forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Response must mention/indicate involvement of hydroxyl group Point earned for "Ethanol is more polar than dimethyl ether", but no point earned for "dim ...
LECTURE_pptnotes Fipps Stochiometry
... may not be the simplest ratio of elements. If the molar mass of the compound is experimentally shown to be 90.0 g/mol, what is the molecular formula of this covalent compound? ...
... may not be the simplest ratio of elements. If the molar mass of the compound is experimentally shown to be 90.0 g/mol, what is the molecular formula of this covalent compound? ...
Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... The molecular formula can be determined with both % Composition and Molar Mass A sample of a compound contains 30.46% Nitrogen and 69.54% Oxygen by mass In a separate experiment, the molar mass of the compound is estimated to be between 90 g and 95 g. Determine the molecular formula and the accurate ...
... The molecular formula can be determined with both % Composition and Molar Mass A sample of a compound contains 30.46% Nitrogen and 69.54% Oxygen by mass In a separate experiment, the molar mass of the compound is estimated to be between 90 g and 95 g. Determine the molecular formula and the accurate ...
Chemical Quantities(mole).
... Empirical Formulas The formula of a compound having the smallest wholenumber ratio of atoms in the compound is called the empirical formula. Chemical formulas for ionic compounds are the same as their empirical formulas. For covalent compounds they are not the same. For example, many covalent compo ...
... Empirical Formulas The formula of a compound having the smallest wholenumber ratio of atoms in the compound is called the empirical formula. Chemical formulas for ionic compounds are the same as their empirical formulas. For covalent compounds they are not the same. For example, many covalent compo ...
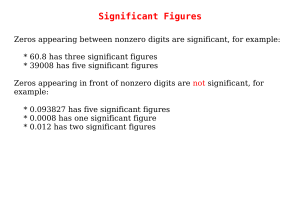
Significant Figures
... The mass of 1 mol of a substance in grams is defined as it’s molar mass. Since a mol of a substance is an Avogadro’s number of particles we can simply use the numerical value of the atomic mass of the element from the periodic table in grams units to find the molar mass. Thus: The molar mass of H at ...
... The mass of 1 mol of a substance in grams is defined as it’s molar mass. Since a mol of a substance is an Avogadro’s number of particles we can simply use the numerical value of the atomic mass of the element from the periodic table in grams units to find the molar mass. Thus: The molar mass of H at ...
book chapter on saddle point searches
... this calculation is the search for the relevant saddle points. Again, the mechanism of the transition is reflected in the saddle point. The reaction coordinate at the saddle point is the direction of the unstable mode (the normal mode with negative eigenvalue). After a saddle point has been found, o ...
... this calculation is the search for the relevant saddle points. Again, the mechanism of the transition is reflected in the saddle point. The reaction coordinate at the saddle point is the direction of the unstable mode (the normal mode with negative eigenvalue). After a saddle point has been found, o ...
Stoichiometry - coercingmolecules
... Cu2S) by a multistep process. After an initial grinding, the first step is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with O2) to form Cu2O and SO2 2Cu2S(s) + 3O2(g) ...
... Cu2S) by a multistep process. After an initial grinding, the first step is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with O2) to form Cu2O and SO2 2Cu2S(s) + 3O2(g) ...
M - coercingmolecules
... Cu2S) by a multistep process. After an initial grinding, the first step is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with O2) to form Cu2O and SO2 2Cu2S(s) + 3O2(g) ...
... Cu2S) by a multistep process. After an initial grinding, the first step is to “roast” the ore (heat it strongly with O2) to form Cu2O and SO2 2Cu2S(s) + 3O2(g) ...
Homework Chapter 6
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
Mole and Energy - Deans Community High School
... Mole and gas volume The molar gas volume of a gas is its volume per mole, litre mol-1 It is temperature and pressure dependant. The molar volume of all gases is approximately 24 litre mol-1 at 20oC and 22.4 litre mol-1 at 0oC. ...
... Mole and gas volume The molar gas volume of a gas is its volume per mole, litre mol-1 It is temperature and pressure dependant. The molar volume of all gases is approximately 24 litre mol-1 at 20oC and 22.4 litre mol-1 at 0oC. ...
Measurements
... Magnesium chloride is an example of a strong electrolyte. In 0.44 M MgCl2 solution, 70% of the magnesium is free Mg2 and 30% is MgCl .3 The concentration of MgCl2 molecules is close to 0. Sometimes the molarity of a strong electrolyte is called the formal concentration (F), to emphasize that the su ...
... Magnesium chloride is an example of a strong electrolyte. In 0.44 M MgCl2 solution, 70% of the magnesium is free Mg2 and 30% is MgCl .3 The concentration of MgCl2 molecules is close to 0. Sometimes the molarity of a strong electrolyte is called the formal concentration (F), to emphasize that the su ...
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
Homework Chapter 6 - Chemistry
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
... natural gas (methane) must be burned to supply this energy? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H°rxn= –890.4 kJ/mol A) 1.4 103 g D) 2.2 104 g B) 3.6 105 g E) 1.4 104 g ...
Stoichiometric Conversions
... Predict the products and write a balanced equation for the following: ...
... Predict the products and write a balanced equation for the following: ...
Unit 1 Mole and enthalpy changes
... Thermochemistry is the study of heat energy taken in or given out in chemical reactions. This heat, absorbed or released, can be related to the internal energy of the substances involved. Such internal energy is called ENTHALPY, symbol H. As it is only possible to measure the change in enthalpy, the ...
... Thermochemistry is the study of heat energy taken in or given out in chemical reactions. This heat, absorbed or released, can be related to the internal energy of the substances involved. Such internal energy is called ENTHALPY, symbol H. As it is only possible to measure the change in enthalpy, the ...