Cell Division - Sehome High School
... • Each duplicated chromosome is pulled apart • one chromatid goes one direction & the other moves the other direction ...
... • Each duplicated chromosome is pulled apart • one chromatid goes one direction & the other moves the other direction ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Study Guide
... Part I. Meiosis vs. Mitosis. For each statement below, identify whether it refers to mitosis or meiosis. Write “MI” for mitosis and “ME” for Meiosis 1. Occurs in body cells, such as skin or bones. ______ 2. Occurs in sex cells. _____ ...
... Part I. Meiosis vs. Mitosis. For each statement below, identify whether it refers to mitosis or meiosis. Write “MI” for mitosis and “ME” for Meiosis 1. Occurs in body cells, such as skin or bones. ______ 2. Occurs in sex cells. _____ ...
MEIOSIS WEBQUEST PART B: Meiosis Please go to the following
... PART B: Meiosis Please go to the following webpage: http://www.lewport.wnyric.org/jwanamaker/animations/meiosis.html or http://www.cellsalive.com/meiosis.htm 1. Why is the meiosis important? _____________________________________________________ 2. Start the animation. What do the chromosomes do in P ...
... PART B: Meiosis Please go to the following webpage: http://www.lewport.wnyric.org/jwanamaker/animations/meiosis.html or http://www.cellsalive.com/meiosis.htm 1. Why is the meiosis important? _____________________________________________________ 2. Start the animation. What do the chromosomes do in P ...
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Test Review Sheet
... 1. Describe the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. 2. Why are cells so small? 3. What is the relationship of surface area to volume ratio? 4. Is it better to have a high (like 600:1) or low (like 2:1) SA/V ratio and why? 5. 90% of the time, DNA can be found in what form? 6. Draw a c ...
... 1. Describe the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. 2. Why are cells so small? 3. What is the relationship of surface area to volume ratio? 4. Is it better to have a high (like 600:1) or low (like 2:1) SA/V ratio and why? 5. 90% of the time, DNA can be found in what form? 6. Draw a c ...
Mitosis
... • The identical chromatids are separated from each other…. But now they are normal sized chromosomes! • Will the two daughter cells be genetically identical? ...
... • The identical chromatids are separated from each other…. But now they are normal sized chromosomes! • Will the two daughter cells be genetically identical? ...
Classroom Presentation
... our dad.) crossing over to exchange material Metaphase I have the homologous pairs line up at the equator of the cell and in Anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and thus reducing the chromosome number in each cell. 2nd Division of Meiosis is exactly like mitosis, except that 2 cells star ...
... our dad.) crossing over to exchange material Metaphase I have the homologous pairs line up at the equator of the cell and in Anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and thus reducing the chromosome number in each cell. 2nd Division of Meiosis is exactly like mitosis, except that 2 cells star ...
Module B Assessment Anchor B
... b. Nuclear division i. The DNA is divided ii. Mitosis divides nuclear material once 1. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase iii. Meiosis divides nuclear material twice 1. Prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II c. Cytokinesis i. Cyto ...
... b. Nuclear division i. The DNA is divided ii. Mitosis divides nuclear material once 1. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase iii. Meiosis divides nuclear material twice 1. Prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II c. Cytokinesis i. Cyto ...
Prophase II
... lengthening of the chromosomes and the disappearance of the spindle. Nuclear envelopes reform and cleavage or cell wall formation eventually produces a total of four daughter cells, each with a haploid set of chromosomes. ...
... lengthening of the chromosomes and the disappearance of the spindle. Nuclear envelopes reform and cleavage or cell wall formation eventually produces a total of four daughter cells, each with a haploid set of chromosomes. ...
Mitosis vs. Meiosis - Ms. Ottolini`s Biology Wiki!
... microscopists identified specific arrangements or patterns of chromosomes that occurred at various stages of the cycle and gave these stages names (e.g. interphase, anaphase, etc.). Later work using time-lapse photography made it clear that mitosis and meiosis are continuous processes. Once division ...
... microscopists identified specific arrangements or patterns of chromosomes that occurred at various stages of the cycle and gave these stages names (e.g. interphase, anaphase, etc.). Later work using time-lapse photography made it clear that mitosis and meiosis are continuous processes. Once division ...
Clicker review w/answers
... D no set number 12 Which function below makes meiosis more complicated than mitosis? A decreasing the chromosome number to haploid B introducing genetic variation among the daughter cells C ensuring that each daughter cell gets a single, complete set of chromosomes D undergoing two rounds of cytokin ...
... D no set number 12 Which function below makes meiosis more complicated than mitosis? A decreasing the chromosome number to haploid B introducing genetic variation among the daughter cells C ensuring that each daughter cell gets a single, complete set of chromosomes D undergoing two rounds of cytokin ...
Homologous chromosome
... If a normal gamete fertilizes a gamete with nondisjunction, the fertilized egg will have either one more or one less copy of an autosomal or gonosomal chromosome. ...
... If a normal gamete fertilizes a gamete with nondisjunction, the fertilized egg will have either one more or one less copy of an autosomal or gonosomal chromosome. ...
You Light Up My Life
... poles • The cytoplasm divides • There are now two haploid cells • This completes Meiosis I ...
... poles • The cytoplasm divides • There are now two haploid cells • This completes Meiosis I ...
Document
... • A cell containing 40 chromatids at the beginning of meiosis would, at its completion, produce cells containing how many chromosomes? ...
... • A cell containing 40 chromatids at the beginning of meiosis would, at its completion, produce cells containing how many chromosomes? ...
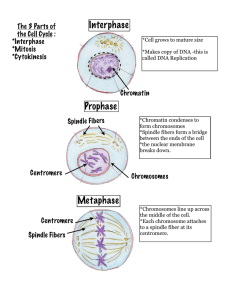
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
Lesson 15d Meiosis PPT - Educational Excellence
... with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. ...
... with each daughter containing only one chromosome of the homologous pair. ...
Cell Division - cloudfront.net
... - Gametes contain only a , and therefore only a single set of genes. These cells are ...
... - Gametes contain only a , and therefore only a single set of genes. These cells are ...
Name
... meiosis. This produces a cell that is said to be haploid. o Regular cells (called __________________) have their chromosomes arranged in pairs called _____________________________. Homologous chromosomes: Pairs of chromosomes are called _______________________________. Homologous chromosomes are the ...
... meiosis. This produces a cell that is said to be haploid. o Regular cells (called __________________) have their chromosomes arranged in pairs called _____________________________. Homologous chromosomes: Pairs of chromosomes are called _______________________________. Homologous chromosomes are the ...
LEARNING GOALS - CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
... course and the AP Exam. c. Meiosis, a reduction division, followed by fertilization ensures genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms. 1. Meiosis ensures that each gamete receives one complete haploid (1n) set of chromosomes. 2. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes are paired, with one h ...
... course and the AP Exam. c. Meiosis, a reduction division, followed by fertilization ensures genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms. 1. Meiosis ensures that each gamete receives one complete haploid (1n) set of chromosomes. 2. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes are paired, with one h ...
Academic Biology Need to Know List Cell Division: Mitosis and
... Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle where one copy of the DNA is distributed into each of the daughter cells. a. Cytokinesis is the part of the cell cycle where the cytoplasm divides. b. Chromosomes are condensed forms of the chromatin. You only see them during cell division. c. Histones d. Nucle ...
... Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle where one copy of the DNA is distributed into each of the daughter cells. a. Cytokinesis is the part of the cell cycle where the cytoplasm divides. b. Chromosomes are condensed forms of the chromatin. You only see them during cell division. c. Histones d. Nucle ...
The Cell Cycle
... The Cell Cycle • Consists of G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis ...
... The Cell Cycle • Consists of G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.