Meiosis II
... cells and gametes. • Somatic Cells: • Are body cells • Make up all cells in body except for egg and sperm cells ...
... cells and gametes. • Somatic Cells: • Are body cells • Make up all cells in body except for egg and sperm cells ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Powerpoint Notes
... single or double stranded? 91. After one division, how many chromosomes are in the cells? Are they single or double stranded? 92. After the second division, how many chromosomes are in the cells? Are they double or single stranded? 93. Is meiosis sexual or asexual reproduction? 94. Are eggs & sperm ...
... single or double stranded? 91. After one division, how many chromosomes are in the cells? Are they single or double stranded? 92. After the second division, how many chromosomes are in the cells? Are they double or single stranded? 93. Is meiosis sexual or asexual reproduction? 94. Are eggs & sperm ...
celldivision ppt questions
... 80a. Do chromosomes replicate or double before meiosis? 81a. How many divisions occur in meiosis? Is this the same as mitosis? Explain. ...
... 80a. Do chromosomes replicate or double before meiosis? 81a. How many divisions occur in meiosis? Is this the same as mitosis? Explain. ...
File - Ms. Richards IB Biology HL
... Independent Assortment of chromosomes 1. Orientation of the homologous pair of chromosomes (one maternal and one paternal) is RANDOM. 50-50 chance that each gamete receives maternal or paternal derived chromosome 2. Each homologous pair of chromosomes orients independently of the other pairs at met ...
... Independent Assortment of chromosomes 1. Orientation of the homologous pair of chromosomes (one maternal and one paternal) is RANDOM. 50-50 chance that each gamete receives maternal or paternal derived chromosome 2. Each homologous pair of chromosomes orients independently of the other pairs at met ...
Cell Division Vocabulary Mitosis and Meiosis Directions: Complete
... Humans have 22 pairs or 44 total autosomes. Genes such as height and hair color are on these. ...
... Humans have 22 pairs or 44 total autosomes. Genes such as height and hair color are on these. ...
Name________________________ Date____________
... 1. How many single chromosomes do humans have in their body cells? ______ 2. How many chromosome pairs do humans have in their body cells? ______ 3. How many single chromosomes do humans have in their sex cells? ______ 4. How many chromosome pairs do humans have in their sex cells? ______ 5. How man ...
... 1. How many single chromosomes do humans have in their body cells? ______ 2. How many chromosome pairs do humans have in their body cells? ______ 3. How many single chromosomes do humans have in their sex cells? ______ 4. How many chromosome pairs do humans have in their sex cells? ______ 5. How man ...
Week 6 Notes Probability and Heredity & The Cell and
... II. The Cell and Inheritance A. CHROMOSOMES and INHERITANCE a. Sex cells have __HALF__ the number of __CHROMOSOMES__ than other __CELLS__ ...
... II. The Cell and Inheritance A. CHROMOSOMES and INHERITANCE a. Sex cells have __HALF__ the number of __CHROMOSOMES__ than other __CELLS__ ...
Study Guide for AP Biology Mid-term Biochemistry What is
... 2. What environmental conditions can decrease photosynthetic yield? 3. The most ATP is made during which part of aerobic respiration? 4. Why would club soda cause a plant to grow bigger? 5. Metabolic process common in aerobic respiration and alcoholic fermentation 6. How are simple diffusion and fac ...
... 2. What environmental conditions can decrease photosynthetic yield? 3. The most ATP is made during which part of aerobic respiration? 4. Why would club soda cause a plant to grow bigger? 5. Metabolic process common in aerobic respiration and alcoholic fermentation 6. How are simple diffusion and fac ...
File - Mr. Doyle SUIS Science
... meiosis, and all three occur in meiosis l (detailed descriptions are level 2 items): 1. Synapsis and crossing over in prophase I: Homologous chromosomes physically connect and exchange genetic information. ...
... meiosis, and all three occur in meiosis l (detailed descriptions are level 2 items): 1. Synapsis and crossing over in prophase I: Homologous chromosomes physically connect and exchange genetic information. ...
File - Varsity Field
... During sexual reproduction: Diploid parental cells meiosis Haploid gametes or spores Male and female gametes fuse during fertilisation to form a diploid zygote. ...
... During sexual reproduction: Diploid parental cells meiosis Haploid gametes or spores Male and female gametes fuse during fertilisation to form a diploid zygote. ...
Ch. 10.4: Meiosis & Mendel`s Principles
... meiosis & fertilization accounts for inheritance patterns. ...
... meiosis & fertilization accounts for inheritance patterns. ...
chapter 6 lesson 2
... cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • When cells have pairs of similar chromosomes, they are said to be diploid. • Because sex cells do not have pairs of chromosomes, they are said to be haploid. • They have only HALF the number of chromosomes as body cells. • Haploid means “single form.” ...
... cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes. • When cells have pairs of similar chromosomes, they are said to be diploid. • Because sex cells do not have pairs of chromosomes, they are said to be haploid. • They have only HALF the number of chromosomes as body cells. • Haploid means “single form.” ...
Unit 3
... chromosomes (each pole will form a new nucleus that will have half the number of chromosomes, but each chromosome will contain two chromatids. Prophase 2: the nuclear envelope disappears and the spindle apparatus develops (no chiasmata and no crossing over). Metaphase 2: chromosomes align singly on ...
... chromosomes (each pole will form a new nucleus that will have half the number of chromosomes, but each chromosome will contain two chromatids. Prophase 2: the nuclear envelope disappears and the spindle apparatus develops (no chiasmata and no crossing over). Metaphase 2: chromosomes align singly on ...
Reading: The Cells of Genetic Continuity
... Meiosis is the process that produces sex cells. This process reduces the chromosome number to half. The female reproductive cell (ovum or egg) develops by a process called oogenesis. At birth, a human female contains about 400,000 primary oocytes in her ovary. These oocytes contain 46 chromosomes (t ...
... Meiosis is the process that produces sex cells. This process reduces the chromosome number to half. The female reproductive cell (ovum or egg) develops by a process called oogenesis. At birth, a human female contains about 400,000 primary oocytes in her ovary. These oocytes contain 46 chromosomes (t ...
Cell Division! - Cipriano`s Science Spot
... Meiosis is the type of cell division by which gametes (eggs and sperm) are produced. Makes gametes used in sexual reproduction. ...
... Meiosis is the type of cell division by which gametes (eggs and sperm) are produced. Makes gametes used in sexual reproduction. ...
Ch 11 RNO
... 7. Summarize the following phases of Meiosis I: a. Prophase I i. What is a tetrad? ii. What is the effect of crossing over? b. Metaphase I and Anaphase I c. Telophase I and Cytokinesis d. What is the end product of Meiosis I? BE SPECIFIC 8. Summarize the following phases of Meiosis II: a. Prophase I ...
... 7. Summarize the following phases of Meiosis I: a. Prophase I i. What is a tetrad? ii. What is the effect of crossing over? b. Metaphase I and Anaphase I c. Telophase I and Cytokinesis d. What is the end product of Meiosis I? BE SPECIFIC 8. Summarize the following phases of Meiosis II: a. Prophase I ...
Meiosis and Genetic Variation
... with one another: – Some of the chromatids are very clos to each other. – One chromatid from each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to the other chromosome (there is a swap of DNA between chromatids). – Crossing over (the swap of DNA) can occur multiple times within the same pair of homologous ch ...
... with one another: – Some of the chromatids are very clos to each other. – One chromatid from each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to the other chromosome (there is a swap of DNA between chromatids). – Crossing over (the swap of DNA) can occur multiple times within the same pair of homologous ch ...
Mitosis, Meiosis, Chromosomes and DNA Replication
... 22. If a cell is diploid with 40 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each new cell have after MEIOSIS? ______ 23. What is the advantage of sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction? ____________________________ 24. Which type of cell, somatic or gamete, is more likely to pass a change/ ...
... 22. If a cell is diploid with 40 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each new cell have after MEIOSIS? ______ 23. What is the advantage of sexual reproduction compared to asexual reproduction? ____________________________ 24. Which type of cell, somatic or gamete, is more likely to pass a change/ ...
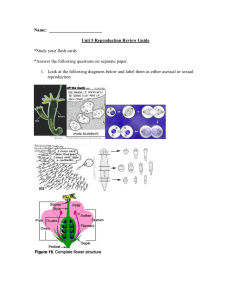
Name - gst boces
... *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
... *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
Biology Notes - Chapter 6 SECTION 1
... This is basically like the PMAT of a regular mitosis. Prophase I the duplicated DNA condenses into compact structures, the nuclear envelope surrounding the DNA begins to break down. Metaphase I the chromosomes align in the center of the cell, centrioles move to the polar ends of the cell and p ...
... This is basically like the PMAT of a regular mitosis. Prophase I the duplicated DNA condenses into compact structures, the nuclear envelope surrounding the DNA begins to break down. Metaphase I the chromosomes align in the center of the cell, centrioles move to the polar ends of the cell and p ...
Meiosis PPT
... are pulled apart - the end result is four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes. These develop into gametes. ...
... are pulled apart - the end result is four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes. These develop into gametes. ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.