cell and cell division - Sinoe Medical Association
... Mitosis identically replicates this information ...
... Mitosis identically replicates this information ...
Date
... d. usually involves one origin of replication per chromosome e. in eukaryotes takes place only in the cytoplasm ...
... d. usually involves one origin of replication per chromosome e. in eukaryotes takes place only in the cytoplasm ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Colorado Mountain College
... How Meiosis Introduces Variations in Traits • Two events in meiosis introduce novel combinations of alleles into gametes: • Crossing over in prophase I • Segregation of chromosomes into gametes • Along with fertilization, these events contribute to the variation in combinations of traits among the ...
... How Meiosis Introduces Variations in Traits • Two events in meiosis introduce novel combinations of alleles into gametes: • Crossing over in prophase I • Segregation of chromosomes into gametes • Along with fertilization, these events contribute to the variation in combinations of traits among the ...
genetics_self learning
... 1. Meiosis is a kind of cell division. Meiosis involves division of nucleus alone. This is only a kind of nuclear division. Cell division includes cytoplasmic and nuclear division. 2. Every characteristic is controlled by a pair of genes. Many characteristics are controlled not by one of genes, but ...
... 1. Meiosis is a kind of cell division. Meiosis involves division of nucleus alone. This is only a kind of nuclear division. Cell division includes cytoplasmic and nuclear division. 2. Every characteristic is controlled by a pair of genes. Many characteristics are controlled not by one of genes, but ...
B2.5 simple inheritance in plant and animals exam question
... Meiosis and mitosis are different types of division in human cells. Compare the two processes by referring to where each takes place and the kind of products that are made. ...
... Meiosis and mitosis are different types of division in human cells. Compare the two processes by referring to where each takes place and the kind of products that are made. ...
File
... Meiosis Versus Mitosis 2 major Differences 1st major difference Meiosis produces 4 new offspring cells, each with 1 set of chromosomes o 1/2 the # of chromosomes as parent cell Mitosis produces 2 offspring cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 2nd major ...
... Meiosis Versus Mitosis 2 major Differences 1st major difference Meiosis produces 4 new offspring cells, each with 1 set of chromosomes o 1/2 the # of chromosomes as parent cell Mitosis produces 2 offspring cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 2nd major ...
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
... variation by combining DNA, producing chromosomes with new combinations of maternal and paternal alleles Animation: Genetic Variation ...
... variation by combining DNA, producing chromosomes with new combinations of maternal and paternal alleles Animation: Genetic Variation ...
The Protista: Evolution`s 2nd Wave Evidence for the Endosymbiotic
... Chloroplast containing algae ...
... Chloroplast containing algae ...
Bio 103 Lecture - Mitosis and Meiosis
... what do we call cells that have two sets of chromosomes? what do we call cells that have one set of chromosomes? what is the diploid chromosome number for humans? what is the haploid chromosome number for humans? if a dog's somatic cells have 66 chromosomes then what would we say is the dog's diploi ...
... what do we call cells that have two sets of chromosomes? what do we call cells that have one set of chromosomes? what is the diploid chromosome number for humans? what is the haploid chromosome number for humans? if a dog's somatic cells have 66 chromosomes then what would we say is the dog's diploi ...
The cell cycle Section review model answers The cell cycle
... The cell cycle Section review model answers 1. The cell cycle describes all of the stages a cell goes through in its life. Cytokinesis is the last stage of cell reproduction when a cell’s cytoplasm is split between the two new cells. 2. C 3. Chromosomes need to be copied so that the two new cells ha ...
... The cell cycle Section review model answers 1. The cell cycle describes all of the stages a cell goes through in its life. Cytokinesis is the last stage of cell reproduction when a cell’s cytoplasm is split between the two new cells. 2. C 3. Chromosomes need to be copied so that the two new cells ha ...
Biology 50 - BrainMass
... paternal chromosomes). Another student in your lab tells you that only one-fourth of the gametes produced by meiosis in this parasite will have all of it’s chromosomes from either maternal or paternal origin (i.e. all the chromosomes from dad or all the chromosomes from mom). Assume that meiosis in ...
... paternal chromosomes). Another student in your lab tells you that only one-fourth of the gametes produced by meiosis in this parasite will have all of it’s chromosomes from either maternal or paternal origin (i.e. all the chromosomes from dad or all the chromosomes from mom). Assume that meiosis in ...
Chapter Expectations Language of Biology
... • Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in reproductive organs. (5.2) • Meiosis involves two sequences known as Meiosis I and Meiosis II. (5.2) • Genetic variation in gametes is a result of the re-assortment of genes on chromosomes by the processes of crossing over and random assortment. (5 ...
... • Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in reproductive organs. (5.2) • Meiosis involves two sequences known as Meiosis I and Meiosis II. (5.2) • Genetic variation in gametes is a result of the re-assortment of genes on chromosomes by the processes of crossing over and random assortment. (5 ...
Meiosis I
... have sets of chromosomes and alleles that are different from each other and from the diploid parent cell that entered meiosis I. ...
... have sets of chromosomes and alleles that are different from each other and from the diploid parent cell that entered meiosis I. ...
Chapter 8 Cell Reproduction
... chromosomes (“tetra” means 4)….because there are 4 chromatids in each pair. Chromosomes line up lengthwise gene for gene. Crossing Over – sometimes occurs at this point (see fig. 8-10 on pg. 154). This results in a mixing of genes = more variety. ...
... chromosomes (“tetra” means 4)….because there are 4 chromatids in each pair. Chromosomes line up lengthwise gene for gene. Crossing Over – sometimes occurs at this point (see fig. 8-10 on pg. 154). This results in a mixing of genes = more variety. ...
Cell Division
... Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells-each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes ...
... Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells-each with its own nucleus with identical chromosomes ...
Name Date ______ Period
... the chromosomes and C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ which divides the cytoplasm. 2. Bacteria divide using B __ __ __ __ __ F __ __ __ __ __ __ instead of mitosis. 3. In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell; In M __ __ ...
... the chromosomes and C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ which divides the cytoplasm. 2. Bacteria divide using B __ __ __ __ __ F __ __ __ __ __ __ instead of mitosis. 3. In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell; In M __ __ ...
What is Meiosis? - Manhasset Public Schools
... This is the ONLY time during meiosis that the chromosomes replicate ...
... This is the ONLY time during meiosis that the chromosomes replicate ...
Cell division and chromosomes - questions
... 9 Give two examples in each case of organs or tissues in which you would expect (a) meiosis, (b) mitosis to be taking place. ...
... 9 Give two examples in each case of organs or tissues in which you would expect (a) meiosis, (b) mitosis to be taking place. ...
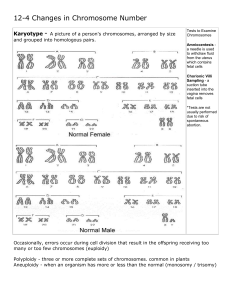
Changes in Chromosome Number
... A picture of a person's chromosomes, arranged by size and grouped into homologous pairs. ...
... A picture of a person's chromosomes, arranged by size and grouped into homologous pairs. ...
Chapter 11 Powerpoint File
... • The reappearance indicated that at some point the allele for shortness had been separated from the allele for tallness • Mendel suggested that the alleles for tallness and shortness in the F1 plants were segregated from each other during the formation of sex cells or gametes • When each F1 plant f ...
... • The reappearance indicated that at some point the allele for shortness had been separated from the allele for tallness • Mendel suggested that the alleles for tallness and shortness in the F1 plants were segregated from each other during the formation of sex cells or gametes • When each F1 plant f ...
AP Biology 2015 - 2016 Cerveny Lab Bench Investigation: Mitosis
... Explain what is meant by the statement, homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical? ...
... Explain what is meant by the statement, homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical? ...
Text and cd/web guide for meiosis
... Refer to Key words on page 202 while you work through this exercise. You may omit the following words: adult stem cell, blastocyst, cell plate, centrosome, crossing over, embryonic stem cell, G0 phase, genetic recombination, inner cell mass, karyotype, kinetochore, morula, multipotent, pluripotent, ...
... Refer to Key words on page 202 while you work through this exercise. You may omit the following words: adult stem cell, blastocyst, cell plate, centrosome, crossing over, embryonic stem cell, G0 phase, genetic recombination, inner cell mass, karyotype, kinetochore, morula, multipotent, pluripotent, ...
I. What is Meiosis? II. Chromosomes and Chromosome Number
... This is the ONLY time during meiosis that the chromosomes replicate ...
... This is the ONLY time during meiosis that the chromosomes replicate ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.