Practice Exam 3- 4/3 Below are sample questions from your book, a
... 5. Which of the following does not occur during mitosis? a. condensation of the chromosomes b. replication of the DNA c. separation of sister chromatids d. spindle formation e. separation of the spindle poles 6. A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome in a. a sperm b. an egg c. a zy ...
... 5. Which of the following does not occur during mitosis? a. condensation of the chromosomes b. replication of the DNA c. separation of sister chromatids d. spindle formation e. separation of the spindle poles 6. A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome in a. a sperm b. an egg c. a zy ...
Cell Division When a cell reaches its maximum size, the nucleus
... b. cell division (mitosis) B. Interphase: 1. occurs between divisions 2. during interphase, the cell produces all of the material necessary for cell growth and for cell division 3. Interphase – longest part of the cell cycle (90%) 4. Includes replication (copying) of the genetic material before cell ...
... b. cell division (mitosis) B. Interphase: 1. occurs between divisions 2. during interphase, the cell produces all of the material necessary for cell growth and for cell division 3. Interphase – longest part of the cell cycle (90%) 4. Includes replication (copying) of the genetic material before cell ...
Human Genome notes
... • In pedigrees, circles represent females and squares represent males • Symbols that are shaded indicates the individual expresses the trait • No shading means the trait is not exhibited • Important to understand that most traits are polygenic and also can be influenced by ...
... • In pedigrees, circles represent females and squares represent males • Symbols that are shaded indicates the individual expresses the trait • No shading means the trait is not exhibited • Important to understand that most traits are polygenic and also can be influenced by ...
Name:
... 11. How many chromosomes do human somatic cells have during prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase? a. 1N b. 2N c. 4N d. 8N 12. Describe the phase of mitosis that occurs after chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. ...
... 11. How many chromosomes do human somatic cells have during prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase? a. 1N b. 2N c. 4N d. 8N 12. Describe the phase of mitosis that occurs after chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. ...
Goal 3 Guided Worksheet
... a. Transgenic organisms (plants, animals, & bacteria) are used in agriculture and industry pharmaceutical applications such as the production of _____________________ b. The steps in bacterial transformation i. insertion of a ______________into a bacterial plasmid, ii. getting bacteria to take in th ...
... a. Transgenic organisms (plants, animals, & bacteria) are used in agriculture and industry pharmaceutical applications such as the production of _____________________ b. The steps in bacterial transformation i. insertion of a ______________into a bacterial plasmid, ii. getting bacteria to take in th ...
Question 1 The female gamete is the spore. sperm. egg. zygote
... Mitosis produces gametes. Gametes are haploid. ...
... Mitosis produces gametes. Gametes are haploid. ...
MITOSIS HW
... 2. As a result of mitosis, a cell having 10 chromosomes will give rise to two cells each that have 20 chromosomes _____. 3. DNA replication occurs during prophase _____. 4. Anaphase is the first phase of mitosis _____. 5. During prophase, the centrioles separate from each other and take up positions ...
... 2. As a result of mitosis, a cell having 10 chromosomes will give rise to two cells each that have 20 chromosomes _____. 3. DNA replication occurs during prophase _____. 4. Anaphase is the first phase of mitosis _____. 5. During prophase, the centrioles separate from each other and take up positions ...
10 Biology Exam Review 2015
... Genetic diversity results from sexual reproduction because of: combination of DNA from two different parents; independent assortment of a person’s pairs of chromosomes into different gametes; crossing over, mutation. Genetic diversity allows some members of populations to have more fit traits than o ...
... Genetic diversity results from sexual reproduction because of: combination of DNA from two different parents; independent assortment of a person’s pairs of chromosomes into different gametes; crossing over, mutation. Genetic diversity allows some members of populations to have more fit traits than o ...
Practice Exam 3
... 4.) Mitosis is important because: a. cells that wear out and die need to be replaced b. it produces genetically identical cells c. some organisms use it to reproduce asexually d. all of the above are true 5.) A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is: a. a somatic cell of a male b. ...
... 4.) Mitosis is important because: a. cells that wear out and die need to be replaced b. it produces genetically identical cells c. some organisms use it to reproduce asexually d. all of the above are true 5.) A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is: a. a somatic cell of a male b. ...
Science EQT Study Guide: 2nd Quarter
... An organism with the genotype Dd is crossed with an organism of the same 31 genotype. Using a Punnett square, what is the RATIO of offspring displaying the dominant allele to offspring displaying the recessive allele? During the formation of gametes, the 2 alleles responsible for a trait separate fr ...
... An organism with the genotype Dd is crossed with an organism of the same 31 genotype. Using a Punnett square, what is the RATIO of offspring displaying the dominant allele to offspring displaying the recessive allele? During the formation of gametes, the 2 alleles responsible for a trait separate fr ...
2014 Quiz IA Answers
... Biochemical pathways that permit energy stored in complex molecules to be released The capacity to reproduce Ability to respond to stimuli in the natural world ...
... Biochemical pathways that permit energy stored in complex molecules to be released The capacity to reproduce Ability to respond to stimuli in the natural world ...
Cell Cycle & Mitosis
... Prophase is the first and longest phase of mitosis. The chromatin condenses into chromosomes. The centrioles separate, and a spindle begins to form. The nuclear envelope breaks down. ...
... Prophase is the first and longest phase of mitosis. The chromatin condenses into chromosomes. The centrioles separate, and a spindle begins to form. The nuclear envelope breaks down. ...
Reebop Lab - The Green Isle
... 5. The "father" should arbitrarily take one green chromosome from each pair and put it in a pile called "sperm." E) Is the sperm diploid or haploid? ________________ F) What type of cell division makes sperm (mitosis or meiosis)? ___________ 6. The "mother" should arbitrarily take one red chromosome ...
... 5. The "father" should arbitrarily take one green chromosome from each pair and put it in a pile called "sperm." E) Is the sperm diploid or haploid? ________________ F) What type of cell division makes sperm (mitosis or meiosis)? ___________ 6. The "mother" should arbitrarily take one red chromosome ...
LECTURE 34
... (ii) Allopolyploids originate through what is called the “amphidiploid” cycle, where two species (e.g., AA and A’A’) cross (hybridize), but where their “homeologous” chromosomes (A and A’) cannot pair at meiosis. The lack of structural homology between chromosomes bearing A and A’ is generally due t ...
... (ii) Allopolyploids originate through what is called the “amphidiploid” cycle, where two species (e.g., AA and A’A’) cross (hybridize), but where their “homeologous” chromosomes (A and A’) cannot pair at meiosis. The lack of structural homology between chromosomes bearing A and A’ is generally due t ...
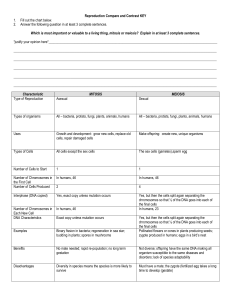
Characteristic #4
... have 23 chromosome pairs (46 chromosomes). The picture above shows the chromosomes in a diploid cell. Autosome: body cells (every type of cell except for sex cells). All autosomes are diploid. Human autosomes have 46 chromosomes. Haploid: a sex cell that has only one set of chromosomes (one from eac ...
... have 23 chromosome pairs (46 chromosomes). The picture above shows the chromosomes in a diploid cell. Autosome: body cells (every type of cell except for sex cells). All autosomes are diploid. Human autosomes have 46 chromosomes. Haploid: a sex cell that has only one set of chromosomes (one from eac ...
Document
... • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half. • Daughter cells differ from parent, and each other. • Meiosis involves two divisions, Mitosis only one. ...
... • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half. • Daughter cells differ from parent, and each other. • Meiosis involves two divisions, Mitosis only one. ...
Chapter 11 Mitosis Review Sheet
... c. diploid d. gemate 23. What is one-half of a chromosome called? a. chromatin b. chromatid c. chromosome d. centrosome 24. During which phase of mitosis are the sister chromatids pulled apart? a. anaphase b. prophase c. metaphase d. telophase 25. Normal human cells can go on dividing indefinitely. ...
... c. diploid d. gemate 23. What is one-half of a chromosome called? a. chromatin b. chromatid c. chromosome d. centrosome 24. During which phase of mitosis are the sister chromatids pulled apart? a. anaphase b. prophase c. metaphase d. telophase 25. Normal human cells can go on dividing indefinitely. ...
Compare and Contrast – Mitosis and Meiosis
... All – bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, animals, humans ...
... All – bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, animals, humans ...
Unit 19 Handout - Chavis Biology
... 3.3.U1: One of diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei . Compare divisions of meiosis I and meiosis II. 3.3.S1: Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. Outline the events of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telop ...
... 3.3.U1: One of diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei . Compare divisions of meiosis I and meiosis II. 3.3.S1: Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. Outline the events of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telop ...
1. How many main types of RNA are there?(B4.2g) a.1 b.3 c
... 40.Which system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external changes? (B2.3d) a.lymphatic system b.nervous system c.excretory system d.reproductive system ...
... 40.Which system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external changes? (B2.3d) a.lymphatic system b.nervous system c.excretory system d.reproductive system ...
Guided Reading: Meiosis (p188-193)
... crossed with a female plant that is true breeding for the dominant trait for round seeds, what shape will the offspring’s seeds have? Explain why. ...
... crossed with a female plant that is true breeding for the dominant trait for round seeds, what shape will the offspring’s seeds have? Explain why. ...
CELL DIVISION
... duplicated to produce 2 sister chromatids. The G2 phase, is the second growth phase that occurs after DNA replication. 4. Now that the cell has successfully copied it’s DNA into to sister chromatids that are attached by a centromere, the nucleus and cytoplasm will divide to produce two cells during ...
... duplicated to produce 2 sister chromatids. The G2 phase, is the second growth phase that occurs after DNA replication. 4. Now that the cell has successfully copied it’s DNA into to sister chromatids that are attached by a centromere, the nucleus and cytoplasm will divide to produce two cells during ...
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 11/3
... between diploid and haploid cells. 7. Do all organisms that experience Explain the purpose for this. meiosis also undergo mitosis? What is the difference between a diploid cell and a haploid cell? Draw an example of a cell that has 6 chromosomes in metaphase would What are the major differences of a ...
... between diploid and haploid cells. 7. Do all organisms that experience Explain the purpose for this. meiosis also undergo mitosis? What is the difference between a diploid cell and a haploid cell? Draw an example of a cell that has 6 chromosomes in metaphase would What are the major differences of a ...
Chapter 10 - Vocabulary Review
... spindle fibers so duplicated chromosomes can be separated during mitosis centromere, chromatid: A centromere is an area on chromosomes where spindle fibers attach and pull apart sister chromatids during mitosis binary fission, mitosis: Binary fission is the process by which duplicated DNA in prokary ...
... spindle fibers so duplicated chromosomes can be separated during mitosis centromere, chromatid: A centromere is an area on chromosomes where spindle fibers attach and pull apart sister chromatids during mitosis binary fission, mitosis: Binary fission is the process by which duplicated DNA in prokary ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.