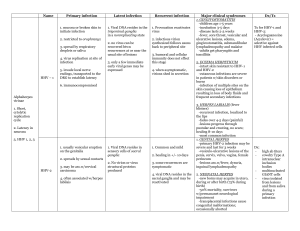
Lecture 12: HIV Infection
... HIV-1-infected cells- 2.2 days ~ 300 replication cycles/year Because RT does not proof-read, one mutation/104 bases occurs. With a genome of 104 bases, a mutation occurs at each position HIV-1 over 10,000 times every day. This generates resistant mutants that will selectively become the predominan ...
... HIV-1-infected cells- 2.2 days ~ 300 replication cycles/year Because RT does not proof-read, one mutation/104 bases occurs. With a genome of 104 bases, a mutation occurs at each position HIV-1 over 10,000 times every day. This generates resistant mutants that will selectively become the predominan ...
Microbiology CA
... MicroB CA The general properties of bacteria are as follows: They contain both RNA and DNA T They have ribosomes T They are smaller than 0.1micrometer F Most have peptidoglycan T Some may have flagella T Regarding endotoxins and exotoxins: Gram positive bacteria all produce endotoxin F Exotoxins are ...
... MicroB CA The general properties of bacteria are as follows: They contain both RNA and DNA T They have ribosomes T They are smaller than 0.1micrometer F Most have peptidoglycan T Some may have flagella T Regarding endotoxins and exotoxins: Gram positive bacteria all produce endotoxin F Exotoxins are ...
Herpes Viruses - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... 2. no virus can be recovered btwn recurrences at or near the usual site of lesions 3. only a few immediate early viral genes may be expressed ...
... 2. no virus can be recovered btwn recurrences at or near the usual site of lesions 3. only a few immediate early viral genes may be expressed ...
Virus Notes
... E. New viruses form inside of the host cell. F. New viruses are released as the host cell bursts open and is destroyed. ...
... E. New viruses form inside of the host cell. F. New viruses are released as the host cell bursts open and is destroyed. ...
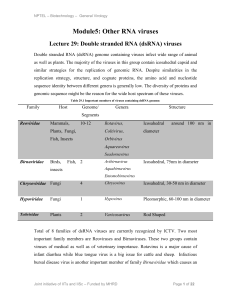
Module5: Other RNA viruses
... The envelope proteins are synthesized by the “env” gene following splicing. The proteins (gp 120 and gp41) become glycosylated in the endopolasmic reticulum and transported through Golgi apparatus to the surface of plasma membrane. Gag and Pol are produced as polyprotein which later on are cleaved b ...
... The envelope proteins are synthesized by the “env” gene following splicing. The proteins (gp 120 and gp41) become glycosylated in the endopolasmic reticulum and transported through Golgi apparatus to the surface of plasma membrane. Gag and Pol are produced as polyprotein which later on are cleaved b ...
Viruses - Fulton County Schools
... • A person can be contagious for more than 10 years before any sign of the disease is apparent • HIV becomes AIDS when the number of immune cells drops below a predetermined number • No one dies from HIV or AIDS; people die from secondary infections (ranging from the common cold to cancer) • More th ...
... • A person can be contagious for more than 10 years before any sign of the disease is apparent • HIV becomes AIDS when the number of immune cells drops below a predetermined number • No one dies from HIV or AIDS; people die from secondary infections (ranging from the common cold to cancer) • More th ...
Name date period
... Viruses are very successful at invading the cells of other organisms. After a virus attaches itself to the outside of a host cell, a viral enzyme damages the cell membrane and allows the virus to enter the host cell. Some viruses inject their DNA into the host cell & leave their protein coat outside ...
... Viruses are very successful at invading the cells of other organisms. After a virus attaches itself to the outside of a host cell, a viral enzyme damages the cell membrane and allows the virus to enter the host cell. Some viruses inject their DNA into the host cell & leave their protein coat outside ...
Viruses Scavenger Hunt Guiding Worksheet
... reproductive cycle of a virus. This occurs in viruses that do not have an envelope. Use the following letters and descriptions to label the diagram. By hovering over the box with the curser and right clicking. Then choose edit text to add the letter to the box A. Host enzymes transcribe the viral ge ...
... reproductive cycle of a virus. This occurs in viruses that do not have an envelope. Use the following letters and descriptions to label the diagram. By hovering over the box with the curser and right clicking. Then choose edit text to add the letter to the box A. Host enzymes transcribe the viral ge ...
X - Wikispaces
... Secondary Response : • the response will be more rapid • more antibodies will be produced to prevent the spread of the disease inside the body • the immune system’s memory lasts longer ...
... Secondary Response : • the response will be more rapid • more antibodies will be produced to prevent the spread of the disease inside the body • the immune system’s memory lasts longer ...
After the synthesis of viral nucleic acid and viral proteins
... multiplication in parasitized host cells are : 1- Attachment: The first step in viral infection is attachment, interaction of a virion with aspecific receptor site on the surface of a cell. Receptor molecules differ for different viruses but are generally glycoproteins. In some cases the virus binds ...
... multiplication in parasitized host cells are : 1- Attachment: The first step in viral infection is attachment, interaction of a virion with aspecific receptor site on the surface of a cell. Receptor molecules differ for different viruses but are generally glycoproteins. In some cases the virus binds ...
7 Ascherio A. Epstein-Barr virus in the development of
... EBV DNA present in saliva, we have found that there is good correlation between EBV in lower and upper respiratory tract specimens, which is not consistent with contamination. We and other labs see little evidence of latent EBV when testing whole blood or white blood cells, making the presence of Bc ...
... EBV DNA present in saliva, we have found that there is good correlation between EBV in lower and upper respiratory tract specimens, which is not consistent with contamination. We and other labs see little evidence of latent EBV when testing whole blood or white blood cells, making the presence of Bc ...
Viruses Scavenger Hunt Guiding Worksheet
... 4. Virus Reproduction: Basic reproduction (virus without envelope), The Lytic Cycle (for bacteriophages) & The Lysogenic Cycle 4a. Virus Reproduction: BASIC REPRODUCTION host cell ...
... 4. Virus Reproduction: Basic reproduction (virus without envelope), The Lytic Cycle (for bacteriophages) & The Lysogenic Cycle 4a. Virus Reproduction: BASIC REPRODUCTION host cell ...
Viruses Scavenger Hunt Guiding Worksheet
... 4. Virus Reproduction: Basic reproduction (virus without envelope), The Lytic Cycle (for bacteriophages) & The Lysogenic Cycle 4a. Virus Reproduction: BASIC REPRODUCTION host cell ...
... 4. Virus Reproduction: Basic reproduction (virus without envelope), The Lytic Cycle (for bacteriophages) & The Lysogenic Cycle 4a. Virus Reproduction: BASIC REPRODUCTION host cell ...
Is some segment of the HIV-infected population
... – monoclonal antibodies, – vaccine, – gene therapy ...
... – monoclonal antibodies, – vaccine, – gene therapy ...
Positive Wellness North Island Rapid Fire LS5 30
... Advocacy to explain life situations news gently (someone to and talk and help you challenges access supports) ...
... Advocacy to explain life situations news gently (someone to and talk and help you challenges access supports) ...
HIV and AIDS - cloudfront.net
... A person that cannot fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually harmless is said to have which of the following? ...
... A person that cannot fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually harmless is said to have which of the following? ...
Detecting Infectious HIV in Human Milk
... mononuclear cells from other cell types. 4. Magnetic bead sorting to retain CD4 lymphocytes and ...
... mononuclear cells from other cell types. 4. Magnetic bead sorting to retain CD4 lymphocytes and ...
Signs and Symptoms of HIV DiseaseThree stages
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
Dermatological manifestations of HIV
... People who are taking medicine to treat HIV the right way, every day may be in this stage for several decades because treatment helps keep the virus in check. people can still transmit HIV to others during this phase even if they are asymptomatic , although people who are on ART and stay virally sup ...
... People who are taking medicine to treat HIV the right way, every day may be in this stage for several decades because treatment helps keep the virus in check. people can still transmit HIV to others during this phase even if they are asymptomatic , although people who are on ART and stay virally sup ...
HIV Virus Questions
... 3. How important are the receptors on the cell membrane to HIV entry? Why? 4. Why do some HIV+ individuals show no sign of the disease? 5. What must RNA do before it can become incorporated into the host cell’s DNA? 6. How are new viral proteins built using the host cell’s ...
... 3. How important are the receptors on the cell membrane to HIV entry? Why? 4. Why do some HIV+ individuals show no sign of the disease? 5. What must RNA do before it can become incorporated into the host cell’s DNA? 6. How are new viral proteins built using the host cell’s ...
Chapter Eighteen
... • Diagnosis: sample of fluid from lesions or blood test • Treatment: antiviral medications reduce symptoms even though a cure is not available ...
... • Diagnosis: sample of fluid from lesions or blood test • Treatment: antiviral medications reduce symptoms even though a cure is not available ...
HIV

The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that causes HIV infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. Infection with HIV occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells), macrophages, and dendritic cells. HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through a number of mechanisms, including apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells, direct viral killing of infected cells, and killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8 cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells. When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections.