February 3, 2014 Dear Colleague,
... February 3, 2014 Dear Colleague, We are asking for your help in protecting all pregnant and postpartum women against influenza. Influenza activity in the U.S. remains high overall and may continue for weeks. H1N1 viruses have been dominant so far. This is the H1N1 virus that caused the 2009 pandemic ...
... February 3, 2014 Dear Colleague, We are asking for your help in protecting all pregnant and postpartum women against influenza. Influenza activity in the U.S. remains high overall and may continue for weeks. H1N1 viruses have been dominant so far. This is the H1N1 virus that caused the 2009 pandemic ...
Antibiotic Overuse May be Bad for Body’s Good Bacteria
... • DNA VIRUS: Use the Host By…. 1. Directly produce RNA that then makes viral proteins OR 2. Joins with host cells DNA for direct synthesis of new viruses • RNA VIRUS: Use the Host By…. 1. Viral RNA is released into host cells cytoplasm and uses its ribosomes to produce new viral proteins 2. “Retrovi ...
... • DNA VIRUS: Use the Host By…. 1. Directly produce RNA that then makes viral proteins OR 2. Joins with host cells DNA for direct synthesis of new viruses • RNA VIRUS: Use the Host By…. 1. Viral RNA is released into host cells cytoplasm and uses its ribosomes to produce new viral proteins 2. “Retrovi ...
Microbes and diseases: what to study-1
... • Changes in H and N (antigenic shift) – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
... • Changes in H and N (antigenic shift) – Mixing of viruses that infect birds, pigs, produce new strains able to jump to humans. – New antigenic type leaves population unprotected – Numerous epidemics throughout history • Flu of 1918-1919 killed 20 million – Asia watched very carefully: bird flu? ...
Emerging Infections Emerging/Re
... – Latter illustrates potential to be misled and damage it can cause ...
... – Latter illustrates potential to be misled and damage it can cause ...
Chapter 18: The Genetics of Viruses & Bacteria
... Symptoms usually related to body’s attempt to defend itself Vaccines stimulate immune system to mount defenses before actual infection Effective anti-viral drugs interfere with viral nucleic acid synthesis Viruses mutate rapidly new outbreaks & new host organisms (emergent viruses) ...
... Symptoms usually related to body’s attempt to defend itself Vaccines stimulate immune system to mount defenses before actual infection Effective anti-viral drugs interfere with viral nucleic acid synthesis Viruses mutate rapidly new outbreaks & new host organisms (emergent viruses) ...
Newcastle Disease
... The neurotropic velogenic form of ND has been reported mainly in the United States. In chickens, it is marked by sudden onset of severe respiratory disease followed a day or two later by neurologic signs. Egg production falls dramatically, but diarrhea is usually absent. Morbidity may reach 100%. Mo ...
... The neurotropic velogenic form of ND has been reported mainly in the United States. In chickens, it is marked by sudden onset of severe respiratory disease followed a day or two later by neurologic signs. Egg production falls dramatically, but diarrhea is usually absent. Morbidity may reach 100%. Mo ...
Viruses
... Viral DNA is injected into the host cell Viral DNA inserts itself into the host’s DNA Remains inactive for days, months, or years As the cell reproduces, more cells are produced that have the viral DNA in them Eventually, when the conditions are favorable (like when your immune system is wea ...
... Viral DNA is injected into the host cell Viral DNA inserts itself into the host’s DNA Remains inactive for days, months, or years As the cell reproduces, more cells are produced that have the viral DNA in them Eventually, when the conditions are favorable (like when your immune system is wea ...
Unit 2 PPT 11 (Macroparasites and microparasites)
... • Viruses are infectious agents that can only replicate inside a host cell. Viruses contain genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA, packaged in a protective protein coat. • Some viruses have a lipid membrane surround derived from host cell materials. The outer surface of a virus contains antigen ...
... • Viruses are infectious agents that can only replicate inside a host cell. Viruses contain genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA, packaged in a protective protein coat. • Some viruses have a lipid membrane surround derived from host cell materials. The outer surface of a virus contains antigen ...
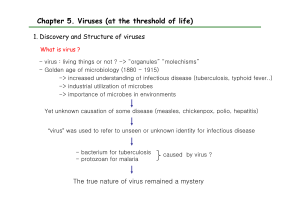
Chapter 5. Viruses (at the threshold of life)
... -> diluted filtered juice -> still infectious -> called contagious living fluid - 1930s, Wendell M. Stanley : crystalization of tobacco mosaic virus ...
... -> diluted filtered juice -> still infectious -> called contagious living fluid - 1930s, Wendell M. Stanley : crystalization of tobacco mosaic virus ...
Judul
... ability to replicate themselves on an ever increasing number of computers. They originally spread by people sharing floppy disks. Now they spread primarily over the Internet (a Worm). • Other Malicious Programs may be installed by hand on a single machine. They may also be built into widely distribu ...
... ability to replicate themselves on an ever increasing number of computers. They originally spread by people sharing floppy disks. Now they spread primarily over the Internet (a Worm). • Other Malicious Programs may be installed by hand on a single machine. They may also be built into widely distribu ...
BIOL 191 Introductory Microbiology
... 1. Chap. 8 pp. 211-212, Fig. 8.2 p. 213 The Flow of Genetic Information ii. Clinical Focus pp. 370-371 Influenza Virus A iii. What types of nucleic acids may viruses have? See Table 13.2 p. 375-376 b. Capsid and Envelope i. Spikes 1. H (Hemagglutinin) proteins1 2. N (Neuraminidase) proteins2 1 Hemag ...
... 1. Chap. 8 pp. 211-212, Fig. 8.2 p. 213 The Flow of Genetic Information ii. Clinical Focus pp. 370-371 Influenza Virus A iii. What types of nucleic acids may viruses have? See Table 13.2 p. 375-376 b. Capsid and Envelope i. Spikes 1. H (Hemagglutinin) proteins1 2. N (Neuraminidase) proteins2 1 Hemag ...
After the synthesis of viral nucleic acid and viral proteins
... A variety of different viral strategies have evolved for accomplishing multiplication in parasitized host cells are : 1- Attachment: The first step in viral infection is attachment, interaction of a virion with aspecific receptor site on the surface of a cell. Receptor molecules differ for different ...
... A variety of different viral strategies have evolved for accomplishing multiplication in parasitized host cells are : 1- Attachment: The first step in viral infection is attachment, interaction of a virion with aspecific receptor site on the surface of a cell. Receptor molecules differ for different ...
Viruses & Bacteria
... and divide extremely rapidly under optimal conditions; can double very quickly • Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics; ...
... and divide extremely rapidly under optimal conditions; can double very quickly • Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics; ...
Viruses
... Vaccines: weakened versions of the virus, harmless and triggers the production of antibodies. ...
... Vaccines: weakened versions of the virus, harmless and triggers the production of antibodies. ...
Validation of Viral Safety of Recombinant Proteins
... because of their wide spread use in the production of biologic drugs. In this presentation on viral safety aspects in downstream development of recombinant proteins, Nothelfer introduced the topic by discussing some general rules for comprehensive evaluation of this complex issue. He stated that val ...
... because of their wide spread use in the production of biologic drugs. In this presentation on viral safety aspects in downstream development of recombinant proteins, Nothelfer introduced the topic by discussing some general rules for comprehensive evaluation of this complex issue. He stated that val ...
disease emergence and re-emergence
... genome, which has eight genes, facilitates reassortment; up to 256 gene combinations are possible during coinfection with human and non-human viruses. Antigenic shift can arise when genes encoding at least the haemagglutinin surface glycoprotein are introduced into people, by direct transmission of ...
... genome, which has eight genes, facilitates reassortment; up to 256 gene combinations are possible during coinfection with human and non-human viruses. Antigenic shift can arise when genes encoding at least the haemagglutinin surface glycoprotein are introduced into people, by direct transmission of ...
Andrew Kilianski
... Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) caused a deadly outbreak and epidemic in 2002-2003. SARS is characterized by a lack of early recognition and signaling by the immune system, and it has since been discovered that SARS-CoV encodes many proteins that are important in blocking our innate immu ...
... Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) caused a deadly outbreak and epidemic in 2002-2003. SARS is characterized by a lack of early recognition and signaling by the immune system, and it has since been discovered that SARS-CoV encodes many proteins that are important in blocking our innate immu ...
Children - Simcoe Muskoka District Health Unit
... Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by influenza A and B viruses. In Canada influenza infection generally occurs in the late fall and winter months. Influenza is easily spread by direct contact or droplets expelled during breathing, talking, sneezing or coughing. Symptoms include sudden onse ...
... Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by influenza A and B viruses. In Canada influenza infection generally occurs in the late fall and winter months. Influenza is easily spread by direct contact or droplets expelled during breathing, talking, sneezing or coughing. Symptoms include sudden onse ...
Pathogens Practice Quiz - Science with Mrs. Barton
... What type of pathogen is malaria? a. A virus b. A bacterium c. A fungus d. A protist 4. How can the rate of an infectious disease be ...
... What type of pathogen is malaria? a. A virus b. A bacterium c. A fungus d. A protist 4. How can the rate of an infectious disease be ...
Viruses_and_Infectious_Disease
... have an envelope surrounding their capsid. – Made of lipids, just like the plasma membrane of cells. – Makes viruses more infectious because they can more easily infect living cells. ...
... have an envelope surrounding their capsid. – Made of lipids, just like the plasma membrane of cells. – Makes viruses more infectious because they can more easily infect living cells. ...
What are Viruses?
... Most people say no! They have some properties of life but not others For example, viruses can be killed, even crystallized like table salt However, they can’t maintain a constant internal state (homeostasis) and aren’t made of cells ...
... Most people say no! They have some properties of life but not others For example, viruses can be killed, even crystallized like table salt However, they can’t maintain a constant internal state (homeostasis) and aren’t made of cells ...
Pathogen
... Transmit by Inhalation of droplets,Ingestion of food or water contaminated by the excreta of host. Symptom: diarrhea, fever, vomit What can do: drank more water, keep fresh air, cook the food completely, wash your before eat and after go to toilet. ...
... Transmit by Inhalation of droplets,Ingestion of food or water contaminated by the excreta of host. Symptom: diarrhea, fever, vomit What can do: drank more water, keep fresh air, cook the food completely, wash your before eat and after go to toilet. ...
MICR 201 Microbiology for Health Related Sciences
... Virus serves as vector for bacterial DNA During virus assembly a segment of bacterial DNA is accidentally packed into virus capsids Specialized transduction: a segment of bacterial ...
... Virus serves as vector for bacterial DNA During virus assembly a segment of bacterial DNA is accidentally packed into virus capsids Specialized transduction: a segment of bacterial ...
Influenza A virus

Influenza A virus causes influenza in birds and some mammals, and is the only species of influenza virus A. Influenza virus A is a genus of the Orthomyxoviridae family of viruses. Strains of all subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated from wild birds, although disease is uncommon. Some isolates of influenza A virus cause severe disease both in domestic poultry and, rarely, in humans. Occasionally, viruses are transmitted from wild aquatic birds to domestic poultry, and this may cause an outbreak or give rise to human influenza pandemics.Influenza A viruses are negative-sense, single-stranded, segmented RNA viruses.The several subtypes are labeled according to an H number (for the type of hemagglutinin) and an N number (for the type of neuraminidase). There are 18 different known H antigens (H1 to H18) and 11 different known N antigens (N1 to N11). H17 was isolated from fruit bats in 2012. H18N11 was discovered in a Peruvian bat in 2013.Each virus subtype has mutated into a variety of strains with differing pathogenic profiles; some are pathogenic to one species but not others, some are pathogenic to multiple species.A filtered and purified influenza A vaccine for humans has been developed, and many countries have stockpiled it to allow a quick administration to the population in the event of an avian influenza pandemic. Avian influenza is sometimes called avian flu, and colloquially, bird flu. In 2011, researchers reported the discovery of an antibody effective against all types of the influenza A virus.