cell division review - Paint Valley Local Schools
... 26. Tell how you can tell this is an animal cell and NOT a plant cell. ...
... 26. Tell how you can tell this is an animal cell and NOT a plant cell. ...
Chapter on Mitosis
... nuclear envelope disappear centromeres are at poles condensation increases kinetochore present microtubules attach to kinetochore ...
... nuclear envelope disappear centromeres are at poles condensation increases kinetochore present microtubules attach to kinetochore ...
Class Test
... 3. What stain did you use for viewing plant cells on the slide? _____________________ 4. State two features visible under a light microscope that indicate that cells are typical plant cells. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the stain that y ...
... 3. What stain did you use for viewing plant cells on the slide? _____________________ 4. State two features visible under a light microscope that indicate that cells are typical plant cells. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the stain that y ...
File
... 1. What does the cytoplasm contain? Tiny structures called organelles 2. Define organelle. Tiny structures inside the cell 3. Fg.1 shows? Animal cell 4. What is a mitochondrion often called? Power plant for cells 5. What is its function? provide energy for the cell by undergoing cellular respiration ...
... 1. What does the cytoplasm contain? Tiny structures called organelles 2. Define organelle. Tiny structures inside the cell 3. Fg.1 shows? Animal cell 4. What is a mitochondrion often called? Power plant for cells 5. What is its function? provide energy for the cell by undergoing cellular respiration ...
Why are cells small?
... happens to the cell’s surface area? B) As the cell gets larger (grows) what happens to the cell’s volume? C) Which one increases faster? D) Why is this a problem? ...
... happens to the cell’s surface area? B) As the cell gets larger (grows) what happens to the cell’s volume? C) Which one increases faster? D) Why is this a problem? ...
File
... The smallest unit able to perform the activities of life is called ____Cell______ Cells without a nucleus are called _Prokaryotic___________ Cells with a nucleus are called __Eukaryotic________ The three parts of cell theory are: o Every living thing is made of cells o The cell is the basic unit of ...
... The smallest unit able to perform the activities of life is called ____Cell______ Cells without a nucleus are called _Prokaryotic___________ Cells with a nucleus are called __Eukaryotic________ The three parts of cell theory are: o Every living thing is made of cells o The cell is the basic unit of ...
Cells - Krum ISD
... • On your Cells page of your IAN, make chart and list the major structures found in each cell. (see example on chalk board) • Which cells are prokaryotes and eukaryotes? • How do you know? Animal Cell ...
... • On your Cells page of your IAN, make chart and list the major structures found in each cell. (see example on chalk board) • Which cells are prokaryotes and eukaryotes? • How do you know? Animal Cell ...
Name: Homeroom
... 12. What is the function of the cell wall? __It is a covering on the outside of the cell that gives the plant cell strength and extra support._______________________________________ 13. What is the function of the chloroplasts? _____A green structure where the energy from sunlight is used to produce ...
... 12. What is the function of the cell wall? __It is a covering on the outside of the cell that gives the plant cell strength and extra support._______________________________________ 13. What is the function of the chloroplasts? _____A green structure where the energy from sunlight is used to produce ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 3. Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. mitochondria and chloroplasts c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. rough endoplasmic reticulum d. Golgi apparatus and ribosomes 4. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion c. chloroplast b. rib ...
... 3. Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. mitochondria and chloroplasts c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. rough endoplasmic reticulum d. Golgi apparatus and ribosomes 4. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion c. chloroplast b. rib ...
CARBOHYDRATES, lipids and proteins handout
... Combinations of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) (usual ratio = 1:2:1)(e.g. glucose is C6H12O6) – sugars and starches Carbohydrate means "hydrated carbon" Primary use = fuel to make energy. The energy molecule of the cell is ATP. Glucose is broken down and the energy released from the ...
... Combinations of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) (usual ratio = 1:2:1)(e.g. glucose is C6H12O6) – sugars and starches Carbohydrate means "hydrated carbon" Primary use = fuel to make energy. The energy molecule of the cell is ATP. Glucose is broken down and the energy released from the ...
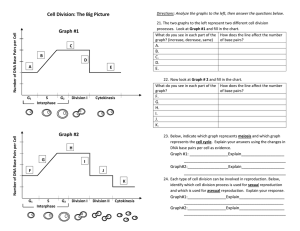
Cell Division Graphing
... 25. _______Which of these must occur during S phase of the cell cycle so that two daughter cells can be produced during Mphase? A. The DNA must be replicated. B. The chromosomes must be joined. C. The cytoplasm must be separated. D. The cell membrane must be expanded. 26. _______Crossing-over betwe ...
... 25. _______Which of these must occur during S phase of the cell cycle so that two daughter cells can be produced during Mphase? A. The DNA must be replicated. B. The chromosomes must be joined. C. The cytoplasm must be separated. D. The cell membrane must be expanded. 26. _______Crossing-over betwe ...
cells
... Cell Division—Mitosis Notes Cell Division — process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells •Why do cells need to divide? ...
... Cell Division—Mitosis Notes Cell Division — process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells •Why do cells need to divide? ...
Cell Membrane Reading Guide
... ________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What is the diffusion of water called? ___________________________ 10. Water generally osmoses from areas of ___________________ water concentration to areas of ___________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What is the diffusion of water called? ___________________________ 10. Water generally osmoses from areas of ___________________ water concentration to areas of ___________ ...
product data sheet
... peptide can bind two copies of BRD2-2 (BRD2, bromodomain 2), each interacting with one of the two acetylated lysines . In an in vitro RNA polymerase II transcription system, binding of either BRD2 or BRD3 to a chromatin template assembled with hyperacetylated ...
... peptide can bind two copies of BRD2-2 (BRD2, bromodomain 2), each interacting with one of the two acetylated lysines . In an in vitro RNA polymerase II transcription system, binding of either BRD2 or BRD3 to a chromatin template assembled with hyperacetylated ...
CELLS - Clever Teach
... I will show success by… Draw a diagram of an animal and Explain why each component in a plant cell. cell is vital Describe the functions of each ...
... I will show success by… Draw a diagram of an animal and Explain why each component in a plant cell. cell is vital Describe the functions of each ...
pbioch3quiz frisci blog
... 14. Use the following words to complete the paragraph. Endoplasmic Reticulum, DNA, Golgi complex, amino acids, ribosome. In order to make a protein, _______ that is found in the nucleus is copied. RNA is then taken to a ______________, which are small organelles found on the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... 14. Use the following words to complete the paragraph. Endoplasmic Reticulum, DNA, Golgi complex, amino acids, ribosome. In order to make a protein, _______ that is found in the nucleus is copied. RNA is then taken to a ______________, which are small organelles found on the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
Ch 4 Study Guide
... Phase 1 – Chromosomes condense into rodlike structures Phase 2 – Chromatids line up in the center of the cell Phase 3 – Chromosomes get pulled to opposite sides of the cell Phase 4 – The nuclear membrane reforms around the chromosomes 15. What type of cell forms a cell plate? Plant cell 16. In which ...
... Phase 1 – Chromosomes condense into rodlike structures Phase 2 – Chromatids line up in the center of the cell Phase 3 – Chromosomes get pulled to opposite sides of the cell Phase 4 – The nuclear membrane reforms around the chromosomes 15. What type of cell forms a cell plate? Plant cell 16. In which ...
Osmosis Virtual Lab Logon to http://www.glencoe.com/sites
... Logon to http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Read the information that is listed in the box on the left of your computer screen. Use it to answer the following questions. 1. What is a selectively permeable membrane? ...
... Logon to http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Read the information that is listed in the box on the left of your computer screen. Use it to answer the following questions. 1. What is a selectively permeable membrane? ...
Cell Organelles
... outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists which provides support and protection • The cell wall allows the cell to become quite turgid without bursting ...
... outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists which provides support and protection • The cell wall allows the cell to become quite turgid without bursting ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.