Name
... cell swells up Plant Cell- swell beyond their normal size as pressure increases; the plasma membrane presses against the cell wall and makes the cell more firm. (why grocers keeping misting vegetables at the market) Animal Cell- swell until they burst ...
... cell swells up Plant Cell- swell beyond their normal size as pressure increases; the plasma membrane presses against the cell wall and makes the cell more firm. (why grocers keeping misting vegetables at the market) Animal Cell- swell until they burst ...
Intro to Cells Webquest
... 1. Within a __________________________organism there is a __________________________________________. Division of labor means that the work of keeping the organism alive is_______________________________________ ____________________________________. Each part has a ____________________________ to do ...
... 1. Within a __________________________organism there is a __________________________________________. Division of labor means that the work of keeping the organism alive is_______________________________________ ____________________________________. Each part has a ____________________________ to do ...
organelle
... through a process called “cellular respiration” *fluid-filled sacs *store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) *breaks down *small, round, food into smaller with a membrane molecules *digests old cell parts ...
... through a process called “cellular respiration” *fluid-filled sacs *store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) *breaks down *small, round, food into smaller with a membrane molecules *digests old cell parts ...
Section 3 - HCABIOLOGY
... 5. The process in which a cell membrane engulfs large particles through vesicles is called ________________________. 6. The process in which a cell membrane expels substances out of a cell through vesicles is called ___________________. ...
... 5. The process in which a cell membrane engulfs large particles through vesicles is called ________________________. 6. The process in which a cell membrane expels substances out of a cell through vesicles is called ___________________. ...
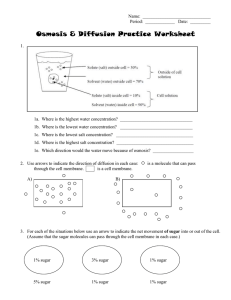
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
... 3. For each of the situations below use an arrow to indicate the net movement of sugar into or out of the cell. (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
Regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
... Chromatids: the 2 identical parts of a chromosome Centromere: the middle, round part of the chromosome that holds the sister chromatids together Centromere Sister chromatids ...
... Chromatids: the 2 identical parts of a chromosome Centromere: the middle, round part of the chromosome that holds the sister chromatids together Centromere Sister chromatids ...
BIOLOGY CLASS NOTES UNIT 6 Cell Growth and Division
... Chromosomes break into separate sister chromatids (think “chromosome kids”) and begin to move apart. ...
... Chromosomes break into separate sister chromatids (think “chromosome kids”) and begin to move apart. ...
The Cell
... • Responsible for keeping the cell from bursting when there are large differences in osmotic pressure between the cytoplasm and the environment. ...
... • Responsible for keeping the cell from bursting when there are large differences in osmotic pressure between the cytoplasm and the environment. ...
Student Exploration: Cell Structure
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi body is the cell’s _________________ room • Organelles that _________________ cellular material (_________________) & _ ...
... • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi body is the cell’s _________________ room • Organelles that _________________ cellular material (_________________) & _ ...
Cell Growth and Division
... • In plants, a cell plate is formed in the center of the cell and grows outward to separate the two cells. • A cell wall will eventually form on each side of the cell plate. ...
... • In plants, a cell plate is formed in the center of the cell and grows outward to separate the two cells. • A cell wall will eventually form on each side of the cell plate. ...
CellStructureSE
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
... – movement of the chromosomes is driven by addition or subtraction of protein subunits to the kinetochore end of spindle microtubules Nonkinetechore microtubules from opposite poles overlap and push against each other, elongating the cell • In telophase genetically identical daughter nuclei form at ...
... – movement of the chromosomes is driven by addition or subtraction of protein subunits to the kinetochore end of spindle microtubules Nonkinetechore microtubules from opposite poles overlap and push against each other, elongating the cell • In telophase genetically identical daughter nuclei form at ...
Cell Structure Gizmo
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
... Vocabulary: cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear membrane, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle ...
The Cell Theory
... • They can live without oxygen • Some can even make their own food • Bacteria are the only prokaryotic cells ...
... • They can live without oxygen • Some can even make their own food • Bacteria are the only prokaryotic cells ...
Bacterial Cell Division
... Anaphase: -removal of cohesin proteins causes the centromeres to separate -microtubules pull sister chromatids toward the poles ...
... Anaphase: -removal of cohesin proteins causes the centromeres to separate -microtubules pull sister chromatids toward the poles ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Found in plants, fungi, & many protists • Surrounds plasma membrane ...
... • Found in plants, fungi, & many protists • Surrounds plasma membrane ...
“The Cell”
... 1) Chromatin – protein with DNA bound to it 2) Chromosomes – chromatin condensed; distinct, threadlike structure containing genetic information 3) Nucleolus – small, dense region within nucleus; ribosomes made here 4) Nuclear Envelope – double membrane layer that surrounds nucleus; contains thousand ...
... 1) Chromatin – protein with DNA bound to it 2) Chromosomes – chromatin condensed; distinct, threadlike structure containing genetic information 3) Nucleolus – small, dense region within nucleus; ribosomes made here 4) Nuclear Envelope – double membrane layer that surrounds nucleus; contains thousand ...
Cell division functions in reproduction, growth and repair
... Mitosis = nuclear division during which duplicated chromosomes are evenly distributed into two daughter nuclei. Results in cells genetically identical to parent cell. o before mitosis, cells replicate their chromosomes, forming two identical sister chromatids joined together at the centromere. o dur ...
... Mitosis = nuclear division during which duplicated chromosomes are evenly distributed into two daughter nuclei. Results in cells genetically identical to parent cell. o before mitosis, cells replicate their chromosomes, forming two identical sister chromatids joined together at the centromere. o dur ...
Cells Outline
... 1. Interphase – divided into G1 , S, G2 a. G1 (gap between mitosis & DNA synthesis) - Normal cellular function, metabolism, and protein synthesis; centrioles formed and start to migrate to poles b. S (DNA Synthesis) DNA replication c. G2 (gap between DNA synthesis & Mitosis) Enzymes required for cel ...
... 1. Interphase – divided into G1 , S, G2 a. G1 (gap between mitosis & DNA synthesis) - Normal cellular function, metabolism, and protein synthesis; centrioles formed and start to migrate to poles b. S (DNA Synthesis) DNA replication c. G2 (gap between DNA synthesis & Mitosis) Enzymes required for cel ...
Parts of a Cell Notes
... 22. The ____________________________________________ is in charge of processing and shipping __________________________ and other materials out of the cell. 23. Lipids and proteins from the ___________________ are delivered to the Golgi complex, where they are _______________________________________ ...
... 22. The ____________________________________________ is in charge of processing and shipping __________________________ and other materials out of the cell. 23. Lipids and proteins from the ___________________ are delivered to the Golgi complex, where they are _______________________________________ ...
3d cell model directions1
... You may use any materials you want to make the cell and organelles in the cell. Each organel!e should be a different material. Ideas for materials include- yarn, beads, toothpicks, pipe cleaners, shoe boxes, Styrofoam, string, straws, food, play-doh ... Materials can be things you have at home alrea ...
... You may use any materials you want to make the cell and organelles in the cell. Each organel!e should be a different material. Ideas for materials include- yarn, beads, toothpicks, pipe cleaners, shoe boxes, Styrofoam, string, straws, food, play-doh ... Materials can be things you have at home alrea ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.