Chapter 5 Lesson 1 and 2 PPt
... Cell Membrane Function • Hydrophilic outside lets the membrane and organelles interact with water-based solutions. • Hydrophobic inside limits what can enter or exit the cell. • Cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane ...
... Cell Membrane Function • Hydrophilic outside lets the membrane and organelles interact with water-based solutions. • Hydrophobic inside limits what can enter or exit the cell. • Cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane ...
Cell Organelles - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... • Controls most activities in the cell • Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins & other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
... • Controls most activities in the cell • Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins & other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
Mitosis
... Observe your preparation under the low power (X10) of a microscope Search the slide to find cells in various stages of cell division, once you have located cells in division, change to high power (X40) & try to observe several stages of division. Record the number of cells in each stage. Count at le ...
... Observe your preparation under the low power (X10) of a microscope Search the slide to find cells in various stages of cell division, once you have located cells in division, change to high power (X40) & try to observe several stages of division. Record the number of cells in each stage. Count at le ...
Organelles - kambryabiology
... • Mitochondrion takes chemical energy from food (glucose): – produces energy molecule ATP ...
... • Mitochondrion takes chemical energy from food (glucose): – produces energy molecule ATP ...
What is a cell Cell is the basic living, structural and
... Cell is the basic living, structural and functional unit of the body The human body develops from a single cell called the zygote, which results from the fusion of the ovum(Female egg cell) & spermatozoon (Male germ cell) What is a cell Functions of membrane proteins Branched carbohydrate molecules ...
... Cell is the basic living, structural and functional unit of the body The human body develops from a single cell called the zygote, which results from the fusion of the ovum(Female egg cell) & spermatozoon (Male germ cell) What is a cell Functions of membrane proteins Branched carbohydrate molecules ...
Name - Issaquah Connect
... Root Cells- Absorb water. Nerve Cells- Relay information between your brain and body. Skin Cell- Protect the body from foreign objects. 7. Are the cells of small and large organisms the same size? Explain. All cells are about the same size, larger organisms just have more cells. 8. What cells should ...
... Root Cells- Absorb water. Nerve Cells- Relay information between your brain and body. Skin Cell- Protect the body from foreign objects. 7. Are the cells of small and large organisms the same size? Explain. All cells are about the same size, larger organisms just have more cells. 8. What cells should ...
Animal Cell
... located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the centrosome. cytoplasm ...
... located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the centrosome. cytoplasm ...
Eukaryote PowerPoint
... Composed of flattened sacs called cisternae Functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell One side is always close to the rough ER (cis side) receiving products from the ER Movement occurs to discharge the product from the opposite (trans ...
... Composed of flattened sacs called cisternae Functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell One side is always close to the rough ER (cis side) receiving products from the ER Movement occurs to discharge the product from the opposite (trans ...
Organelle Analogy Posters
... in cars like the ER transports proteins in the cell. You will be creating an analogy as you compare the cell to a place, thing or event and relate at least 8 organelles to parts of your place, thing or event. 1. Decide what your analogy will be… the more creative the better. Pick something you are i ...
... in cars like the ER transports proteins in the cell. You will be creating an analogy as you compare the cell to a place, thing or event and relate at least 8 organelles to parts of your place, thing or event. 1. Decide what your analogy will be… the more creative the better. Pick something you are i ...
organs inside the cell Golgi complex
... Lipids – the fats in a cell – lipids are hydrophobic (they hate water) they also store energy – cell membranes are made of these Carbohydrates – the energy in a cell (cellulose in plants – Chitin in animals) Nucleic Acids – hold all the instructions for the cell (DNA & RNA) The Cell Theory: All li ...
... Lipids – the fats in a cell – lipids are hydrophobic (they hate water) they also store energy – cell membranes are made of these Carbohydrates – the energy in a cell (cellulose in plants – Chitin in animals) Nucleic Acids – hold all the instructions for the cell (DNA & RNA) The Cell Theory: All li ...
Cells Lab
... Talk about leaf cells and how they are specialized for photosynthesis. Draw a leaf cell. • What is the function of a leaf? • Why are leaves green? Why aren’t tree trunks green? • What specific steps does a leaf cell need to make to perform its function? o Photosynthesize o Stay upright o Pass food t ...
... Talk about leaf cells and how they are specialized for photosynthesis. Draw a leaf cell. • What is the function of a leaf? • Why are leaves green? Why aren’t tree trunks green? • What specific steps does a leaf cell need to make to perform its function? o Photosynthesize o Stay upright o Pass food t ...
Document
... Cytokinesis – cleavage of the cell into equal halves -in animal cells – constriction of actin filaments produces a cleavage furrow -in plant cells – plasma membrane forms a cell plate between the nuclei -in fungi and some protists – mitosis occurs within the nucleus; division of the nucleus occurs w ...
... Cytokinesis – cleavage of the cell into equal halves -in animal cells – constriction of actin filaments produces a cleavage furrow -in plant cells – plasma membrane forms a cell plate between the nuclei -in fungi and some protists – mitosis occurs within the nucleus; division of the nucleus occurs w ...
Cell division
... A cell with n = 2 can have how many different combinations? A cell with n = 3 can have how many different combinations? ...
... A cell with n = 2 can have how many different combinations? A cell with n = 3 can have how many different combinations? ...
Red Black - Raleigh Charter High School
... 6- What type of organic macromolecule are enzymes? 7- What is the molecule that an enzyme works upon? 8- What part of the microscope do you use to focus? 9- What two reactants does a plant need for photosynthesis to occur? 10- What is the energy molecule of the cell? Jack- The movement of molecules ...
... 6- What type of organic macromolecule are enzymes? 7- What is the molecule that an enzyme works upon? 8- What part of the microscope do you use to focus? 9- What two reactants does a plant need for photosynthesis to occur? 10- What is the energy molecule of the cell? Jack- The movement of molecules ...
Specialised Cells
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
Specialised Cells
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
Web Quest- Cells Alive student worksheet
... 3. From here, you will access the links “How Big is a…”, the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Part A. “HOW BIG IS A….” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to estimate the length of each in nanometers (nm), micrometers (μm) or mi ...
... 3. From here, you will access the links “How Big is a…”, the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Part A. “HOW BIG IS A….” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to estimate the length of each in nanometers (nm), micrometers (μm) or mi ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
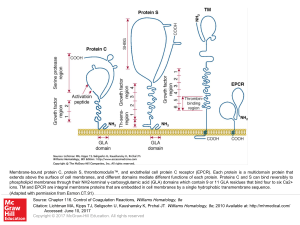
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Study Guide - Issaquah Connect
... A cell membrane has other types of molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, List function of each type of molecule in the table below ...
... A cell membrane has other types of molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, List function of each type of molecule in the table below ...
Cell Organelles - ESC-2
... function: smooth er makes hormones and controls calcium release. Rough er is covered in ribosomes and makes proteins. ...
... function: smooth er makes hormones and controls calcium release. Rough er is covered in ribosomes and makes proteins. ...
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
... • Some organisms are unicellular (single celled); the cell carries out all life functions. Unicellular organisms are prokaryotic. • Multicellular organisms have many cells that work together to carry out life processes. • Tissues are groups of cells that perform the same function. Organs are several ...
... • Some organisms are unicellular (single celled); the cell carries out all life functions. Unicellular organisms are prokaryotic. • Multicellular organisms have many cells that work together to carry out life processes. • Tissues are groups of cells that perform the same function. Organs are several ...
Cells - sandsbiochem
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
Modified Ch. 6 PPT Chou (1)
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Contains DNA Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.