Study Guide for Exam 1: Cell Biology
... Notebook: Topic 4: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles CA Science Biology Standard 1e: Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 1f: Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar f ...
... Notebook: Topic 4: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles CA Science Biology Standard 1e: Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 1f: Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar f ...
Essay 2
... a plasmid DNA. This illustrates both a contrast of size and function between pro- and eukaryotes, but also of the hazy division between their respective defining properties. Close collaboration between pro- and eukaryotic cells is only possible because of their shared basic characteristics, like the ...
... a plasmid DNA. This illustrates both a contrast of size and function between pro- and eukaryotes, but also of the hazy division between their respective defining properties. Close collaboration between pro- and eukaryotic cells is only possible because of their shared basic characteristics, like the ...
10-4-16 Cells Study Guide - KEY
... 10. What is a nucleoid region? What type of cell has a nucleoid region? Prokaryotes have a nucleoid region because they do not have a nucleus. It is the area in the cytoplasm where their DNA is located. 11. What are the 3 types of fiber that makes up the cytoskeleton? Which is the biggest and smalle ...
... 10. What is a nucleoid region? What type of cell has a nucleoid region? Prokaryotes have a nucleoid region because they do not have a nucleus. It is the area in the cytoplasm where their DNA is located. 11. What are the 3 types of fiber that makes up the cytoskeleton? Which is the biggest and smalle ...
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction PP
... Some details of meiosis… • As with mitosis, meiosis begins after the chromosomes have been duplicated during Interphase • Meiosis consists of two distinct parts – Meiosis I – Meiosis II ...
... Some details of meiosis… • As with mitosis, meiosis begins after the chromosomes have been duplicated during Interphase • Meiosis consists of two distinct parts – Meiosis I – Meiosis II ...
Cell Transport
... Remember Homeostasis? In order to live, cells must obtain certain materials from their environment. They must also get rid of waste products. The cell membrane allows this. ...
... Remember Homeostasis? In order to live, cells must obtain certain materials from their environment. They must also get rid of waste products. The cell membrane allows this. ...
Solve the following word problems using the formulas for geometric
... 3. On Monday, the first day of a flu epidemic, three employees of a company were absent. Throughout the week, absences mounted geometrically, peaking at 48 employees on Friday. How many employees were absent on Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday? ...
... 3. On Monday, the first day of a flu epidemic, three employees of a company were absent. Throughout the week, absences mounted geometrically, peaking at 48 employees on Friday. How many employees were absent on Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday? ...
The ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE from Chapters 6
... Order is maintained by coupling cellular processes that increase entropy (and so have negative changes in free energy) with those that decrease entropy (and so have positive changes in free energy). Energy input must exceed free energy lost to entropy to maintain order and power cellular process ...
... Order is maintained by coupling cellular processes that increase entropy (and so have negative changes in free energy) with those that decrease entropy (and so have positive changes in free energy). Energy input must exceed free energy lost to entropy to maintain order and power cellular process ...
241083_Cell_City
... between cell structures and their functions in order to better understand the role of the various organelles and how they interact. How we will do this - Make analogies between the functional parts of a city and the functional parts of a cell. ...
... between cell structures and their functions in order to better understand the role of the various organelles and how they interact. How we will do this - Make analogies between the functional parts of a city and the functional parts of a cell. ...
Functions of a Cell
... nucleus surrounded by a membranous nuclear envelope that is present in only eukaryotic cells. Both types of cells share many common features. The genetic information is stored in genes. Proteins serve as the main structural material. Ribosomes are used to synthesize proteins. And a cell membrane con ...
... nucleus surrounded by a membranous nuclear envelope that is present in only eukaryotic cells. Both types of cells share many common features. The genetic information is stored in genes. Proteins serve as the main structural material. Ribosomes are used to synthesize proteins. And a cell membrane con ...
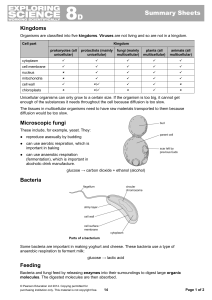
8D Unicellular Organisms
... Organisms are classified into five kingdoms. Viruses are not living and so are not in a kingdom. Cell part ...
... Organisms are classified into five kingdoms. Viruses are not living and so are not in a kingdom. Cell part ...
Biology Unit 5: Cellular Structure and Function
... 20. *Which of these directly allows blood cells to transport oxygen to various parts of the body? a. carbon dioxide b. hemoglobin c. antibodies d. platelets 3.2.A.c 21. The cell cycle describes the life activities of a cell. Which of the following describes the cell cycle of a typical cell? a. growt ...
... 20. *Which of these directly allows blood cells to transport oxygen to various parts of the body? a. carbon dioxide b. hemoglobin c. antibodies d. platelets 3.2.A.c 21. The cell cycle describes the life activities of a cell. Which of the following describes the cell cycle of a typical cell? a. growt ...
3-D Cell Model
... Objective: Make a 3-D model of a cell to learn about the structure and function of the cell and cell organelle. Guidelines: A.) This Project involves the construction and identification of a “typical” animal cell B.) Your cell must be 3- dimensional with front, back and sides. C.) The model may be m ...
... Objective: Make a 3-D model of a cell to learn about the structure and function of the cell and cell organelle. Guidelines: A.) This Project involves the construction and identification of a “typical” animal cell B.) Your cell must be 3- dimensional with front, back and sides. C.) The model may be m ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... ► They come in many different shapes and sizes ► They perform a variety of functions. ...
... ► They come in many different shapes and sizes ► They perform a variety of functions. ...
Plasmodesmata 2004. Surfing the Symplasm
... the role of the microtubule (MT) cytoskeleton in delivering MP-RNA complexes to plasmodesmata. Although both groups agreed that the decoration of MT later in the infection process is not involved in cellto-cell transport, debate continues as to whether the targeting of MP-RNA to plasmodesmata requir ...
... the role of the microtubule (MT) cytoskeleton in delivering MP-RNA complexes to plasmodesmata. Although both groups agreed that the decoration of MT later in the infection process is not involved in cellto-cell transport, debate continues as to whether the targeting of MP-RNA to plasmodesmata requir ...
Ice Mantle Maker Data Sheet
... Are you fed up with cold wet hands, and hours of frustration when you produce an ice mantle in your Triple Point Cell? Change your life and try the Isotech Ice Mantle Maker. We developed it, like so many of our products, for our own use in our UKAS facility. It is so easy that we actually want to ma ...
... Are you fed up with cold wet hands, and hours of frustration when you produce an ice mantle in your Triple Point Cell? Change your life and try the Isotech Ice Mantle Maker. We developed it, like so many of our products, for our own use in our UKAS facility. It is so easy that we actually want to ma ...
toward a `visible cell`… and beyond
... interactions, networks and signalling − from molecule-tocell and from cell-to-tissue − new generations of biologists will benefit from a more 'holistic' understanding of molecular organisation and biochemistry in situ. One such effort with an underlying focus on mammalian cell imaging is the Visible ...
... interactions, networks and signalling − from molecule-tocell and from cell-to-tissue − new generations of biologists will benefit from a more 'holistic' understanding of molecular organisation and biochemistry in situ. One such effort with an underlying focus on mammalian cell imaging is the Visible ...
Print edition PDF
... justification for the work: “Cell populations are heterogeneous. And these differences between individual cells in large populations sometimes become very important.” Consider cancer stem cells, for instance. Or drugresistant bacteria. Or the many subtly different neuronal cell types in the brain. I ...
... justification for the work: “Cell populations are heterogeneous. And these differences between individual cells in large populations sometimes become very important.” Consider cancer stem cells, for instance. Or drugresistant bacteria. Or the many subtly different neuronal cell types in the brain. I ...
The Three Major Parts of the Cell
... that change their shape along the membrane which allows a molecule known as a SIGNAL MOLECULE to bind to it. ...
... that change their shape along the membrane which allows a molecule known as a SIGNAL MOLECULE to bind to it. ...
Ch 7: A View of the Cell
... Transport Proteins: Proteins that span the entire membrane and form channels for specific molecules to enter and leave (like a ...
... Transport Proteins: Proteins that span the entire membrane and form channels for specific molecules to enter and leave (like a ...
A Tour Through the Cell Zellular Biology 2014
... A big dark spot found floating in the middle of the cytoplasm (liquid that fills cell) Not on edge of cell because that would be dangerous ...
... A big dark spot found floating in the middle of the cytoplasm (liquid that fills cell) Not on edge of cell because that would be dangerous ...
1. What is the product of mitosis? 2.What is the product of meiosis?
... • You need to know: • Structure of DNA • Structures from DNA -> Chromosome • Steps of protein synthesis • Organelles involved in protein synthesis • How cancer occurs ...
... • You need to know: • Structure of DNA • Structures from DNA -> Chromosome • Steps of protein synthesis • Organelles involved in protein synthesis • How cancer occurs ...
Viruses - I Heart Science
... Infected cells sometimes produce interferons which are proteins that can protect noninfected cells. Antiviral drugs often have adverse side effects, limiting their use. Public health measures can prevent or slow disease. ...
... Infected cells sometimes produce interferons which are proteins that can protect noninfected cells. Antiviral drugs often have adverse side effects, limiting their use. Public health measures can prevent or slow disease. ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... network of proteins which give cells their shape also responsible for shape of plant cells because guide cell wall formation left intact by detergents that extract rest of cell ...
... network of proteins which give cells their shape also responsible for shape of plant cells because guide cell wall formation left intact by detergents that extract rest of cell ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.