Score 3.0 The student will understand cell theory and be able
... The student will understand cell theory and be able identify structures and functions of major components of plant and animal cells. Performs complex skills: o Investigate and explain the components of the scientific theory of cells (cell theory); all organisms are composed of cells (single-celled o ...
... The student will understand cell theory and be able identify structures and functions of major components of plant and animal cells. Performs complex skills: o Investigate and explain the components of the scientific theory of cells (cell theory); all organisms are composed of cells (single-celled o ...
1 2
... Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm (sí„tó-plazm; kytos = a hollow, plasma = a thing formed) is a general term for all cellular contents located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. The ...
... Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm (sí„tó-plazm; kytos = a hollow, plasma = a thing formed) is a general term for all cellular contents located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. The ...
Tutorial 6
... -Some of the terms will also become clearer as they are used during lecture Descriptive Embryology -Understanding the normal and abnormal events that happen during embryological events through direct study of the embryos without experimental intervention -Comes about through observation using light ...
... -Some of the terms will also become clearer as they are used during lecture Descriptive Embryology -Understanding the normal and abnormal events that happen during embryological events through direct study of the embryos without experimental intervention -Comes about through observation using light ...
Developmental modifications of the cell cycle involving S phase
... S phase + M phase cells fused: S phase cells prematurely enter mitosis and since chromosomes are not yet completely replicated they cannot do this properly, resulting in “mitotic catastrophe”. Shows that factors are present in M phase cells that can “push” S phase cells prematurely into M phase. 1. ...
... S phase + M phase cells fused: S phase cells prematurely enter mitosis and since chromosomes are not yet completely replicated they cannot do this properly, resulting in “mitotic catastrophe”. Shows that factors are present in M phase cells that can “push” S phase cells prematurely into M phase. 1. ...
ALL LIFE IS CELLULAR!
... Cells have a support structure called the cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is composed of microtubules and microfilaments. Microtubules are thin, hollow cylinders made of protein and microfilaments are thin solid protein fibers. ...
... Cells have a support structure called the cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is composed of microtubules and microfilaments. Microtubules are thin, hollow cylinders made of protein and microfilaments are thin solid protein fibers. ...
cell membrane - Cloudfront.net
... Large molecules and clumps of material can be taken into the cell by a process known as ___________. endocytosis The two kinds of endocytosis are: 1. Phagocytosis= ‘Cell eating’ 2. Pinocytosis= ‘cell drinking’ Exocytosis release of large amounts of material ___________= ...
... Large molecules and clumps of material can be taken into the cell by a process known as ___________. endocytosis The two kinds of endocytosis are: 1. Phagocytosis= ‘Cell eating’ 2. Pinocytosis= ‘cell drinking’ Exocytosis release of large amounts of material ___________= ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... requires of specific receptor proteins located in the cell membrane. Cell receptors interact with the molecule to be transported into the cell through a ligand — a molecule that binds specifically to the receptor Receptor-mediated endocytosis is highly specific. Human cells use receptor-mediated end ...
... requires of specific receptor proteins located in the cell membrane. Cell receptors interact with the molecule to be transported into the cell through a ligand — a molecule that binds specifically to the receptor Receptor-mediated endocytosis is highly specific. Human cells use receptor-mediated end ...
Oregonism
... concentrated by centrifugation. Prior to freeze-drying the concentrated cells are exposed to pre freeze-drying treatments such as cryoprotectants. The cells are then freeze-dried for packaging and storage. ...
... concentrated by centrifugation. Prior to freeze-drying the concentrated cells are exposed to pre freeze-drying treatments such as cryoprotectants. The cells are then freeze-dried for packaging and storage. ...
Ch 6 – Viruses - Mr-Paullers-wiki
... 3. some events (DNA pol or RNA pol occur in nucleus) others protein assembly occur in the cytoplasm (at ribosomes) 10a receptors (usually glycoproteins) on the cell membrane determine if viruses can dock on cells or not. These types of receptors are often species specific, which means that a virus t ...
... 3. some events (DNA pol or RNA pol occur in nucleus) others protein assembly occur in the cytoplasm (at ribosomes) 10a receptors (usually glycoproteins) on the cell membrane determine if viruses can dock on cells or not. These types of receptors are often species specific, which means that a virus t ...
Contents
... Chapter 3 The Protoplast: Endomembrane System, Secretory Pathways, Cytoskeleton, and Stored Compounds ...
... Chapter 3 The Protoplast: Endomembrane System, Secretory Pathways, Cytoskeleton, and Stored Compounds ...
5.5 Living Systems
... a. Shape of eyes b. Number of legs c. Presence of wings d. Location of antenni NOTE – the 2010 VDOE Curriculum Framework no longer mentions the five kingdoms, so questions like the following will presumably no longer be included on the 5th grade test. 30. A kingdom is the largest classification of l ...
... a. Shape of eyes b. Number of legs c. Presence of wings d. Location of antenni NOTE – the 2010 VDOE Curriculum Framework no longer mentions the five kingdoms, so questions like the following will presumably no longer be included on the 5th grade test. 30. A kingdom is the largest classification of l ...
Substances enter and leave cells through the cell membrane
... Questions you’ll be answer by the end! How do substances enter and leave cells? What is diffusion? What is osmosis? Why does some transport need energy? ...
... Questions you’ll be answer by the end! How do substances enter and leave cells? What is diffusion? What is osmosis? Why does some transport need energy? ...
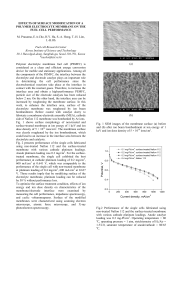
[Frontiers in Bioscience, 5, d50-57, January 1, 2000] THE CONTROL
... mediated by a specific ubiquitin ligase complex known as the Anaphase-Promoting Complex or Cyclosome (APC/C) (figure 2) (45-49). APC/C targets contain a conserved nine amino acid motif called the destruction box that is required for APC/C-mediated ubiquitination (46, 50-55). During this process, ubi ...
... mediated by a specific ubiquitin ligase complex known as the Anaphase-Promoting Complex or Cyclosome (APC/C) (figure 2) (45-49). APC/C targets contain a conserved nine amino acid motif called the destruction box that is required for APC/C-mediated ubiquitination (46, 50-55). During this process, ubi ...
Biol 1406 Ch 8
... Which stage of respiration produces the most ATP? Which produces the least? Which stage(s) must invest energy to create energy? ...
... Which stage of respiration produces the most ATP? Which produces the least? Which stage(s) must invest energy to create energy? ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... During meiosis, a cell undergoes two divisions to produce four gametes, each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. ...
... During meiosis, a cell undergoes two divisions to produce four gametes, each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell)
... Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins explain. Explain the different types of lipids and proteins found on cell membrane. Distinguish between peripheral and integral proteins. Functions of each. Role of membrane carbohydrates in cell-cell recognition. Membrane permeability. Wha ...
... Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins explain. Explain the different types of lipids and proteins found on cell membrane. Distinguish between peripheral and integral proteins. Functions of each. Role of membrane carbohydrates in cell-cell recognition. Membrane permeability. Wha ...
Cell Structurewoyce2010
... some have no vacuoles • No cell wall and no chloroplast • More lysosomes • More mitochondria ...
... some have no vacuoles • No cell wall and no chloroplast • More lysosomes • More mitochondria ...
Ch 6 Nutrition Study Guide
... Aerobes Microaerophiles Facultative anaerobes Anaerobes Aerotolerent anaerobes How can pH be damaging to cells? How does variation is osmoic pressure effect microbes? How do we use osmotic pressure to control microbial growth in some food types? What effect does radiation have on the ...
... Aerobes Microaerophiles Facultative anaerobes Anaerobes Aerotolerent anaerobes How can pH be damaging to cells? How does variation is osmoic pressure effect microbes? How do we use osmotic pressure to control microbial growth in some food types? What effect does radiation have on the ...
Cell Structure All living things are made of cells. Biology is the study
... A typical animal cell has the common structures shown in the diagram above. These include: Cell Membrane: The cell membrane contains the contents of the cell and provides a barrier to control what enters and leaves the cell. The cell membrane is often described as ‘selectively permeable’ as it allow ...
... A typical animal cell has the common structures shown in the diagram above. These include: Cell Membrane: The cell membrane contains the contents of the cell and provides a barrier to control what enters and leaves the cell. The cell membrane is often described as ‘selectively permeable’ as it allow ...
Effects of Surface Modification of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
... Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is considered as a clean and efficient energy conversion device for mobile and stationary applications. Among all the components of the PEMFC, the interface between the electrolyte and electrode catalyst plays an important role in determining the cell p ...
Bacterial morphology, metabolism and growth
... • Bacterial 70S chromosome (30+50S) • Proteins and RNA of the ribosome are significantly different • Major targets for antibacterial drugs ...
... • Bacterial 70S chromosome (30+50S) • Proteins and RNA of the ribosome are significantly different • Major targets for antibacterial drugs ...
LIQUID CRYSTAL CELLS
... molecular turbulence causes light to be scattered in all directions and the cell appears to be bright. this phenomenon is called Dynamic Scattering. FIELD EFECT TYPE Two thin polarising optical filters are placed at the inside of each glass sheet. The LCD material is of twisted nematic type which tw ...
... molecular turbulence causes light to be scattered in all directions and the cell appears to be bright. this phenomenon is called Dynamic Scattering. FIELD EFECT TYPE Two thin polarising optical filters are placed at the inside of each glass sheet. The LCD material is of twisted nematic type which tw ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.












![[Frontiers in Bioscience, 5, d50-57, January 1, 2000] THE CONTROL](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017171575_1-70635603f98612e3c5ac310e8691f919-300x300.png)