Biology Second Semester Exam Review Answers Bacteria and
... 3. Describe Gram staining and what the results mean. 473 Gram Staining identifies bacteria with large amounts of peptidoglycan in their cell walls (Gram +) Or small amounts of peptidoglycan in their cell walls (Gram -). Gram Negative bacteria are much more difficult to kill with antibiotics. 4. What ...
... 3. Describe Gram staining and what the results mean. 473 Gram Staining identifies bacteria with large amounts of peptidoglycan in their cell walls (Gram +) Or small amounts of peptidoglycan in their cell walls (Gram -). Gram Negative bacteria are much more difficult to kill with antibiotics. 4. What ...
Bacteria
... Bacteria differ from Eukaryotes No nucleus or membrane bound organelles 10 times smaller Unicellular, activities not specialized Single chromosome Reproduce by binary fission Simple flagella that spins, pili for adherence Many metabolic abilities, perform any aerobic ...
... Bacteria differ from Eukaryotes No nucleus or membrane bound organelles 10 times smaller Unicellular, activities not specialized Single chromosome Reproduce by binary fission Simple flagella that spins, pili for adherence Many metabolic abilities, perform any aerobic ...
Classification:
... • Phylum- several different classes that share important characteristics. • Kingdom - largest taxonomic group, consisting of closely related phyla ...
... • Phylum- several different classes that share important characteristics. • Kingdom - largest taxonomic group, consisting of closely related phyla ...
Biology Study Guide
... Binomial nomenclature –____________________________________________________ Write the levels of classification in order: class, domain, family, genus, kingdom, order, phylum, species 1.______________________ ...
... Binomial nomenclature –____________________________________________________ Write the levels of classification in order: class, domain, family, genus, kingdom, order, phylum, species 1.______________________ ...
Wildlife Diseases Worksheet
... caused by this collection of slightly different viruses rather than by a single virus type. The virus subtypes are identified and classified on the basis of two broad types of antigens, _______________________________ (H) and ___________________________(N); 16 H and 9 N antigens have been identified ...
... caused by this collection of slightly different viruses rather than by a single virus type. The virus subtypes are identified and classified on the basis of two broad types of antigens, _______________________________ (H) and ___________________________(N); 16 H and 9 N antigens have been identified ...
Bacteria Taxonomy – Slide Viewer Set 217
... Bacteria Taxonomy – Slide Viewer Set 217 Introduction: 1. What is taxonomy? __________________________________________________________ 2. Who devised the present system of classification? _________________________________________ 3. Describe the two word naming system. ______________________________ ...
... Bacteria Taxonomy – Slide Viewer Set 217 Introduction: 1. What is taxonomy? __________________________________________________________ 2. Who devised the present system of classification? _________________________________________ 3. Describe the two word naming system. ______________________________ ...
Kingdom Prokaryotae (Monera)
... that breaks down atmospheric (N2) into a form usable by plants (NH4) ...
... that breaks down atmospheric (N2) into a form usable by plants (NH4) ...
Bacterial cultivation
... Colony- A bacterial population derived from one bacterial cell. The cells within the colony have ...
... Colony- A bacterial population derived from one bacterial cell. The cells within the colony have ...
Chapter 27
... peptidoglycan = polysaccharides + amino acid chains important for lipopolysaccharides = lipids + polysaccharides your doctor to know! outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria lipopolysaccharides ...
... peptidoglycan = polysaccharides + amino acid chains important for lipopolysaccharides = lipids + polysaccharides your doctor to know! outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria lipopolysaccharides ...
Bacteria
... usable by plants • The difference: Make dif, chemicals, react to dif antibiotics and disinfectants ...
... usable by plants • The difference: Make dif, chemicals, react to dif antibiotics and disinfectants ...
Bacteria
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
Chapter 18 Bacteria Notes
... Earth. E. coli is the most studied bacterium. All bacteria are prokaryotic meaning they have no true nucleus (they do still have genetic material). Bacteria do contain cell walls containing acids & sugars that provide support as well as a cell membrane inside of this cell wall. Some antibiotics work ...
... Earth. E. coli is the most studied bacterium. All bacteria are prokaryotic meaning they have no true nucleus (they do still have genetic material). Bacteria do contain cell walls containing acids & sugars that provide support as well as a cell membrane inside of this cell wall. Some antibiotics work ...
Testing for Chemotaxis in Earthworm Bacterial Symbiont
... capsule. V. eiseniae is grown in culture in the lab; the remaining species are still difficult to grow. Previous work has shown that the V. eiseniae colonizes into the nephridia through the use of both a flagella and type IV pili. This current project seeks to test for motility through chemotaxis an ...
... capsule. V. eiseniae is grown in culture in the lab; the remaining species are still difficult to grow. Previous work has shown that the V. eiseniae colonizes into the nephridia through the use of both a flagella and type IV pili. This current project seeks to test for motility through chemotaxis an ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... chromosome, some members of each domain can fix nitrogen, and some members of each domain can grow at temperatures above 80oC. The two groups have cell walls made of different substances, bacteria use chlorophyll in photosynthesis whereas archaea do not, some archaea generate methane while no bacter ...
... chromosome, some members of each domain can fix nitrogen, and some members of each domain can grow at temperatures above 80oC. The two groups have cell walls made of different substances, bacteria use chlorophyll in photosynthesis whereas archaea do not, some archaea generate methane while no bacter ...
Helpful Bacteria - Use microviewers and slide set #19
... Purpose: To observe examples of various types of bacteria and to learn more information about their relationships with other organisms. Method: – Use microviewers and slide set 105 to answer the following questions. Results Part 1: Harmful Bacteria 1. Who is responsible for introducing the science o ...
... Purpose: To observe examples of various types of bacteria and to learn more information about their relationships with other organisms. Method: – Use microviewers and slide set 105 to answer the following questions. Results Part 1: Harmful Bacteria 1. Who is responsible for introducing the science o ...
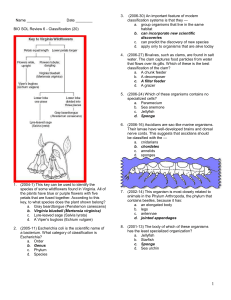
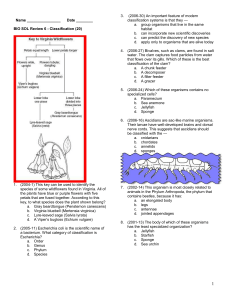
BIO SOL Review 6
... lives in the lakes of two caves in Augusta County, Virginia. Its primary food source appears to be fine bits of organic matter that drift into the cave lakes. This cave-dwelling species belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
... lives in the lakes of two caves in Augusta County, Virginia. Its primary food source appears to be fine bits of organic matter that drift into the cave lakes. This cave-dwelling species belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
BIO SOL Review 6 - Classification
... lives in the lakes of two caves in Augusta County, Virginia. Its primary food source appears to be fine bits of organic matter that drift into the cave lakes. This cave-dwelling species belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
... lives in the lakes of two caves in Augusta County, Virginia. Its primary food source appears to be fine bits of organic matter that drift into the cave lakes. This cave-dwelling species belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
Biofilms
... designed bacteria with many different conditions → more time than actual engineering ? Lots of economical interest in this ...
... designed bacteria with many different conditions → more time than actual engineering ? Lots of economical interest in this ...
Kingdom – Monera
... 2.) ___heterotrophic___ organisms cannot make their own food. These organisms may live off of dead and decaying matter. They are called ___chemotrophes__. If an organism can make its own food it is called a(n) ___autotrophe___. 3.) Since bacteria are single-celled organisms it is very difficult to s ...
... 2.) ___heterotrophic___ organisms cannot make their own food. These organisms may live off of dead and decaying matter. They are called ___chemotrophes__. If an organism can make its own food it is called a(n) ___autotrophe___. 3.) Since bacteria are single-celled organisms it is very difficult to s ...
Culturing Bacteria
... they are cultured on agar so you can see the colony. • Colony is a large group of bacteria that has grown from one single bacteria • Bacteria reproduce by dividing in half • To see with microscope you must magnify a minimum of 400 times and then still look like the head of a pin. ...
... they are cultured on agar so you can see the colony. • Colony is a large group of bacteria that has grown from one single bacteria • Bacteria reproduce by dividing in half • To see with microscope you must magnify a minimum of 400 times and then still look like the head of a pin. ...
Survey of Microbes Part I: Important prokaryotes
... great ecological importance in the global carbon, oxygen and nitrogen cycles ...
... great ecological importance in the global carbon, oxygen and nitrogen cycles ...
Presentation
... Previously extracted from citrus fruit, which became less available during WWI. A new source was discovered soon after that with the fungus Aspergillus niger and molasses as a carbon source. A continuous culture allows a steady state of growth and higher production of citric acid. ...
... Previously extracted from citrus fruit, which became less available during WWI. A new source was discovered soon after that with the fungus Aspergillus niger and molasses as a carbon source. A continuous culture allows a steady state of growth and higher production of citric acid. ...