The Cell Cycle and Mitosis - sciencestuffyabc / FrontPage
... cell division can take place) chromosomes are replicated to form an identical copy of itself. Two identical copies of a chromosome are called “sister” chromatids – (one of two identical “sister” parts of a duplicated chromosome) Centromere - area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached ...
... cell division can take place) chromosomes are replicated to form an identical copy of itself. Two identical copies of a chromosome are called “sister” chromatids – (one of two identical “sister” parts of a duplicated chromosome) Centromere - area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached ...
lesson 4 PC 2.3 Cell Structure & Keratinisation
... follicle. While the cells travel along the follicle to eventually become the hair we see, they go through a number of changes. This process is called Keratinisation. ...
... follicle. While the cells travel along the follicle to eventually become the hair we see, they go through a number of changes. This process is called Keratinisation. ...
Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
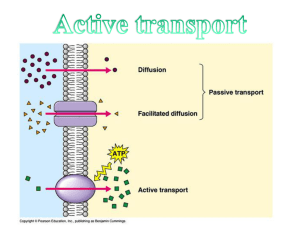
... • ATP energy needed to fight diffusion – ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate • ATP activates pumps (see animation) ...
... • ATP energy needed to fight diffusion – ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate • ATP activates pumps (see animation) ...
CHAPTER 1: THE CELL 1.1 (p. 15) 1. Name four characteristics of
... 2. How did the microscope change human understanding of life? It allows us to see cells, inside cells and even molecules. Before the microscope, people didn’t realize that life could be so small. 3. Explain the three concepts that make up cell theory All life is composed of cells; cells carry out li ...
... 2. How did the microscope change human understanding of life? It allows us to see cells, inside cells and even molecules. Before the microscope, people didn’t realize that life could be so small. 3. Explain the three concepts that make up cell theory All life is composed of cells; cells carry out li ...
Research into human body cell behaviour reveals
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Organelle
... A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA Surrounds the nucleus. A round struc ...
... A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles. The control center of the cell. Contains the DNA Surrounds the nucleus. A round struc ...
Ch. 7-Cells Lecture #1 blanks
... A. ____- The basic unit of living organisms B. The ______ was developed by several scientists including Hooke, Schleiden andSchwann. ...
... A. ____- The basic unit of living organisms B. The ______ was developed by several scientists including Hooke, Schleiden andSchwann. ...
Animal Mitosis - New Braunfels ISD
... In eukaryotic cells, there are two growth phases, and cell division includes mitosis. The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins at three key checkpoints in the cycle. The proteins signal the cell to either start or delay the next phase of the cycle. Cancer is a disease that occurs when the ...
... In eukaryotic cells, there are two growth phases, and cell division includes mitosis. The cell cycle is controlled by regulatory proteins at three key checkpoints in the cycle. The proteins signal the cell to either start or delay the next phase of the cycle. Cancer is a disease that occurs when the ...
Organelles found in both plant and animal cells
... slide past one another enable cells to move, as observed in white blood cells and amoebae, and also account for movement of organelles within the cell. Notes: The cell is the basic structural unit of life, and the smallest unit of living things that are considered “alive”. Each cell performs necessa ...
... slide past one another enable cells to move, as observed in white blood cells and amoebae, and also account for movement of organelles within the cell. Notes: The cell is the basic structural unit of life, and the smallest unit of living things that are considered “alive”. Each cell performs necessa ...
The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell
... strength and rigidity. It is permeable to solutes. ...
... strength and rigidity. It is permeable to solutes. ...
Reproduction - Websupport1
... Metaphase plate Represents plane through which mother cell will be divided ...
... Metaphase plate Represents plane through which mother cell will be divided ...
http://sciencespot.net/Media/CellsOrganellesWkst.pdf
... Directions: Match the function cards and memory items by gluing them into the correct locations in the chart below. ...
... Directions: Match the function cards and memory items by gluing them into the correct locations in the chart below. ...
CELL THEORY
... Membranes are SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out Controls what enters and leaves cell Helps with HOMEOSTASIS CYTOPLASM= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell membrane ...
... Membranes are SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out Controls what enters and leaves cell Helps with HOMEOSTASIS CYTOPLASM= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell membrane ...
Flipbook with answers filled in
... Membranes are SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out Controls what enters and leaves cell Helps with HOMEOSTASIS CYTOPLASM= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell membrane ...
... Membranes are SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE (=Semi-permeable) Allow certain molecules to pass through; but keep others out Controls what enters and leaves cell Helps with HOMEOSTASIS CYTOPLASM= gel-like material + organelles between nucleus and cell membrane ...
Unit 4: Microscopes and Structure and Function of Cells Study Guide
... 1. Explain the significance of The Cell Theory. List the scientists and their specific contributions to The Cell Theory and our knowledge of cells. State the three principles of The Cell Theory. 2. Why is cell size limited? What is the mathematical model that describes the size limitations of cells? ...
... 1. Explain the significance of The Cell Theory. List the scientists and their specific contributions to The Cell Theory and our knowledge of cells. State the three principles of The Cell Theory. 2. Why is cell size limited? What is the mathematical model that describes the size limitations of cells? ...
6th Grade Science
... *Hint: The number in parentheses after each clue tells you which lesson the vocabulary word can be found in. Across 2. The first stage of the cell cycle that takes place before cell division occurs; the cell grows and makes a copy of its DNA (5) 5. The diffusion of water molecules across a selectiv ...
... *Hint: The number in parentheses after each clue tells you which lesson the vocabulary word can be found in. Across 2. The first stage of the cell cycle that takes place before cell division occurs; the cell grows and makes a copy of its DNA (5) 5. The diffusion of water molecules across a selectiv ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... Have many different organelles in the cytoplasm About 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells DNA in the nucleus and linear Plant and fungi have a cell wall, other eukaryotic cells do not First appeared on Earth 2 billion years ago ...
... Have many different organelles in the cytoplasm About 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells DNA in the nucleus and linear Plant and fungi have a cell wall, other eukaryotic cells do not First appeared on Earth 2 billion years ago ...
1. Which organelles are most closely associated with the process of
... (2) B 19. Which organelles' activity contributes most directly to muscle contraction in an earthworm? ...
... (2) B 19. Which organelles' activity contributes most directly to muscle contraction in an earthworm? ...
Plasma Membrane
... • The proteins move throughout the phospholipids like boats. – They make up the “Mosaic” ...
... • The proteins move throughout the phospholipids like boats. – They make up the “Mosaic” ...
Cell Division Learning Goals
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A4: The student can explain how a homologous pair of chromosomes is alike and different. B4/C4: Given scenarios the student will predict ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A4: The student can explain how a homologous pair of chromosomes is alike and different. B4/C4: Given scenarios the student will predict ...
Document
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2) ( ) Chitin is a polysaccharide composes the plant cell wall: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3) ( ) Fats are polymers composed from 3 molecules of fatty ac ...
... ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2) ( ) Chitin is a polysaccharide composes the plant cell wall: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3) ( ) Fats are polymers composed from 3 molecules of fatty ac ...
UNIT 1: Reproduction
... THE MODERN CELL THEORY All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms. All cells come from previously existing cells. The activity of an entire organism depends on the total activity of its independent cells. TYPES ...
... THE MODERN CELL THEORY All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms. All cells come from previously existing cells. The activity of an entire organism depends on the total activity of its independent cells. TYPES ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.