Cells
... Development of Electron Microscopes There are two basic types of electron microscopes. The scanning electron microscope scans the surface of cells to learn their three dimensional shape. The transmission electron microscope allows scientists to study the structures contained within a cell. ...
... Development of Electron Microscopes There are two basic types of electron microscopes. The scanning electron microscope scans the surface of cells to learn their three dimensional shape. The transmission electron microscope allows scientists to study the structures contained within a cell. ...
Subject - Currituck County Schools
... mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their general structures (plasma membrane and genetic material) and degree of complexity. B ...
... mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their general structures (plasma membrane and genetic material) and degree of complexity. B ...
File
... Long, tangled strands of genetic material (DNA). An organelle with a system of flattened tubular membranes. The central membrane-bound organelle surrounded by a double membrane. Surrounded by a pair of membranes, with stacks of flattened disks inside. Composed of a double layer membrane (phospholipi ...
... Long, tangled strands of genetic material (DNA). An organelle with a system of flattened tubular membranes. The central membrane-bound organelle surrounded by a double membrane. Surrounded by a pair of membranes, with stacks of flattened disks inside. Composed of a double layer membrane (phospholipi ...
COMPARISON OF CHEEK AND ONION CELLS
... Swish the toothpick in the drop of water and add a drop of methylene blue solution. ...
... Swish the toothpick in the drop of water and add a drop of methylene blue solution. ...
Introduction to Cells Notes File
... b. They all hold the blueprints of how an animal is put together. c. They are vital to all life functions. d. They can ______________________!! e. They can change the physical form of an animal. Good______________ and bad. There are basically two cell types Eukaryotic cells (____________________ ...
... b. They all hold the blueprints of how an animal is put together. c. They are vital to all life functions. d. They can ______________________!! e. They can change the physical form of an animal. Good______________ and bad. There are basically two cell types Eukaryotic cells (____________________ ...
Teacher Manual with Worksheets
... of the most important cellular processes. Nonetheless, memorizing the process, complexes, and molecules involved is not a lot of fun. But the process by which energy is created is reminiscent of games within the ‘infinite runner’ genre (think Temple Run). Therefore, to make learning the concepts a b ...
... of the most important cellular processes. Nonetheless, memorizing the process, complexes, and molecules involved is not a lot of fun. But the process by which energy is created is reminiscent of games within the ‘infinite runner’ genre (think Temple Run). Therefore, to make learning the concepts a b ...
Diapositiva 1
... renewable resources and are often present in by-products of industrial production. Genetic engineering of crop plant cell walls can identify biopolymers with novel functional properties, as well as simplify their extraction, thus increasing the value of these "waste-products." Cell walls will become ...
... renewable resources and are often present in by-products of industrial production. Genetic engineering of crop plant cell walls can identify biopolymers with novel functional properties, as well as simplify their extraction, thus increasing the value of these "waste-products." Cell walls will become ...
midterm exam review
... Draw the stages of mitosis and tell what occurs during each stage. Draw the stages of meiosis (I and II) and tell what occurs in each stage. When does crossing over occur? Why is it important? Define gametogenesis. How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ? Where do each occur? What do eac ...
... Draw the stages of mitosis and tell what occurs during each stage. Draw the stages of meiosis (I and II) and tell what occurs in each stage. When does crossing over occur? Why is it important? Define gametogenesis. How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ? Where do each occur? What do eac ...
Chapter 4 - selu moodle
... Move things around Actin filaments (Microfilaments) – thinnest Cellular movement Microtubules – keeps organelles and other structures in place and also facilitates their movement Can be built up or broken down at will – not permanently stable Use motor proteins Intermediate filaments – the most stab ...
... Move things around Actin filaments (Microfilaments) – thinnest Cellular movement Microtubules – keeps organelles and other structures in place and also facilitates their movement Can be built up or broken down at will – not permanently stable Use motor proteins Intermediate filaments – the most stab ...
File
... stimulates repair enzymes to fix DNA forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
... stimulates repair enzymes to fix DNA forces cell into G0 resting stage keeps cell in G1 arrest causes apoptosis of damaged cell ...
video slide - Independent School District 196
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
lecture6(Eukaryote)
... H2O2. They are also involved in breaking down lipids/fa^y acids. • They have a single membrane that separates their contents from the cytoplasm and that contains membrane-‐proteins cri1cal for various ...
... H2O2. They are also involved in breaking down lipids/fa^y acids. • They have a single membrane that separates their contents from the cytoplasm and that contains membrane-‐proteins cri1cal for various ...
AP Cell Organelles
... excessive uptake of water, and supports the plant against the force of gravity. The thickness and chemical composition of cell walls differs among cell types. The basic design consists of microfibrils of cellulose embedded in a matrix of proteins and other polysaccharides. This is like steel-reinf ...
... excessive uptake of water, and supports the plant against the force of gravity. The thickness and chemical composition of cell walls differs among cell types. The basic design consists of microfibrils of cellulose embedded in a matrix of proteins and other polysaccharides. This is like steel-reinf ...
CSP_7-16-01_outline.rtf
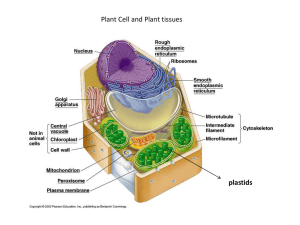
... iv. Again, like the mitochondria chloroplasts have their own DNA and their own ribosomes. v. There are other types of plastids in some plant cells that are used primarily as food storage. c. Plant cells also have vacuoles, which are membrane-bound organelles used primarily as storage for metabolic w ...
... iv. Again, like the mitochondria chloroplasts have their own DNA and their own ribosomes. v. There are other types of plastids in some plant cells that are used primarily as food storage. c. Plant cells also have vacuoles, which are membrane-bound organelles used primarily as storage for metabolic w ...
Biology Standard 1
... Organelles are cell structures that are specialized for different functions. Each type of organelle has a structure that is suited to its function. You will learn more about how organelle structure is related to function as you read about the different types of organelles. Many eukaryotic organisms ...
... Organelles are cell structures that are specialized for different functions. Each type of organelle has a structure that is suited to its function. You will learn more about how organelle structure is related to function as you read about the different types of organelles. Many eukaryotic organisms ...
Cell Transport
... • (4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: ...
... • (4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: ...
Cell Reproduction
... Prokaryotic division differs from eukaryotic division because prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic division requires the replication of the nucleus and genetic material (DNA) as well as the allocation of the organelles into each daughter cell. ...
... Prokaryotic division differs from eukaryotic division because prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic division requires the replication of the nucleus and genetic material (DNA) as well as the allocation of the organelles into each daughter cell. ...
3.2 Cell Organelles
... 3.2 Cell Organelles The cytoskeleton gives eukaryotic cells an internal structure and organization. The cytoskeleton has many functions. • supports and shapes cell • helps position and transport organelles ...
... 3.2 Cell Organelles The cytoskeleton gives eukaryotic cells an internal structure and organization. The cytoskeleton has many functions. • supports and shapes cell • helps position and transport organelles ...
Semester Exam Review Sheet
... In the ABO blood type system the A and B alleles are dominant to O allele, and A and B are codominant to each other. Make a cross between an AO mom and an BO dad. ...
... In the ABO blood type system the A and B alleles are dominant to O allele, and A and B are codominant to each other. Make a cross between an AO mom and an BO dad. ...
the Study Guide for Mr. Brown`s Level 1- Biology Unit 3- "Cells
... *Describe the similarities and differences between bacteria and viruses. (CSDE 10.2) Identify prokaryotic cell structures and explain functions of eukaryotic organelles. (CSDE 10.1) Distinguish between plant and animal cells. (CSDE 10.1) Explain the role of the cell membrane in supporting ce ...
... *Describe the similarities and differences between bacteria and viruses. (CSDE 10.2) Identify prokaryotic cell structures and explain functions of eukaryotic organelles. (CSDE 10.1) Distinguish between plant and animal cells. (CSDE 10.1) Explain the role of the cell membrane in supporting ce ...
cell cycle
... may have evolved from binary fission 7. Explain how the abnormal cell division of cancerous cells escapes normal cell cycle controls 8. Distinguish between benign, malignant, and ...
... may have evolved from binary fission 7. Explain how the abnormal cell division of cancerous cells escapes normal cell cycle controls 8. Distinguish between benign, malignant, and ...
Internal Structure: Bacteria have a very simple internal structure, and
... General Cell Information >The cell is the smallest unit of life. >Your body has about 100 trillion cells. >All cells have DNA and cytoplasm. >There are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. > Eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells in that eukaryotic cells contain many membran ...
... General Cell Information >The cell is the smallest unit of life. >Your body has about 100 trillion cells. >All cells have DNA and cytoplasm. >There are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. > Eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells in that eukaryotic cells contain many membran ...
000A
... MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. ...
... MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.