Bacteria - Auburn City Schools
... “stuffed” inside the cell, along with free floating ribosomes (which help make proteins and have RNA). Reproduces by binary fission Since the cell’s DNA is not concentrated in one area all the bacteria cell has to do is double it’s genetic material, and split in half. ...
... “stuffed” inside the cell, along with free floating ribosomes (which help make proteins and have RNA). Reproduces by binary fission Since the cell’s DNA is not concentrated in one area all the bacteria cell has to do is double it’s genetic material, and split in half. ...
EOC Practice
... a) Cellular respiration consists of two phases. b) Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide. c) Cellular respiration provides energy for the cell. d) Cellular respiration is carried out in one specific organelle. _______ 36) A cell with 24 chromosomes undergoes mitosis twice. How many ...
... a) Cellular respiration consists of two phases. b) Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide. c) Cellular respiration provides energy for the cell. d) Cellular respiration is carried out in one specific organelle. _______ 36) A cell with 24 chromosomes undergoes mitosis twice. How many ...
What are Cells?
... A cell is the basic unit of life. All living organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or more (multicellular) cells. In unicellular organisms, like many protists and bacteria, specialized parts of the cell perform all of the organism’s vital functions. In multicellular organisms, like humans, spe ...
... A cell is the basic unit of life. All living organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or more (multicellular) cells. In unicellular organisms, like many protists and bacteria, specialized parts of the cell perform all of the organism’s vital functions. In multicellular organisms, like humans, spe ...
BIOL 1308
... Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes Stages of the cell cycle Phases, events, and importance of mitosis Cell division and cancer Importance of sexual reproduction in life Genetic variation and its importance Causes and symptoms of Down syndrome Consequences of abnormal numbers of sex ...
... Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes Stages of the cell cycle Phases, events, and importance of mitosis Cell division and cancer Importance of sexual reproduction in life Genetic variation and its importance Causes and symptoms of Down syndrome Consequences of abnormal numbers of sex ...
Types of Transport Passive Transport Active Transport diffusion
... Diffusion can be explained by the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration . Diffusion rates increase with increasing temperature, pressure and concentration. When molecules are finally distributed equally, then equilibrium is reached. ...
... Diffusion can be explained by the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration . Diffusion rates increase with increasing temperature, pressure and concentration. When molecules are finally distributed equally, then equilibrium is reached. ...
AP Biology Chapter Questions – Campbell 7th Edition
... 2. Describe the structural organization of a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic genome. 3. Describe the major events of cell division that enable the genome of one cell to be passed on to two daughter cells. 4. Describe how chromosome number changes throughout the human life cycle. The Mitotic Cell Cycle ...
... 2. Describe the structural organization of a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic genome. 3. Describe the major events of cell division that enable the genome of one cell to be passed on to two daughter cells. 4. Describe how chromosome number changes throughout the human life cycle. The Mitotic Cell Cycle ...
Multicellular Life
... Every cell in your body has a full set of DNA but each type of cell uses only the specific genes it needs to carry out its function- like a cookbook! A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will ...
... Every cell in your body has a full set of DNA but each type of cell uses only the specific genes it needs to carry out its function- like a cookbook! A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will ...
2015 department of medicine research day
... and Arrhythmias, Biology of Perception and Pain, Psychoneuroimmunology ...
... and Arrhythmias, Biology of Perception and Pain, Psychoneuroimmunology ...
Plate #7. Rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum (from a
... reticulum, from an area like that labeled GER in Plate 1 but at more than twice the magnification. Note again the extensive network of membranes and the differences between the spaces around them: on one side of a membrane are numerous dark dots, the ribosomes (for instance, at Y); on the other is a ...
... reticulum, from an area like that labeled GER in Plate 1 but at more than twice the magnification. Note again the extensive network of membranes and the differences between the spaces around them: on one side of a membrane are numerous dark dots, the ribosomes (for instance, at Y); on the other is a ...
Parts of a Cell
... Perixomes are very similar to lysosomes. They also digest material, but they are better at breaking down fatty acids and toxic material, like alcohol. What if a cell has too much food? Or what if the organelles produce waste that can contaminate the rest of the cell? That’s when the organelles calle ...
... Perixomes are very similar to lysosomes. They also digest material, but they are better at breaking down fatty acids and toxic material, like alcohol. What if a cell has too much food? Or what if the organelles produce waste that can contaminate the rest of the cell? That’s when the organelles calle ...
Chapter 7 - North Mac Schools
... –a granular material visible w/in the nucleus. – It consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins. – Most of the time chromatin is spread throughout the nucleus. – However, when a cell divides, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. ...
... –a granular material visible w/in the nucleus. – It consists of DNA tightly coiled around proteins. – Most of the time chromatin is spread throughout the nucleus. – However, when a cell divides, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. ...
Cell-Structure
... • In animal cells, a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules called centrioles duplicate during interphase and move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase ...
... • In animal cells, a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules called centrioles duplicate during interphase and move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase ...
Sodium-Potassium pumps
... The mechanism responsible for this is the sodium-potassium pump which moves these two ions in opposite directions across the plasma membrane. ...
... The mechanism responsible for this is the sodium-potassium pump which moves these two ions in opposite directions across the plasma membrane. ...
Cell-Structure
... • In animal cells, a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules called centrioles duplicate during interphase and move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase ...
... • In animal cells, a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules called centrioles duplicate during interphase and move to opposite ends of the cell during prophase ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... Copy notes or flipbook for students to collect information on. If you use the rotation activity, set up them prior to class Resources – page 196 - 204 Notes 30-45 minutes Key Vocabulary Prokaryote(ic) Eukaryote(ic) membrane-bound organelles bacteria cells nucleus nucleoid ribos ...
... Copy notes or flipbook for students to collect information on. If you use the rotation activity, set up them prior to class Resources – page 196 - 204 Notes 30-45 minutes Key Vocabulary Prokaryote(ic) Eukaryote(ic) membrane-bound organelles bacteria cells nucleus nucleoid ribos ...
Slide ()
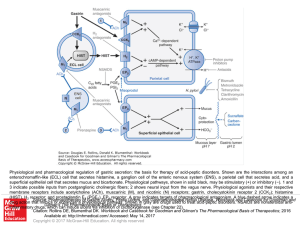
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Homeostasis in Organisms Study Guide Name: 1. Anything living
... 22. Enzymes have an optimum __________________ and ________ to function correctly. However, all enzymes only interact with specific molecules because they are ______________________-specific. They fit together like a “lock and key.” If the shape of an enzyme changes at all, which is called ________ ...
... 22. Enzymes have an optimum __________________ and ________ to function correctly. However, all enzymes only interact with specific molecules because they are ______________________-specific. They fit together like a “lock and key.” If the shape of an enzyme changes at all, which is called ________ ...
B2 Additional Biology - Flintshire County Council
... Place tape measure across the area being investigated (i.e. pond to woods) This forms your TRANSECT line At REGULAR INTERVALS Along the transect, place your quadrat Count the no. of species present, and the no. of individuals of each species Repeat steps along another transect line ...
... Place tape measure across the area being investigated (i.e. pond to woods) This forms your TRANSECT line At REGULAR INTERVALS Along the transect, place your quadrat Count the no. of species present, and the no. of individuals of each species Repeat steps along another transect line ...
Supplementary Infomation (doc 52K)
... Autophagosomes were identified as green dots in the cytosol of RGCs using confocal microscopy with a 63X objective and a 2X digital zoom and analyzing the images in 0.5 μm confocal planes besides the maximal projections. Positive cells were identified according to the following criteria: (1) the pre ...
... Autophagosomes were identified as green dots in the cytosol of RGCs using confocal microscopy with a 63X objective and a 2X digital zoom and analyzing the images in 0.5 μm confocal planes besides the maximal projections. Positive cells were identified according to the following criteria: (1) the pre ...
White blood cells
... What is cell differentiation? • cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. ...
... What is cell differentiation? • cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.