HO HB Exam Study Guide Semester I
... all organelles of plant and animal cells (know the cell chart) relationship between cell volume, surface area and growth compare the structure of plant and animal cells unicellular, colonial and multicellular organisms and relationship to division of labor, interdependence and specialization S ...
... all organelles of plant and animal cells (know the cell chart) relationship between cell volume, surface area and growth compare the structure of plant and animal cells unicellular, colonial and multicellular organisms and relationship to division of labor, interdependence and specialization S ...
Lecture 07, Fungi - Cal State LA
... Fungi grow by extending the tips of their hyphae through cytoplasmic streaming Hyphae can be divided into individual cells by partitions called septa Some fungi grow by repeated mitotic divisions of nuclei without cell division coenocytic condition - giant multi-nucleated cells, similar to slime mo ...
... Fungi grow by extending the tips of their hyphae through cytoplasmic streaming Hyphae can be divided into individual cells by partitions called septa Some fungi grow by repeated mitotic divisions of nuclei without cell division coenocytic condition - giant multi-nucleated cells, similar to slime mo ...
Plant Molecular Biology Reporter
... and solubility, and tissue specificity. A failure of any one of these factors results in the lack of an observable phenotype in the recovered plant. On the other hand, lethality may have been overlooked. Regeneration of transformed plant lines constitutes a process of selection for individuals that ...
... and solubility, and tissue specificity. A failure of any one of these factors results in the lack of an observable phenotype in the recovered plant. On the other hand, lethality may have been overlooked. Regeneration of transformed plant lines constitutes a process of selection for individuals that ...
Cell Apoptosis DAPI Detection Kit
... Ordering Information………………………………………………………..................... ...
... Ordering Information………………………………………………………..................... ...
chapter 11
... • The lifetime of an mRNA molecule helps determine how much protein is made – The protein may need to be activated in some way ...
... • The lifetime of an mRNA molecule helps determine how much protein is made – The protein may need to be activated in some way ...
Idioblastic mucilage - Modern Phytomorphology
... Idioblastic cells are individual cells which prominently differ from their neighbouring cells in size, content, ontogeny and metabolism. They are considered as secretory structures composed of one cell only. This fact stresses their functional complexity compared to the multicellular glands. Idiobla ...
... Idioblastic cells are individual cells which prominently differ from their neighbouring cells in size, content, ontogeny and metabolism. They are considered as secretory structures composed of one cell only. This fact stresses their functional complexity compared to the multicellular glands. Idiobla ...
Passive and Active Transport Internet Assignment
... Part IV: Passive and Active Transport Summary Go back to the class website on Weebly, and click on “Web site # 3” When you get to the Youtube video, put the “subtitles” on (click on the “cc” button) so that you can read the information as the southern lady is talking. 28. What is the name of the ...
... Part IV: Passive and Active Transport Summary Go back to the class website on Weebly, and click on “Web site # 3” When you get to the Youtube video, put the “subtitles” on (click on the “cc” button) so that you can read the information as the southern lady is talking. 28. What is the name of the ...
HEARTWOOD
... If extractives go into the cell wall, If a lot of extractives deposited in cell wall, Then may be some increase in the compressive strength of the heartwood relative to “like-aged” sapwood. ...
... If extractives go into the cell wall, If a lot of extractives deposited in cell wall, Then may be some increase in the compressive strength of the heartwood relative to “like-aged” sapwood. ...
Chapter 4
... • Plasmids: small circular, doublestranded DNA – extrachromosomal genetic elements, replicate independently of chromosomal DNA – can be transferred from one bacterium to another – used for gene manipulation in biotechnology ...
... • Plasmids: small circular, doublestranded DNA – extrachromosomal genetic elements, replicate independently of chromosomal DNA – can be transferred from one bacterium to another – used for gene manipulation in biotechnology ...
TOB Module Glandular Tissues and How Cells Secrete
... • transport vesicle shuttles across cytoplasm • material exocytosed at opposite surface N.B. Molecules too large to penetrate membranes can be shutted across from one component of the body to another. ...
... • transport vesicle shuttles across cytoplasm • material exocytosed at opposite surface N.B. Molecules too large to penetrate membranes can be shutted across from one component of the body to another. ...
Modulatory Activity of Bifidobacterium sp. BGN4 Cell Fractions on
... 13, 21], in addition to a mitogenic response in the spleen and PP [6, 9, 10, 12]. Macrophages play a critical role in a host’s defense system through physical uptake activity and secretion of immune mediators such as NO and various cytokines [16, 28], which inhibits tumor cells, bacteria, fungi, and ...
... 13, 21], in addition to a mitogenic response in the spleen and PP [6, 9, 10, 12]. Macrophages play a critical role in a host’s defense system through physical uptake activity and secretion of immune mediators such as NO and various cytokines [16, 28], which inhibits tumor cells, bacteria, fungi, and ...
PPT #2 Membrane Diffusion Water
... Paramecium vs. pond water Paramecium is hypertonic H2O continually enters cell to solve problem, specialized ...
... Paramecium vs. pond water Paramecium is hypertonic H2O continually enters cell to solve problem, specialized ...
Cellular Transport Web Activity This Web Activity will take you
... are forms of passive transport. This animation describes a special case of passive transport called facilitated diffusion. Larger molecules such as glucose can then enter the cell by means of a special pathway. Sketch how glucose molecules can pass through a cell membrane. 5. Click “Continue” to obs ...
... are forms of passive transport. This animation describes a special case of passive transport called facilitated diffusion. Larger molecules such as glucose can then enter the cell by means of a special pathway. Sketch how glucose molecules can pass through a cell membrane. 5. Click “Continue” to obs ...
Recommended literature
... Meiosis Table 1 Prophase I: stages and landmark events of chromosome behavior Leptotene Chromatin condensation begins and the chromosomes ®rst become visible as long, extended thread-like structures. As part of this condensation process, the chromosomes form a proteinaceous core (axial element) com ...
... Meiosis Table 1 Prophase I: stages and landmark events of chromosome behavior Leptotene Chromatin condensation begins and the chromosomes ®rst become visible as long, extended thread-like structures. As part of this condensation process, the chromosomes form a proteinaceous core (axial element) com ...
Emerging patterns of organization at the plant cell surface
... indicate a role involving molecular recognition and cellcell interaction in relation to cell identity or position. An extracellular glycoprotein, rich in aspartic acid, serine, threonine and possessing N-linked oligosaccharide chains, has been found in the conditioned medium of auxin-supplied carrot ...
... indicate a role involving molecular recognition and cellcell interaction in relation to cell identity or position. An extracellular glycoprotein, rich in aspartic acid, serine, threonine and possessing N-linked oligosaccharide chains, has been found in the conditioned medium of auxin-supplied carrot ...
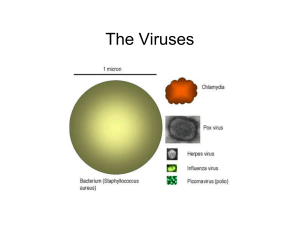
Microorganisms A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic
... Practically all surfaces that have not been specially sterilized are covered by prokaryotes. The number of prokaryotes on Earth is estimated to account for at least half the biomass on Earth. Bacteria Almost all bacteria are invisible to the naked eye, with a few extremely rare exceptions. They lac ...
... Practically all surfaces that have not been specially sterilized are covered by prokaryotes. The number of prokaryotes on Earth is estimated to account for at least half the biomass on Earth. Bacteria Almost all bacteria are invisible to the naked eye, with a few extremely rare exceptions. They lac ...
CELL ORGANELLES I.
... TRAFFICKING BETWEEN THE NUCLEUS AND CYTOPLASM (MACROMOLECULES, RNA) NUCLEAR MATRIX DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID), GENETIC CODE, EU- AND HETEROCHROMATIN RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA), TRANSFER, MESSENGER AND RIBOSOMAL NUCLEOPROTEINS, HISTONE- AND NON-HISTONE TYPES, REGULATE TRANSCRIPTION, BARR BODY, FEMALE SE ...
... TRAFFICKING BETWEEN THE NUCLEUS AND CYTOPLASM (MACROMOLECULES, RNA) NUCLEAR MATRIX DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID), GENETIC CODE, EU- AND HETEROCHROMATIN RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA), TRANSFER, MESSENGER AND RIBOSOMAL NUCLEOPROTEINS, HISTONE- AND NON-HISTONE TYPES, REGULATE TRANSCRIPTION, BARR BODY, FEMALE SE ...
Cellular Transport PDF
... Have students study the following information to respond to the prompt. Cells draw on materials from their environments to sustain cellular functions. The structure of a cell membrane plays an essential role in maintaining a cell's health. As a semi-permeable plasma membrane it serves as a barrier b ...
... Have students study the following information to respond to the prompt. Cells draw on materials from their environments to sustain cellular functions. The structure of a cell membrane plays an essential role in maintaining a cell's health. As a semi-permeable plasma membrane it serves as a barrier b ...
View PDF
... KEYWORDS compression; forces; kinetochores; k-fibers; mitotic spindle; microtubules; mitosis; metaphase; PRC1; tension ...
... KEYWORDS compression; forces; kinetochores; k-fibers; mitotic spindle; microtubules; mitosis; metaphase; PRC1; tension ...
Hypersensitivity and Allergy Principles of Immunology 4/11/06
... Rabbit Ab against serum from ragweed sensitive individuals could neutralize allergic reaction ...
... Rabbit Ab against serum from ragweed sensitive individuals could neutralize allergic reaction ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.