The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... complete, the cell is ready to divide. That division consists of two linked, but independent events known as mitosis and cytokinesis. Mitosis is the division of the nucleus into two equal parts whereas cytokinesis is the separation of the cell’s organelles into the formation of two new cells. ...
... complete, the cell is ready to divide. That division consists of two linked, but independent events known as mitosis and cytokinesis. Mitosis is the division of the nucleus into two equal parts whereas cytokinesis is the separation of the cell’s organelles into the formation of two new cells. ...
Microtubules and the shape of plant cells
... Microtubules and the shape of plant cells Clive Lloyd, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, John Innes Centre, NORWICH NR4 7UH, UK Microtubules provide the tracks that membrane-bound cellulose synthases follow as they are propelled along the membrane by the extrusion of microfibrils. Ultima ...
... Microtubules and the shape of plant cells Clive Lloyd, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, John Innes Centre, NORWICH NR4 7UH, UK Microtubules provide the tracks that membrane-bound cellulose synthases follow as they are propelled along the membrane by the extrusion of microfibrils. Ultima ...
Document
... Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
... Metabolism: photosynthesis, respiration, fermentation, digestion, gas exchange, secretion, excretion, circulation--processing materials and energy Growth: cell enlargement, cell number Movement: intracellular, movement, locomotion ...
Cell division - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... to survive. Preparing for division- cell produces structures that it will use to divide into two new cells. ...
... to survive. Preparing for division- cell produces structures that it will use to divide into two new cells. ...
Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells
... Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows ...
... Nanolive AG from Ecublens (VD) – 3D research on living cells Nanolive SA is a start-up operating from the EPFL Innovation Park at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (ETHL). The biotech company was founded in 2013 and developed a tomographic microscope which, for the first time ever, allows ...
Classifying Living Things A2-A11
... -tissue= similar cells that have the same job working together (examples celery stalks in a plant or muscles in an animal) -organ= tissues of different kinds coming together (examples- heart, lungs, brain in animals) -organ system= group of organs that work together to do a certain job (examples- fo ...
... -tissue= similar cells that have the same job working together (examples celery stalks in a plant or muscles in an animal) -organ= tissues of different kinds coming together (examples- heart, lungs, brain in animals) -organ system= group of organs that work together to do a certain job (examples- fo ...
MEIOSIS 19 FEBRUARY 2014 Lesson Description
... ultraviolet light and the other one (B) was left in the dark. The two Petri dishes were examined after 5 days. In A, all but one of the bacterial colonies were red. One bacterial colony was white. In B, all the ...
... ultraviolet light and the other one (B) was left in the dark. The two Petri dishes were examined after 5 days. In A, all but one of the bacterial colonies were red. One bacterial colony was white. In B, all the ...
Cell Division
... the sister chromatids until they are all arranged at the imaginary plane equidistant between the poles, defining metaphase. ...
... the sister chromatids until they are all arranged at the imaginary plane equidistant between the poles, defining metaphase. ...
Cell division -1
... the sister chromatids until they are all arranged at the imaginary plane equidistant between the poles, defining metaphase. ...
... the sister chromatids until they are all arranged at the imaginary plane equidistant between the poles, defining metaphase. ...
Chapter 8 (cont…) Meiosis and Reproduction
... 4. There are 2 main stages of mitosis. List them & state what the overall task of each of the 2 stages is. 5. What are sister chromatids? Why do the look like an X when condensed? 6. Sketch each of the following phases of Mitosis & state what is occurring in each: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, ...
... 4. There are 2 main stages of mitosis. List them & state what the overall task of each of the 2 stages is. 5. What are sister chromatids? Why do the look like an X when condensed? 6. Sketch each of the following phases of Mitosis & state what is occurring in each: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, ...
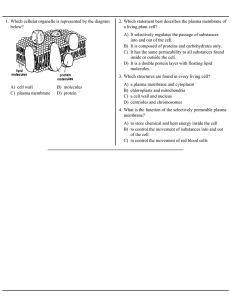
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures are found in every living cell? ...
... B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures are found in every living cell? ...
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
... • Chromatin condenses • Nuclear envelope breaks down • Mitotic spindle assembles – MTOC’s move to opposite sides of cell – Microtubules form (tubulin) between – MT attach to centromere at kinetochore ...
... • Chromatin condenses • Nuclear envelope breaks down • Mitotic spindle assembles – MTOC’s move to opposite sides of cell – Microtubules form (tubulin) between – MT attach to centromere at kinetochore ...
Name - Marissa Elementary School
... Look up the following answers in your Chapter 1 ISN notes. 1. What is a species? A group of organisms that have the same characteristics and produce offspring ...
... Look up the following answers in your Chapter 1 ISN notes. 1. What is a species? A group of organisms that have the same characteristics and produce offspring ...
Lecture 19: Powerpoint
... along the spindle microtubule to each pole of the cell. Cell still diploid, but chromosomes now are only single chromatids ...
... along the spindle microtubule to each pole of the cell. Cell still diploid, but chromosomes now are only single chromatids ...
cell death
... 2. The Mitotic Phase Equal distribution of 2 sets of chromosomes (DNA) into 2 identical daughter cells Divided into 4 stages of Mitosis: A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase ...
... 2. The Mitotic Phase Equal distribution of 2 sets of chromosomes (DNA) into 2 identical daughter cells Divided into 4 stages of Mitosis: A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase ...
sgCh1Cell
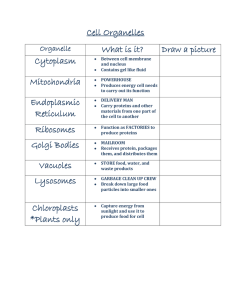
... 12. Microscopes made it possible to discover _______________________. 13. Cell Theory states (3 ideas). 14. Resolution means _____________________ 15. Cell Membranes function is _____________________________________. 16. State what Mitochondria‘s function is _________________________ 17. Many celled ...
... 12. Microscopes made it possible to discover _______________________. 13. Cell Theory states (3 ideas). 14. Resolution means _____________________ 15. Cell Membranes function is _____________________________________. 16. State what Mitochondria‘s function is _________________________ 17. Many celled ...
Cell Cycle
... • Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of chromatin, a complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division • Every eukaryotic species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus • Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes • Gametes (reproductive cel ...
... • Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of chromatin, a complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division • Every eukaryotic species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus • Somatic cells (nonreproductive cells) have two sets of chromosomes • Gametes (reproductive cel ...
Biology 162 Discussion Section Week 7 The Chromosome Dance
... Chapters 12 & 13 (the Cell Cycle; Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles) are challenging ones. They describe a process of fundamental significance to life, cell division, but they are filled with so much factual information that it is easy for the important principles to be obscured. Unfortunately, a full ...
... Chapters 12 & 13 (the Cell Cycle; Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles) are challenging ones. They describe a process of fundamental significance to life, cell division, but they are filled with so much factual information that it is easy for the important principles to be obscured. Unfortunately, a full ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.