Cell Division (Mitosis) and Death
... Mitosis- division of the nucleus Cytokinesis- division of the cytoplasm www.cellsalive.com ...
... Mitosis- division of the nucleus Cytokinesis- division of the cytoplasm www.cellsalive.com ...
Nucleus 1
... Generally located in the center of the nucleus. It is made of proteins and ribonucleic acids. It is the location where the assembly of ribosomes begin. ...
... Generally located in the center of the nucleus. It is made of proteins and ribonucleic acids. It is the location where the assembly of ribosomes begin. ...
Sample 5.3.B.2 Complete
... expression or alteration in hormonal balance may have an impact on development. 14. List some of the problems in cell division when control is lost. 15. Recognize that cancer is a result of mutations that affect the ability of cells to regulate the cell cycle. 16. Describe early embryonic developmen ...
... expression or alteration in hormonal balance may have an impact on development. 14. List some of the problems in cell division when control is lost. 15. Recognize that cancer is a result of mutations that affect the ability of cells to regulate the cell cycle. 16. Describe early embryonic developmen ...
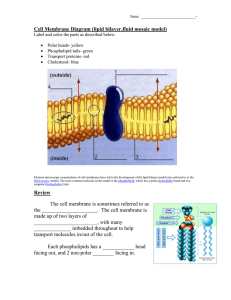
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
A Cell Is Like A Castle
... wall. • Plants go through chemical processes such as photosynthesis and cell respiration. • They are green in color because of chlorophyll. • They have chloroplasts. • They are square in shape due to the cell wall. • They have one large central vacuole. • They provide structure and support. ...
... wall. • Plants go through chemical processes such as photosynthesis and cell respiration. • They are green in color because of chlorophyll. • They have chloroplasts. • They are square in shape due to the cell wall. • They have one large central vacuole. • They provide structure and support. ...
CAC
... Mitosis: A form of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells, each with the same complement of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the same time as mitosis, the process of cytokinesis occurs. Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm. ...
... Mitosis: A form of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells, each with the same complement of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the same time as mitosis, the process of cytokinesis occurs. Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm. ...
Mitosis Meiosis Both
... Mitosis 1) Make cells identical to parent cells 2) Makes 2 daughter cells 3) All cells in body reproduce this way (except sex cells and brain cells) 4) Makes same cells for male and female 5) All plant and animal cells divide this way when growing or repairing 6) Six steps- each with names 7) One ce ...
... Mitosis 1) Make cells identical to parent cells 2) Makes 2 daughter cells 3) All cells in body reproduce this way (except sex cells and brain cells) 4) Makes same cells for male and female 5) All plant and animal cells divide this way when growing or repairing 6) Six steps- each with names 7) One ce ...
The Cell - CCRI Faculty Web
... We have TRILLIONS of them!! (@65) Every organism is composed of one or more cells Basic unit of structure and function in organisms All come from pre-existing cells ...
... We have TRILLIONS of them!! (@65) Every organism is composed of one or more cells Basic unit of structure and function in organisms All come from pre-existing cells ...
What the Cell? - Effingham County Schools
... • Have enzymes used to break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins • breaking down old organelles – even old cells can be broken down in a process called autolysis. ...
... • Have enzymes used to break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins • breaking down old organelles – even old cells can be broken down in a process called autolysis. ...
Unit 4: Cells and Transport Short Answer Five of
... 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
... 2. How can you tell the difference between a plant and an animal cell? List at least 3 differences. ...
Cell structure
... Organelles are membrane-bound structures with particular functions within eukaryotic cells. ...
... Organelles are membrane-bound structures with particular functions within eukaryotic cells. ...
Section 10-2 Cell Division
... Interphase: G1 – growth S - DNA copies itself G2 – cell prepares for cell division Cell begins division in M phase = ___________________ ________________________: nuclear division of a cell that results in 2 cells with the same genetic information. Four phases: PMAT ...
... Interphase: G1 – growth S - DNA copies itself G2 – cell prepares for cell division Cell begins division in M phase = ___________________ ________________________: nuclear division of a cell that results in 2 cells with the same genetic information. Four phases: PMAT ...
Meiosis student note js
... will have the same number of chromosomes as the original cell _________________________________. ...
... will have the same number of chromosomes as the original cell _________________________________. ...
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
... Robert Brown (1833) • Observed that cells had a dark structure within plant cells • Brown observed the nucleus ...
... Robert Brown (1833) • Observed that cells had a dark structure within plant cells • Brown observed the nucleus ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
Name Date Period # Cell Test Review Across Down
... 9. A large storage compartment in plant cells used for water and other materials. When filled, turgor pressure makes a plant stand up straight. 11. The powerhouse of the cell. 12. They are used as storage and transportation vesicles. The animal cell has a small one. 13. Make proteins in the cell. ...
... 9. A large storage compartment in plant cells used for water and other materials. When filled, turgor pressure makes a plant stand up straight. 11. The powerhouse of the cell. 12. They are used as storage and transportation vesicles. The animal cell has a small one. 13. Make proteins in the cell. ...
Lecture 9 Summary – Cell Division and Differentiation
... divide again eg: some neurons, red blood cells. G1 phase; the active cell duplicates most of its organelles and cytosolic components. The replication of chromosomes begins. S phase; DNA is replicated by semi-conservative replication. G2 phase; further cell growth and final preparations for mit ...
... divide again eg: some neurons, red blood cells. G1 phase; the active cell duplicates most of its organelles and cytosolic components. The replication of chromosomes begins. S phase; DNA is replicated by semi-conservative replication. G2 phase; further cell growth and final preparations for mit ...
Cell Chart Review
... some adult cells can be induced to turn back the clock and become stem cells. Stem cell research may hold the answer to many questions about human health and disease. It can be controversial due to the harvesting of cells from human embryos. ...
... some adult cells can be induced to turn back the clock and become stem cells. Stem cell research may hold the answer to many questions about human health and disease. It can be controversial due to the harvesting of cells from human embryos. ...
Cell Cycle Basics - Lyndhurst Schools
... Because each of these cells divides for a different reason, it uses a different process to divide: o ______________________________________________________________________________ o ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Because each of these cells divides for a different reason, it uses a different process to divide: o ______________________________________________________________________________ o ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.