A. 4 Variability in drug response a. Define tachyphylaxis
... N-acetylation of isoniazid and hydralazine varies in the normal population with a bimodal distribution. Slow acetylation is an AR condition with an incidence variable by race (rare in Asians and Inuit, more common in Northern Europeans). Slow acetylators metabolize these drugs much more slowly due t ...
... N-acetylation of isoniazid and hydralazine varies in the normal population with a bimodal distribution. Slow acetylation is an AR condition with an incidence variable by race (rare in Asians and Inuit, more common in Northern Europeans). Slow acetylators metabolize these drugs much more slowly due t ...
Core Curriculum Slides - Austin Community College
... cultures convert to negative After 3 months of therapy, if cultures are positive or symptoms do not resolve, reevaluate for Potential drug-resistant disease Nonadherence to drug regimen If cultures do not convert to negative despite 3 months of therapy, consider initiating DOT ...
... cultures convert to negative After 3 months of therapy, if cultures are positive or symptoms do not resolve, reevaluate for Potential drug-resistant disease Nonadherence to drug regimen If cultures do not convert to negative despite 3 months of therapy, consider initiating DOT ...
Book Review - Portsmouth Research Portal
... about drugs and how a metaphor like ‘mind food’ can distort crucial disparities. Such mass prescribing is also paradoxical, though more people are consuming treatments; the disorders they treat are also increasing. In analysing how Calcuttans perceive mood medicines and their efficacy for treating s ...
... about drugs and how a metaphor like ‘mind food’ can distort crucial disparities. Such mass prescribing is also paradoxical, though more people are consuming treatments; the disorders they treat are also increasing. In analysing how Calcuttans perceive mood medicines and their efficacy for treating s ...
Pharmacokinetics for the Non-Specialist
... rate. At the point of Cmax, these two rates are equal and after this the elimination rate is greater than the absorption rate. Eventually the concentration of the drug decreases and the effect diminishes. ...
... rate. At the point of Cmax, these two rates are equal and after this the elimination rate is greater than the absorption rate. Eventually the concentration of the drug decreases and the effect diminishes. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... large portion of the drug meta. (1) Hi-protein, Lo-CHO diet →↑the hepatic metabolism of theophylline (antiasthma drug) (2) Substance found in grapefruit can inhibit the intestinal metabolism of drugs →↑drug in the circulation →↑toxicity. (3) Competition between food and drugs with hepatic enzymes →↑ ...
... large portion of the drug meta. (1) Hi-protein, Lo-CHO diet →↑the hepatic metabolism of theophylline (antiasthma drug) (2) Substance found in grapefruit can inhibit the intestinal metabolism of drugs →↑drug in the circulation →↑toxicity. (3) Competition between food and drugs with hepatic enzymes →↑ ...
Most Often Missed Pharmacology
... positive symptoms include: hallucinations, paranoia, agitation, and disordered thinking/speech. Negative symptoms include: social/emotional withdrawal, poor insight, judgment, and self-care. 4. Antimycobacterial-evaluating effectiveness of treatment for tuberculosis. Needs to be 2 drug regime, drug ...
... positive symptoms include: hallucinations, paranoia, agitation, and disordered thinking/speech. Negative symptoms include: social/emotional withdrawal, poor insight, judgment, and self-care. 4. Antimycobacterial-evaluating effectiveness of treatment for tuberculosis. Needs to be 2 drug regime, drug ...
However, the frequency of these four genotypes varies depending
... • Genetic variation accounts for inter-individual enzymatic variability (poor vs extensive metabolisers) • Liver disease may also significantly affect drug metabolism Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics, 11 th edn, p 71-91. ...
... • Genetic variation accounts for inter-individual enzymatic variability (poor vs extensive metabolisers) • Liver disease may also significantly affect drug metabolism Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics, 11 th edn, p 71-91. ...
Pharmacodynamics
... • The benefit-risk balance of a drug must be positive in order to gain and maintain product approval. • Benefits are commonly expressed as the proven therapeutic good of a product, but should also include the patient’s subjective assessment of its effects • Risk is the probability of harm being caus ...
... • The benefit-risk balance of a drug must be positive in order to gain and maintain product approval. • Benefits are commonly expressed as the proven therapeutic good of a product, but should also include the patient’s subjective assessment of its effects • Risk is the probability of harm being caus ...
Genetics - Dave Brodbeck
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Acetaminophen - VPR Veterinary Pharmacy Software, Drug Search
... Acetaminophen - General INDICATIONS FOR USE: Your veterinarian has prescribed this medication for pain relief or fever. PRECAUTIONS: As with any medication, there are precautions and side effects associated with their use. This is sometimes complicated by the fact that many of the drugs used in vete ...
... Acetaminophen - General INDICATIONS FOR USE: Your veterinarian has prescribed this medication for pain relief or fever. PRECAUTIONS: As with any medication, there are precautions and side effects associated with their use. This is sometimes complicated by the fact that many of the drugs used in vete ...
Drug Development
... Drug Development Today most drugs are synthesized by chemists in the laboratory. Synthetic drugs are better controlled than those occurring naturally, which ensures that each dose imparts the same effect. Some new synthetic drugs are developed by modifying the structure of existing substances. These ...
... Drug Development Today most drugs are synthesized by chemists in the laboratory. Synthetic drugs are better controlled than those occurring naturally, which ensures that each dose imparts the same effect. Some new synthetic drugs are developed by modifying the structure of existing substances. These ...
Recent changes have been introduced to the Summary of Product
... full explanation), and might then not be asked to provide a blood sample. If the police had evidence that the patient's driving was impaired due to drugs, whether prescribed or not, they can prosecute under the existing offence of driving whilst impaired through drugs offence described in section 4 ...
... full explanation), and might then not be asked to provide a blood sample. If the police had evidence that the patient's driving was impaired due to drugs, whether prescribed or not, they can prosecute under the existing offence of driving whilst impaired through drugs offence described in section 4 ...
Word Definition 1 non-Mendelian genetics rules
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
... genetic traits that are controlled by many genes 6 sex-linked gene a gene that is carried on the X or Y chromosome 7 carrier a person who has one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait 8 genetic disorder an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes a genetic disorder that causes ...
NIMESULIDE - Pediatric Oncall
... in use for considerable period and well accepted. There are no reports of any adverse effects for these formulations which are mostly used on short term basis for relief from pain and inflammation. These formulations may be permitted to be continued. This opinion in respect of Nimesulide has already ...
... in use for considerable period and well accepted. There are no reports of any adverse effects for these formulations which are mostly used on short term basis for relief from pain and inflammation. These formulations may be permitted to be continued. This opinion in respect of Nimesulide has already ...
Drugs Associated - Engaged Patients
... INSULIN, GLARGINE -Insulin glargine is a synthetic (laboratory-made) form of insulin, which lowers levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Insulin glargine is a long-acting form of insulin. Allergic reactions are possible, and some signs of a possible reaction include wheezing, sweating and skin ras ...
... INSULIN, GLARGINE -Insulin glargine is a synthetic (laboratory-made) form of insulin, which lowers levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Insulin glargine is a long-acting form of insulin. Allergic reactions are possible, and some signs of a possible reaction include wheezing, sweating and skin ras ...
TRIAL PHASES:
... associated with increasing doses. Pharmacokinetic as well as drug-drug interaction studies are usually considered as Phase I trials regardless of when they are conducted during drug development as these are generally conducted in healthy volunteers. Phase I trials also include trials in which new dr ...
... associated with increasing doses. Pharmacokinetic as well as drug-drug interaction studies are usually considered as Phase I trials regardless of when they are conducted during drug development as these are generally conducted in healthy volunteers. Phase I trials also include trials in which new dr ...
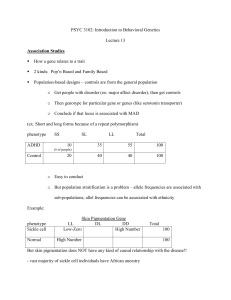
Lecture 13
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
Lecture 4 Outline – Administration, Absorption
... From digestive system – first-pass metabolism b. Directly from the heart ...
... From digestive system – first-pass metabolism b. Directly from the heart ...
Food and Drug Interactions
... Absorption • Milk products alter pH • Metals chelate some medications • Some foods compete for same absorption sites • Food speeds GI speed – reduced absorption • Degree of significance is important ...
... Absorption • Milk products alter pH • Metals chelate some medications • Some foods compete for same absorption sites • Food speeds GI speed – reduced absorption • Degree of significance is important ...
Pharmacology Objectives 1
... 8) Define first-pass (presystemic) drug clearance and state how the physician may avoid or deal with this process. First-pass (presystemic) drug clearance is when a drug is absorbed through the stomach and must pass through the liver before being delivered to other parts of the body. If the metabol ...
... 8) Define first-pass (presystemic) drug clearance and state how the physician may avoid or deal with this process. First-pass (presystemic) drug clearance is when a drug is absorbed through the stomach and must pass through the liver before being delivered to other parts of the body. If the metabol ...