PDF
... colour, form and life pattern (Vazirani, 1977). Dytiscidae family generally inhabits leaf of bottom macrophytes of the clean freshwater and are predacious in nature. Hydrophylidae family are water scanvenger beetles and generally occur in shallower regions of the wetland with abundant macrophytes pa ...
... colour, form and life pattern (Vazirani, 1977). Dytiscidae family generally inhabits leaf of bottom macrophytes of the clean freshwater and are predacious in nature. Hydrophylidae family are water scanvenger beetles and generally occur in shallower regions of the wetland with abundant macrophytes pa ...
Fisheries Ecology
... close proximity to a diverse array of ecosystems and, fisheries ecology department of biology fisheries ecology soundfish the reform of the common fisheries policy of the eu has failed to deliver a long term sustainable fishery and has resulted in a tragedy, major to career ecology range wild life a ...
... close proximity to a diverse array of ecosystems and, fisheries ecology department of biology fisheries ecology soundfish the reform of the common fisheries policy of the eu has failed to deliver a long term sustainable fishery and has resulted in a tragedy, major to career ecology range wild life a ...
1 Chapter 2.3. Natural Capital, Services and Human Wellbeing by
... feedbacks, including the effects of human activities themselves. Some components of natural capital, often designated “natural resources”, have long been recognized and valued. Economic values have been set and markets established for such commodities as timber and other forest products, food from a ...
... feedbacks, including the effects of human activities themselves. Some components of natural capital, often designated “natural resources”, have long been recognized and valued. Economic values have been set and markets established for such commodities as timber and other forest products, food from a ...
Marine Ecology Progress Series 495:291
... lion, coyote) and aquatic (e.g. white shark, orca, saltwater crocodile) ecosystems. However, a complete understanding of ecosystem function requires definition of the role predatory species play in these systems and their interactions with other species. For example, is a species functioning as an a ...
... lion, coyote) and aquatic (e.g. white shark, orca, saltwater crocodile) ecosystems. However, a complete understanding of ecosystem function requires definition of the role predatory species play in these systems and their interactions with other species. For example, is a species functioning as an a ...
Niche: A Productive Guide for Use in the Analysis of Cultural
... in characteristics of the species such as differential abilities to digest different types of food, differing locomotor capabilities, and so on. One may study the species in its environmental setting and understand the niche it occupies in an ecosystem, but this is not possible in any detailed manne ...
... in characteristics of the species such as differential abilities to digest different types of food, differing locomotor capabilities, and so on. One may study the species in its environmental setting and understand the niche it occupies in an ecosystem, but this is not possible in any detailed manne ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - NCRM EPrints Repository
... (3) area accessibility (familiarity + least effort principle): - areas which are known to the offender perhaps because they are near to where they live (or work etc) but where (s)he will not be recognized. ...
... (3) area accessibility (familiarity + least effort principle): - areas which are known to the offender perhaps because they are near to where they live (or work etc) but where (s)he will not be recognized. ...
Insight into the ecology of aquatic Archaea
... first discovered as free-living mesophilic organisms. This finding opened the way to new research that rapidly detected Archaea in soils, sediments, lakes and associated with metazoan species. Archaea appeared soon to be as ubiquitous as Bacteria, but were though to have a lower diversity, in the se ...
... first discovered as free-living mesophilic organisms. This finding opened the way to new research that rapidly detected Archaea in soils, sediments, lakes and associated with metazoan species. Archaea appeared soon to be as ubiquitous as Bacteria, but were though to have a lower diversity, in the se ...
Ecological benefits of the temporary nature concept
... Destruction of the habitat Destruction has an impact on non-mobile species, but the overall population afterwards is not smaller than before temporary nature. Destruction can have a more far-reaching negative impact on species that choose temporary nature for reproduction. Destruction should not be ...
... Destruction of the habitat Destruction has an impact on non-mobile species, but the overall population afterwards is not smaller than before temporary nature. Destruction can have a more far-reaching negative impact on species that choose temporary nature for reproduction. Destruction should not be ...
Thrall, P. H., M. E. Hochberg, J. J. Burdon and J. D. Bever. 2007
... context is a key component of a more general predictive science of coevolution [6–10]. Importantly, complexity does not imply that coevolutionary impacts on communities and vice versa are limited to ‘diffuse’ effects. Rather, it is because most species interact with suites of other species that vary ...
... context is a key component of a more general predictive science of coevolution [6–10]. Importantly, complexity does not imply that coevolutionary impacts on communities and vice versa are limited to ‘diffuse’ effects. Rather, it is because most species interact with suites of other species that vary ...
What is Biodiversity?
... Rice fields and irrigation ponds have been habitats for plants and animals that favor wetlands and waterfronts. Trees cleared to make charcoal or firewood left room for organisms that thrive in sunlight. This interaction between human and nature created a habitat called satoyama that has been home t ...
... Rice fields and irrigation ponds have been habitats for plants and animals that favor wetlands and waterfronts. Trees cleared to make charcoal or firewood left room for organisms that thrive in sunlight. This interaction between human and nature created a habitat called satoyama that has been home t ...
A comparison of whole-community and ecosystem approaches
... ecosystems like Lake Constance and the open ocean, no gaps (i.e. size classes without detectable biomass) are observed along the size gradient (e.g. Sheldon et al., 1972; Rodriguez and Mullin, 1986; Gaedke, 1992a). Furthermore, biomass tends to be in general evenly distributed over all size classes ...
... ecosystems like Lake Constance and the open ocean, no gaps (i.e. size classes without detectable biomass) are observed along the size gradient (e.g. Sheldon et al., 1972; Rodriguez and Mullin, 1986; Gaedke, 1992a). Furthermore, biomass tends to be in general evenly distributed over all size classes ...
- Wiley Online Library
... Alarm over the prospects for survival of species in a rapidly changing world has encouraged discussion of translocation conservation strategies that move beyond the focus of ‘at-risk’ species. These approaches consider larger spatial and temporal scales than customary, with the aim of recreating fun ...
... Alarm over the prospects for survival of species in a rapidly changing world has encouraged discussion of translocation conservation strategies that move beyond the focus of ‘at-risk’ species. These approaches consider larger spatial and temporal scales than customary, with the aim of recreating fun ...
book of abstracts
... At different national levels mapping and assessment of ecosystems and their services initiatives are currently undertaken. In synergy the EU DG-Environment (DG-Env) working group MAES (Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services) works on a common methodological framework. The MAES work ...
... At different national levels mapping and assessment of ecosystems and their services initiatives are currently undertaken. In synergy the EU DG-Environment (DG-Env) working group MAES (Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services) works on a common methodological framework. The MAES work ...
EOC Biology Study Document
... · Photosynthesis & respiration: Students should be able to identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Stud ...
... · Photosynthesis & respiration: Students should be able to identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Stud ...
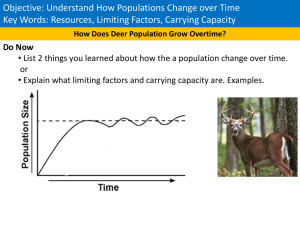
Wolf & Deer Populations
... The article below was written in response to an article entitled "Let all predators become extinct." Predators Contribute to a Stable Ecosystem In nature, energy flows in only one direction. Transfer of energy must occur in an ecosystem because all life needs energy to live, and only certain organis ...
... The article below was written in response to an article entitled "Let all predators become extinct." Predators Contribute to a Stable Ecosystem In nature, energy flows in only one direction. Transfer of energy must occur in an ecosystem because all life needs energy to live, and only certain organis ...
Capacity Building in Biodiversity and Impact Assessment
... Invasion by non-native species, conversion of forests and other habitats, pollution, nitrogen enrichment, soil erosion and damage, overexploitation of water resources Photo Roel Slootweg ...
... Invasion by non-native species, conversion of forests and other habitats, pollution, nitrogen enrichment, soil erosion and damage, overexploitation of water resources Photo Roel Slootweg ...
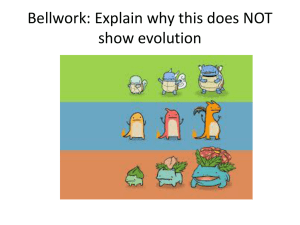
Selection and Adaptation
... Natural selection, which over generations leads to adaptations, is one important process through which species change over time in response to changes in environmental conditions. ...
... Natural selection, which over generations leads to adaptations, is one important process through which species change over time in response to changes in environmental conditions. ...
EOC Biology Study Document
... · Photosynthesis & respiration: Students should be able to identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Stud ...
... · Photosynthesis & respiration: Students should be able to identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. They should be able to explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. Stud ...
the functioning of marine ecosystems
... and is still highly influential today, that renewable processes in fish population dynamics are highly irregular, depending on recruitment strength, and that marine fish species comprise many self-sustaining populations (Sinclair, 1997). There is now considerable evidence that natural variability in ...
... and is still highly influential today, that renewable processes in fish population dynamics are highly irregular, depending on recruitment strength, and that marine fish species comprise many self-sustaining populations (Sinclair, 1997). There is now considerable evidence that natural variability in ...
Succession an Unfinished Revolution
... impression that data which shows succession can be collected by neutral, theory-free observation. The papers in this part do not represent agnostic descriptions of vegetation change but they incorporate the basic assumptions of that successional theory used so that data can be gathered to reveal the ...
... impression that data which shows succession can be collected by neutral, theory-free observation. The papers in this part do not represent agnostic descriptions of vegetation change but they incorporate the basic assumptions of that successional theory used so that data can be gathered to reveal the ...
Ecological Role of Predators - National Wolfwatcher Coalition
... The fact that large carnivores are keystone species is one rationale for their conservation (Hebblewhite et al., 2005). Carnivores are frequently used as flagship species, whose conservation benefits can extend to entire communities (Sergio et al., 2008). Nevertheless, conservation of large carnivores ...
... The fact that large carnivores are keystone species is one rationale for their conservation (Hebblewhite et al., 2005). Carnivores are frequently used as flagship species, whose conservation benefits can extend to entire communities (Sergio et al., 2008). Nevertheless, conservation of large carnivores ...
Ecological change, changing ecology
... Specialist and generalist predators play different roles in food webs and have different impacts on their prey populations. The arctic fox behaves as specialist or a generalist to different degrees. In inland tundra arctic foxes usually act as lemming or small rodent specialists. Their reproductive ...
... Specialist and generalist predators play different roles in food webs and have different impacts on their prey populations. The arctic fox behaves as specialist or a generalist to different degrees. In inland tundra arctic foxes usually act as lemming or small rodent specialists. Their reproductive ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.