Unit 2 Ecology Chp 52 Intro to Ecology and the
... For example, many ecologists and climatologists use sophisticated computer programs to develop models that predict the effects that human activities will have on climate and how the resulting climatic changes will affect geographic distributions of lifeforms during the next century. Of course, such ...
... For example, many ecologists and climatologists use sophisticated computer programs to develop models that predict the effects that human activities will have on climate and how the resulting climatic changes will affect geographic distributions of lifeforms during the next century. Of course, such ...
Biotic-abiotic ocean zones worksheet
... The oceans are a salty place but not uniformly so. This creates a challenge for marine organisms that swim through different areas to deal with differing levels of salinity in their surrounding environment. Heat is conducted much faster in water than in air, which makes the oceans a much colder plac ...
... The oceans are a salty place but not uniformly so. This creates a challenge for marine organisms that swim through different areas to deal with differing levels of salinity in their surrounding environment. Heat is conducted much faster in water than in air, which makes the oceans a much colder plac ...
Qualitative Insight Into Public Knowledge of, and
... adjust behavior in ways that might lessen climate change.5 Much like the case of global warming, it is logical to consider that protection of biodiversity will require public participation and cooperation, therefore comprehension of issues related to species is critical to the political process. Par ...
... adjust behavior in ways that might lessen climate change.5 Much like the case of global warming, it is logical to consider that protection of biodiversity will require public participation and cooperation, therefore comprehension of issues related to species is critical to the political process. Par ...
ORGANISM AND POPULATION
... Archaebacteria (Thermophiles) are ancient forms of bacteria found in hot water springs and deep sea hydrothermal vents. They are able to survive in high temperatures (which far exceed 100°C) because their bodies have adapted to such environmental conditions. These organisms contain specialized therm ...
... Archaebacteria (Thermophiles) are ancient forms of bacteria found in hot water springs and deep sea hydrothermal vents. They are able to survive in high temperatures (which far exceed 100°C) because their bodies have adapted to such environmental conditions. These organisms contain specialized therm ...
Aboriginal Traditional Knowledge and Environmental Management
... peoples to hunt, trap and fish, while at the same time conserving wildlife populations for future generations. In addition to an understanding of environmental systems as a whole and knowledge of appropriate techniques for harvesting, TK includes qualitative information on animals, plants and other ...
... peoples to hunt, trap and fish, while at the same time conserving wildlife populations for future generations. In addition to an understanding of environmental systems as a whole and knowledge of appropriate techniques for harvesting, TK includes qualitative information on animals, plants and other ...
APA 2001 Conference
... Spatial Scale is an implicit classifier at each level Modifiers for Form, Energy, Light, Physico-Chemistry, Anthropogenics ...
... Spatial Scale is an implicit classifier at each level Modifiers for Form, Energy, Light, Physico-Chemistry, Anthropogenics ...
Reading Guide Ch 22-24
... 16. Define neutral variations. Explain why natural selection does not act on these alleles. 17. List four reasons why natural selection cannot produce perfect organisms. CHAPTER 24 THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES 24.1 What Is a Species? 1. Define Ernst Mayr’s biological species concept. 2. Describe five prezy ...
... 16. Define neutral variations. Explain why natural selection does not act on these alleles. 17. List four reasons why natural selection cannot produce perfect organisms. CHAPTER 24 THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES 24.1 What Is a Species? 1. Define Ernst Mayr’s biological species concept. 2. Describe five prezy ...
WORDS BY ALAN WATSON FEATHERSTONE, FOUNDER OF
... concentrated on‘damage limitation’attempting to save species or habitats from destruction. While some initiatives have had success, the overall trend has been a net loss of both species and habitats in most parts of the world. This ecological depletion is readily apparent and the impacts are felt bo ...
... concentrated on‘damage limitation’attempting to save species or habitats from destruction. While some initiatives have had success, the overall trend has been a net loss of both species and habitats in most parts of the world. This ecological depletion is readily apparent and the impacts are felt bo ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... entire ecosystems. Efforts to save eagle habitats are not enough if we don’t consider the habitats of the eagle’s food sources. ...
... entire ecosystems. Efforts to save eagle habitats are not enough if we don’t consider the habitats of the eagle’s food sources. ...
New Approaches to the Study of Human–Environment Interactions
... Soulé 1999). Positive effects can also come about as a result of the engineering activities that are a side effect of some organism’s foraging, housing, or predator evasion strategies. When such processes construct new niches or enhance existing ones, they are often referred to as ecosystem enginee ...
... Soulé 1999). Positive effects can also come about as a result of the engineering activities that are a side effect of some organism’s foraging, housing, or predator evasion strategies. When such processes construct new niches or enhance existing ones, they are often referred to as ecosystem enginee ...
Review for the Ecology Unit Test!
... – The Long Version full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. Includes where in the food chain it is, where an organism feeds ...
... – The Long Version full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. Includes where in the food chain it is, where an organism feeds ...
Biology - Edgbarrow School
... I can describe the I can explain some I can compare and I can explain why some I can explain the impact of exercise, I can discuss the impact effects of recreational contrast animal and plant muscles may need to consequences of asthma and smoking on of maternal lifestyle on drugs on behaviour, ...
... I can describe the I can explain some I can compare and I can explain why some I can explain the impact of exercise, I can discuss the impact effects of recreational contrast animal and plant muscles may need to consequences of asthma and smoking on of maternal lifestyle on drugs on behaviour, ...
Simple in Means, Rich in Ends: Practicing Deep Ecology
... There are many reasons to defend the integrity of landscape from the invasion of industrial civilization. Supporters of deep ecology especially defend the integrity of native plants and animals living in their own habitat unmolested by humans. We also defend the integrity of certain places (the Gran ...
... There are many reasons to defend the integrity of landscape from the invasion of industrial civilization. Supporters of deep ecology especially defend the integrity of native plants and animals living in their own habitat unmolested by humans. We also defend the integrity of certain places (the Gran ...
Invitation to Biology
... Life’s Underlying Unity All organisms consist of one or more cells, which stay alive through ongoing inputs of energy and raw materials All sense and respond to change; all inherited DNA, a type of molecule that encodes information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction ...
... Life’s Underlying Unity All organisms consist of one or more cells, which stay alive through ongoing inputs of energy and raw materials All sense and respond to change; all inherited DNA, a type of molecule that encodes information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction ...
national 4 and national 5 biology homework
... 1. (a) Explain what biotic factors are (b) Give at least two examples of biotic factors 2. (a) State the definition of the term niche (b) Describe the niche of an organism you have looked at in class 3. Copy and complete: A food web with a than one with ...
... 1. (a) Explain what biotic factors are (b) Give at least two examples of biotic factors 2. (a) State the definition of the term niche (b) Describe the niche of an organism you have looked at in class 3. Copy and complete: A food web with a than one with ...
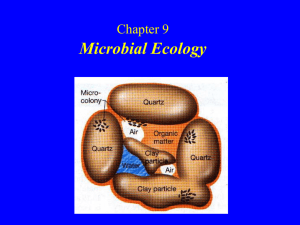
Microbial Ecology 微生物生态学
... Microbial ecology The term microbial ecology is now used in a general way to describe the presence and distributions of microorganisms. Microbial ecology is the the study of the behavior and activities of microorganisms in their natural environments. ...
... Microbial ecology The term microbial ecology is now used in a general way to describe the presence and distributions of microorganisms. Microbial ecology is the the study of the behavior and activities of microorganisms in their natural environments. ...
"Fossils" pdf file
... for reproduction. Some reptiles returned to the water and became good swimmers. Most reptiles were herbivorous, however many carnivorous species evolved. Some, like the feathered dinosaur of the Falcarius genus, which has been recently the subject of much attention, returned to a herbivorous style o ...
... for reproduction. Some reptiles returned to the water and became good swimmers. Most reptiles were herbivorous, however many carnivorous species evolved. Some, like the feathered dinosaur of the Falcarius genus, which has been recently the subject of much attention, returned to a herbivorous style o ...
plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during
... in the Mediterranean region of France. Ecosystem-specific net primary productivity, litter decomposition rate, and total soil carbon and nitrogen varied significantly with field age, and correlated with community-aggregated (i.e., weighed according to the relative abundance of species) functional le ...
... in the Mediterranean region of France. Ecosystem-specific net primary productivity, litter decomposition rate, and total soil carbon and nitrogen varied significantly with field age, and correlated with community-aggregated (i.e., weighed according to the relative abundance of species) functional le ...
Notes for Evolution
... is based on the rate of radioactive decay in isotopes of the particular elements. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that vary in the number of neutrons that they possess. A radioactive nucleus has an unstable nucleus that undergoes spontaneous change, releasing particles and energy. In doing th ...
... is based on the rate of radioactive decay in isotopes of the particular elements. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that vary in the number of neutrons that they possess. A radioactive nucleus has an unstable nucleus that undergoes spontaneous change, releasing particles and energy. In doing th ...
Principles of Evolution
... Describe Charles Darwin’s impact on evolution and the study of biology Identify the individuals who influenced Darwin Describe Darwin’s most important observations Explain the four ways evolutionary change can take place Identify the difference between evolution and natural selection Understand and ...
... Describe Charles Darwin’s impact on evolution and the study of biology Identify the individuals who influenced Darwin Describe Darwin’s most important observations Explain the four ways evolutionary change can take place Identify the difference between evolution and natural selection Understand and ...
Rewilding Europe with large herbivores: insights from Africa
... • If carnivores are lacking at ecologically relevant densities • (How) Should rewilding restore ecology of fear? • Hunting does not simulate ecology of fear ...
... • If carnivores are lacking at ecologically relevant densities • (How) Should rewilding restore ecology of fear? • Hunting does not simulate ecology of fear ...
Ecology

Ecology (from Greek: οἶκος, ""house""; -λογία, ""study of"") is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environment. It is an interdisciplinary field that includes biology and Earth science. Ecology includes the study of interactions organisms have with each other, other organisms, and with abiotic components of their environment. Topics of interest to ecologists include the diversity, distribution, amount (biomass), and number (population) of particular organisms; as well as cooperation and competition between organisms, both within and among ecosystems. Ecosystems are composed of dynamically interacting parts including organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, pedogenesis, nutrient cycling, and various niche construction activities, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. These processes are sustained by organisms with specific life history traits, and the variety of organisms is called biodiversity. Biodiversity, which refers to the varieties of species, genes, and ecosystems, enhances certain ecosystem services.Ecology is not synonymous with environment, environmentalism, natural history, or environmental science. It is closely related to evolutionary biology, genetics, and ethology. An important focus for ecologists is to improve the understanding of how biodiversity affects ecological function. Ecologists seek to explain: Life processes, interactions and adaptations The movement of materials and energy through living communities The successional development of ecosystems The abundance and distribution of organisms and biodiversity in the context of the environment.Ecology is a human science as well. There are many practical applications of ecology in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries), city planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). For example, the Circles of Sustainability approach treats ecology as more than the environment 'out there'. It is not treated as separate from humans. Organisms (including humans) and resources compose ecosystems which, in turn, maintain biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and produce natural capital like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value.The word ""ecology"" (""Ökologie"") was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel (1834–1919). Ecological thought is derivative of established currents in philosophy, particularly from ethics and politics. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Hippocrates and Aristotle laid the foundations of ecology in their studies on natural history. Modern ecology became a much more rigorous science in the late 19th century. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection became the cornerstones of modern ecological theory.