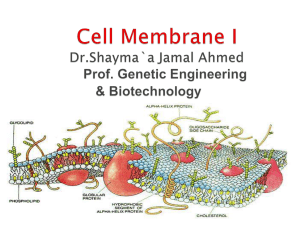
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... A. Mosaic: an object comprised of bits and pieces embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure ...
... A. Mosaic: an object comprised of bits and pieces embedded in a supporting structure 1. membrane lipids form the supporting structure 2. membrane proteins provide the bits and pieces 3. both lipids and proteins may be mobile or 'fluid' B. Membrane lipids: the supporting structure ...
Chapter : 6: A Tour of the Cell
... subcellular objects d) transmission electron microscope, because of its high resolving power e) light microscope, because the specimen is alive 2. Which of the following structures cannot be found in prokaryotic cells? (Concept 6.2) a) cytosol b) plasma membrane c) mitochondria d) ribosomes e) RNA 3 ...
... subcellular objects d) transmission electron microscope, because of its high resolving power e) light microscope, because the specimen is alive 2. Which of the following structures cannot be found in prokaryotic cells? (Concept 6.2) a) cytosol b) plasma membrane c) mitochondria d) ribosomes e) RNA 3 ...
Name: Date - cloudfront.net
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
... 16. Why does the cell membrane arrange into a BILAYER (double layer) of phospholipids, with the heads facing the outside and inside of the cell and the tails facing each other? [HINT: Think about which parts are “water-loving” and which parts are “water-hating?”] ____________________________________ ...
Animal Cell Label # Organelle Function Nuclear membrane
... Makes new proteins (Think pork ribs) Help the cell “Divide” into many new cells. (think of cents) A powerhouse to Change food and oxygen into energy for the body to use. Helps pack and ship the proteins to other parts of the cell. (think of the post office) Jelly like liquid that organelles float in ...
... Makes new proteins (Think pork ribs) Help the cell “Divide” into many new cells. (think of cents) A powerhouse to Change food and oxygen into energy for the body to use. Helps pack and ship the proteins to other parts of the cell. (think of the post office) Jelly like liquid that organelles float in ...
General Microbiology
... Two fundamentally different types of cells are classified in the microbial world, Prokaryotic .. Eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a "true" nucleus.. Prokaryotic cells have a naked nucleus.. composed of a single DNA Chromosome.. not enclosed within a nuclear membrane. The shape of Prokar ...
... Two fundamentally different types of cells are classified in the microbial world, Prokaryotic .. Eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a "true" nucleus.. Prokaryotic cells have a naked nucleus.. composed of a single DNA Chromosome.. not enclosed within a nuclear membrane. The shape of Prokar ...
Plant Cell Labels
... Numerous ribosomes are attached to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pores that perforate the nuclear envelope. It is a single piece of coiled DNA. Chromosomes are normally ...
... Numerous ribosomes are attached to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pores that perforate the nuclear envelope. It is a single piece of coiled DNA. Chromosomes are normally ...
Ch 6 Powerpoint - Plain Local Schools
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
... A. Mitochondria are structures where cellular respiration occurs, a process that most organisms use to access energy B. ATP is the main energy source for the cell and is the end result of cellular respiration C. Mitochondria have many infoldings which allows for a larger surface area which results i ...
Moving Cellular Materials
... The random movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration. (GASES) But what does having a high concentration mean? CLASS DEMO ...
... The random movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration. (GASES) But what does having a high concentration mean? CLASS DEMO ...
Test #1 Notes: Classification and kingdoms` Monera, Protista, and
... 11. What are vaccines and how do they work? (MC) 12. Identify the characteristics of Kingdoms Eubacteria/Archaebacteria. (MC) 13. Draw various bacteria, using a given shape and arrangement. (CR) 14. Describe 4 examples of how bacteria benefit humans. (CR) 15. What is the difference between gram posi ...
... 11. What are vaccines and how do they work? (MC) 12. Identify the characteristics of Kingdoms Eubacteria/Archaebacteria. (MC) 13. Draw various bacteria, using a given shape and arrangement. (CR) 14. Describe 4 examples of how bacteria benefit humans. (CR) 15. What is the difference between gram posi ...
The following is a glossary of plant cell anatomy terms.
... support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made ...
... support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made ...
Membranes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Diffusion: the movement of particles from the area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration to form dynamic equilibrium. • Dynamic Equilibrium: condition of continuous ...
... • Diffusion: the movement of particles from the area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration to form dynamic equilibrium. • Dynamic Equilibrium: condition of continuous ...
Cell Project - WordPress.com
... Are membrane-bound organelles that use light energy and make food - a sugar called glucose – from water and carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis. Arm, legs claws, and antennae are all types of appendages. Are long tail like appendages that whip back and forth a move a cell. Are short ...
... Are membrane-bound organelles that use light energy and make food - a sugar called glucose – from water and carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis. Arm, legs claws, and antennae are all types of appendages. Are long tail like appendages that whip back and forth a move a cell. Are short ...
Lab #5 - Onion Cells (Oct. 21 2014)
... 5. If 10 cells fit across the field of view, estimate the length of a single cell in micrometres (μm or 10-6 meters) assuming that the field of view under high power is approximately 500 μm across. Explain your answer. ...
... 5. If 10 cells fit across the field of view, estimate the length of a single cell in micrometres (μm or 10-6 meters) assuming that the field of view under high power is approximately 500 μm across. Explain your answer. ...
September 26 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... Do Now (Quiz) 3. The chemical reactions involved in respiration are virtually identical between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, ATP is synthesized primarily on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Where are the corresponding reactions likely to occur in prokaryotic respi ...
... Do Now (Quiz) 3. The chemical reactions involved in respiration are virtually identical between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, ATP is synthesized primarily on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Where are the corresponding reactions likely to occur in prokaryotic respi ...
HS Life Sci Standard 2.5 Cells
... 1. What are the differences and similarities between active and passive transport and what factors influence their rates? 2a. How does the direction of osmosis depend on the concentration of the solutes on both sides of a membrane? 2b. Why is it important that cell membranes are selectively permeabl ...
... 1. What are the differences and similarities between active and passive transport and what factors influence their rates? 2a. How does the direction of osmosis depend on the concentration of the solutes on both sides of a membrane? 2b. Why is it important that cell membranes are selectively permeabl ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
... are usually many on cell surface 0.25 microns across & 2 – 20 microns long move like oars (alternating power /recovery ...
... are usually many on cell surface 0.25 microns across & 2 – 20 microns long move like oars (alternating power /recovery ...
Bacteria
... The skeletal remains of large whales are home to a unique genus of gutless polychaete worms called Osedax. These worms harbor heterotrophic bacteria that degrade lipids in whale bones to provide their host with nutrition. ...
... The skeletal remains of large whales are home to a unique genus of gutless polychaete worms called Osedax. These worms harbor heterotrophic bacteria that degrade lipids in whale bones to provide their host with nutrition. ...
cell walls containing peptidoglycan
... Stations Today • Explanation and CHAMPS • If you finish at a station and “have nothing to do” study you chart. There WILL be a memory QUIZ today. ...
... Stations Today • Explanation and CHAMPS • If you finish at a station and “have nothing to do” study you chart. There WILL be a memory QUIZ today. ...
Mycolic acid export to the outer membrane of mycobacteria
... is membrane biogenesis, i.e. how a biological membrane is assembled. Membrane lipid bilayers form the basis for life, physically defining cells and organelles, and modulating the chemical environments within these compartments for optimal metabolism and growth. Despite these fundamental roles, howev ...
... is membrane biogenesis, i.e. how a biological membrane is assembled. Membrane lipid bilayers form the basis for life, physically defining cells and organelles, and modulating the chemical environments within these compartments for optimal metabolism and growth. Despite these fundamental roles, howev ...
Classification
... Rules for Scientific Naming Each species’ name is unique and usually descriptive Scientific names: ...
... Rules for Scientific Naming Each species’ name is unique and usually descriptive Scientific names: ...
Concept Checks: Chapter 6- A Tour of the Cell Concept Check 6.1 1
... 1. Both structures are involved in making energy available to the cell 2. Energy is used to form ATP, energy carrier of the cell 3. Reactions in the chloroplast change light energy into stored energy 4. Both have inner and outer membranes, chemical reactions take place within these membranes. Concep ...
... 1. Both structures are involved in making energy available to the cell 2. Energy is used to form ATP, energy carrier of the cell 3. Reactions in the chloroplast change light energy into stored energy 4. Both have inner and outer membranes, chemical reactions take place within these membranes. Concep ...
Concept Checks: Chapter 6- A Tour of the Cell Concept Check 6.1 1
... 1. Both structures are involved in making energy available to the cell 2. Energy is used to form ATP, energy carrier of the cell 3. Reactions in the chloroplast change light energy into stored energy 4. Both have inner and outer membranes, chemical reactions take place within these membranes. Concep ...
... 1. Both structures are involved in making energy available to the cell 2. Energy is used to form ATP, energy carrier of the cell 3. Reactions in the chloroplast change light energy into stored energy 4. Both have inner and outer membranes, chemical reactions take place within these membranes. Concep ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.























