Respiration (Quick Questions) 1. In what part of cell does respiration
... 8. Glycogen is a storage substance made up of many glucose molecules. It is stored in muscles tissues and converted to glucose when needed. 9. An increase in heart rate (to increase blood flow). An increase in breathing rate (to increase oxygen levels). Glycogen stores in muscles are converted to gl ...
... 8. Glycogen is a storage substance made up of many glucose molecules. It is stored in muscles tissues and converted to glucose when needed. 9. An increase in heart rate (to increase blood flow). An increase in breathing rate (to increase oxygen levels). Glycogen stores in muscles are converted to gl ...
Guide 1406 Ch, 1-5
... Define Matter, inertia, isotope, radioactivity, colloid, suspention Draw the electron shell diagram Differentiate between electrolyte and non-electrolyte The difference between Synthesis or combination reaction and decomposition What factors influence the rate of chemical reactions Difference betwee ...
... Define Matter, inertia, isotope, radioactivity, colloid, suspention Draw the electron shell diagram Differentiate between electrolyte and non-electrolyte The difference between Synthesis or combination reaction and decomposition What factors influence the rate of chemical reactions Difference betwee ...
Saccharides in nutrition
... • Hyperosmolarity (increasing osmotic and blood pressure) – development of atherosclerosis, damage of eyesight • Ketoacidosis – excessive formation of keto acids – see above DIABETES MELLITUS - type II Non - insulin – dependent diabetes About 80 - 90 % of cases; formation mainly from 50 (40; 60) yea ...
... • Hyperosmolarity (increasing osmotic and blood pressure) – development of atherosclerosis, damage of eyesight • Ketoacidosis – excessive formation of keto acids – see above DIABETES MELLITUS - type II Non - insulin – dependent diabetes About 80 - 90 % of cases; formation mainly from 50 (40; 60) yea ...
EXPECTATIONS for Do Now
... ● Breaks down glucose to release Energy/ATP ● The reactants of cellular respiration are oxygen and glucose ● The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. ● The balanced chemical equation: ...
... ● Breaks down glucose to release Energy/ATP ● The reactants of cellular respiration are oxygen and glucose ● The products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. ● The balanced chemical equation: ...
Molecules of Life
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
... – A large molecule that contains many molecules – A large molecule made of smaller, molecules of the same type (monomers) linked together. • A protein (the polymer) is made of many amino acids (monomers) ...
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
... gestation with 50g glucose load (non-fasting). It is extremely important to screen any woman, with past GDM, or glycosuria, or who is over 30 years, or obese or in a risk group for DM. If plasma glucose at 1h is ≥7.8 (≥8.0 if 75g load), then follow with formal OGTT. FPG ≥5.5 and 2h glucose ≥8.0 is d ...
... gestation with 50g glucose load (non-fasting). It is extremely important to screen any woman, with past GDM, or glycosuria, or who is over 30 years, or obese or in a risk group for DM. If plasma glucose at 1h is ≥7.8 (≥8.0 if 75g load), then follow with formal OGTT. FPG ≥5.5 and 2h glucose ≥8.0 is d ...
What is Diabetes?
... 2. Diabetes Association of Pierce County (DAPC) does not monitor or endorse, and is not responsible for any agency, research project, support group, class or event except for the events in which DAPC is the sponsoring agent, e.g. Panther Day Camp, diabetes self-care workshops, and public detection s ...
... 2. Diabetes Association of Pierce County (DAPC) does not monitor or endorse, and is not responsible for any agency, research project, support group, class or event except for the events in which DAPC is the sponsoring agent, e.g. Panther Day Camp, diabetes self-care workshops, and public detection s ...
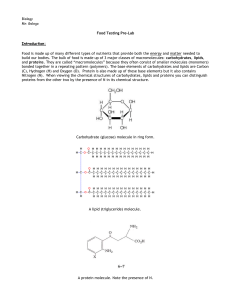
Food Prelab - TeacherWeb
... The body uses lipids for long-term energy storage. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-hating”) and thus much harder to break down for energy than carbohydrates. Lipids, however, contain more energy per unit weight then carbohydrates. Therefore it is more efficient for the body to use lipids as stored en ...
... The body uses lipids for long-term energy storage. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-hating”) and thus much harder to break down for energy than carbohydrates. Lipids, however, contain more energy per unit weight then carbohydrates. Therefore it is more efficient for the body to use lipids as stored en ...
nerves & action potentials - IB
... • Channels allow glucose to diffuse into the cell by facilitated diffusion • If blood high in glucose enters the liver, insulin stimulates the hepatocytes to take in glucose and convert it to glycogen • Glycogen stored as granules in the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes & muscles ...
... • Channels allow glucose to diffuse into the cell by facilitated diffusion • If blood high in glucose enters the liver, insulin stimulates the hepatocytes to take in glucose and convert it to glycogen • Glycogen stored as granules in the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes & muscles ...
Blood Glucose Regulation
... • Hypoglycemia: leads to coma/death • Hyperglycemia leads to long term damage of eyes, blood vessel, organs (kidney) ...
... • Hypoglycemia: leads to coma/death • Hyperglycemia leads to long term damage of eyes, blood vessel, organs (kidney) ...
Concept 12: Glucose Regulation Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1
... b. "The central nervous system cannot store glucose and needs a continuous supply of glucose for fuel." c. "Without a minimum level of glucose circulating in the blood, erythrocytes cannot produce ATP." d. "The presence of glucose in the blood counteracts the formation of lactic acid and ...
... b. "The central nervous system cannot store glucose and needs a continuous supply of glucose for fuel." c. "Without a minimum level of glucose circulating in the blood, erythrocytes cannot produce ATP." d. "The presence of glucose in the blood counteracts the formation of lactic acid and ...
Protein - Duplin County Schools
... best way to check this is to avoid eating all milk and dairy products to see if your symptoms go away ...
... best way to check this is to avoid eating all milk and dairy products to see if your symptoms go away ...
New Software in the Deltec Cozmo® Insulin Pump
... Cozmo Insulin Pump, announces that they have received 510(k) clearance for the CoZmonitor™ blood glucose module. The CoZmonitor™ blood glucose module is attached to the back of the Deltec Cozmo® insulin pump to create an “all-in-one” insulin pump and blood glucose monitoring system.1 The Deltec Cozm ...
... Cozmo Insulin Pump, announces that they have received 510(k) clearance for the CoZmonitor™ blood glucose module. The CoZmonitor™ blood glucose module is attached to the back of the Deltec Cozmo® insulin pump to create an “all-in-one” insulin pump and blood glucose monitoring system.1 The Deltec Cozm ...
Midterm 3 - Creighton Biology
... should fit in the spaces provided. Diagrams may be used but must be accompanied by written explanations. Each question is worth 8 points. Answer the following questions based on the oxygen saturation curve below. ...
... should fit in the spaces provided. Diagrams may be used but must be accompanied by written explanations. Each question is worth 8 points. Answer the following questions based on the oxygen saturation curve below. ...
File - Northwood pe
... 1. Air leaves the trachea and passes through the: bronchioles bronchi capillaries ...
... 1. Air leaves the trachea and passes through the: bronchioles bronchi capillaries ...
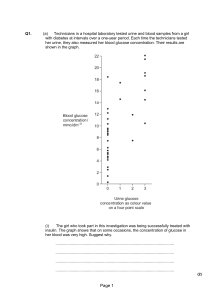
Q1. (a) Technicians in a hospital laboratory tested urine and blood
... with diabetes at intervals over a one-year period. Each time the technicians tested her urine, they also measured her blood glucose concentration. Their results are shown in the graph. ...
... with diabetes at intervals over a one-year period. Each time the technicians tested her urine, they also measured her blood glucose concentration. Their results are shown in the graph. ...
Chapter 25
... Cell response to insulin (membrane sensitivity) Small intestine to absorb glucose Liver to take up & store glucose ...
... Cell response to insulin (membrane sensitivity) Small intestine to absorb glucose Liver to take up & store glucose ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... • Higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms – causes them to have more carbon to hydrogen bonds which store more energy….hence fats having a higher caloric value ...
... • Higher ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms – causes them to have more carbon to hydrogen bonds which store more energy….hence fats having a higher caloric value ...
CHM 132 Spring 2011
... reduce the absorbing surface of the intestines. c. trap the nutrient particles and absorb them into the cells. d. prevent nutrients from being absorbed. 17. The liver converts excess energy-containing nutrients into: a. glycogen. b. protein. c. fat. d. a and b e. a and c ...
... reduce the absorbing surface of the intestines. c. trap the nutrient particles and absorb them into the cells. d. prevent nutrients from being absorbed. 17. The liver converts excess energy-containing nutrients into: a. glycogen. b. protein. c. fat. d. a and b e. a and c ...
Functions - kcpe-kcse
... – Liver, Red meat (beef), Egg yolk, Dark green vegetables • Function: – Essential for the formation of haemoglobin for transport of oxygen around the body. • Deficiency: – Anaemia (smaller and fewer red blood cells – Tiredness – Breathlessness. ...
... – Liver, Red meat (beef), Egg yolk, Dark green vegetables • Function: – Essential for the formation of haemoglobin for transport of oxygen around the body. • Deficiency: – Anaemia (smaller and fewer red blood cells – Tiredness – Breathlessness. ...
6.5 Nerves, hormones and homeostasis – summary of mark schemes
... State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits, including blood pH, carbon dioxide concentration, blood glucose concentration, body temperature and water balance. Mark Scheme A. B. C. ...
... State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits, including blood pH, carbon dioxide concentration, blood glucose concentration, body temperature and water balance. Mark Scheme A. B. C. ...
Science Year 8 Learn Sheet DC4 – Respiration
... because your cells need more oxygen and glucose for respiration. Breathing is the movement of muscles in the diaphragm and attached to the ribs. These movements change the volume of the chest ...
... because your cells need more oxygen and glucose for respiration. Breathing is the movement of muscles in the diaphragm and attached to the ribs. These movements change the volume of the chest ...
How does the body control glucose in the blood?
... where it is stored as GLYCOGEN. At times when extra fuel is needed, such as exercise, the glycogen is turned back to glucose and returned to the blood stream to continue the journey to the brain and muscles. ...
... where it is stored as GLYCOGEN. At times when extra fuel is needed, such as exercise, the glycogen is turned back to glucose and returned to the blood stream to continue the journey to the brain and muscles. ...