Metabolism part 1
... exoenzym is then used to break down large molecules outside of cell into molecules small enough to be transported across the cell membrane. ...
... exoenzym is then used to break down large molecules outside of cell into molecules small enough to be transported across the cell membrane. ...
Cell Structure
... • Saclike structures • Usually large in plant cells and smaller and more numerous in animal cells Function: 1. Stores water, food, & waste 2. Provides pressure for support in plant cells ...
... • Saclike structures • Usually large in plant cells and smaller and more numerous in animal cells Function: 1. Stores water, food, & waste 2. Provides pressure for support in plant cells ...
Specialised Cells
... • Plants and animals are multicellular (consist of many cells). • They contain many different types of cells. • Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. • This is known as CELL SPECIALISM • Not all cells look the same. • Some cells have a special shape and features to ...
... • Plants and animals are multicellular (consist of many cells). • They contain many different types of cells. • Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. • This is known as CELL SPECIALISM • Not all cells look the same. • Some cells have a special shape and features to ...
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
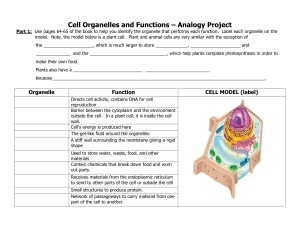
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
Cell Organelles
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
Cell Organelles
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
Biology I Cell Test Review- Answer Key List the 3 parts of the cell
... 3. List the functions of the following organelles and describe how the functions relate to the function of a building in a factory. a. nucleus- stores DNA, info to make proteins located here, controls cell’s processes b. nucleolus-produces ribosomes c. nuclear membrane-regulates materials entering a ...
... 3. List the functions of the following organelles and describe how the functions relate to the function of a building in a factory. a. nucleus- stores DNA, info to make proteins located here, controls cell’s processes b. nucleolus-produces ribosomes c. nuclear membrane-regulates materials entering a ...
Organelles Summary Assignment
... synthesis and assembly. Small structures composed of RNA and protein, which catalyze the synthesis of a cell’s proteins. May be in cytosol, or found attached to ER. Composed of stiff fibers of cellulose and other complex carbohydrates. Found in plant and fungal cells. System of flattened discs that ...
... synthesis and assembly. Small structures composed of RNA and protein, which catalyze the synthesis of a cell’s proteins. May be in cytosol, or found attached to ER. Composed of stiff fibers of cellulose and other complex carbohydrates. Found in plant and fungal cells. System of flattened discs that ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 5. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 6. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color 7. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria 8. Small bumps locat ...
... 5. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 6. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color 7. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria 8. Small bumps locat ...
Cell Organelle Notes
... Allows water and dissolved substances to pass through Controls most activities in the cell Usually one per cell Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules for the cell The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave Small, dense region in th ...
... Allows water and dissolved substances to pass through Controls most activities in the cell Usually one per cell Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules for the cell The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave Small, dense region in th ...
Cell Structure Review
... Scientists have found many different amino acids in protein, but 22 of them are very important to human health. ...
... Scientists have found many different amino acids in protein, but 22 of them are very important to human health. ...
The Case Of The Damaged Cell
... mitochondria is enclosed in a vesicle. The lysosmes bump into these vesicles and pour enzymes into them. Useful amino acids and fatty acids are returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. Lysosomes also digest food particles, and foreign invaders. The cell can make new o ...
... mitochondria is enclosed in a vesicle. The lysosmes bump into these vesicles and pour enzymes into them. Useful amino acids and fatty acids are returned to the cytoplasm and waste particles are removed from the cell. Lysosomes also digest food particles, and foreign invaders. The cell can make new o ...
Investigating Cells - Miss Gleason`s Science
... you actually see as you look through the microscope. Do not scribble or put meaningless dots or cross-hatching. Label structures. Cork Cells: Prepare a cork slide by thinly slicing a piece of cork and looking it under the microscope. Or look at a prepared cork slide. Sketch several cork cells as t ...
... you actually see as you look through the microscope. Do not scribble or put meaningless dots or cross-hatching. Label structures. Cork Cells: Prepare a cork slide by thinly slicing a piece of cork and looking it under the microscope. Or look at a prepared cork slide. Sketch several cork cells as t ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... chemicals (Liver cells have lots of Smooth ER – Structure –Function). • Transport materials too!! ...
... chemicals (Liver cells have lots of Smooth ER – Structure –Function). • Transport materials too!! ...
Microworlds Study Guide
... The vinegar eel is a harmless round worm. It is about 2mm long. Its body is almost transparent and you can see some of their organs. Vinegar eels are made of many cells. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can digest food. It has a mouth and an anus. Females have their babies lined u ...
... The vinegar eel is a harmless round worm. It is about 2mm long. Its body is almost transparent and you can see some of their organs. Vinegar eels are made of many cells. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can digest food. It has a mouth and an anus. Females have their babies lined u ...
You Light Up My Life
... – a) Inside stroma, ATP energy is used to make sugars, then other carbohydrates` ...
... – a) Inside stroma, ATP energy is used to make sugars, then other carbohydrates` ...
Cells Alive-Internet Lesson
... What is the difference between rough and smooth ER? Where is the nucleolus found? What does the nucleolus do? What does the cytoskeleton do? Cytosol goes by what other name? What is the function of cytosol? What is the function of lysosomes? Sketch the mitochondria, rough and smooth ...
... What is the difference between rough and smooth ER? Where is the nucleolus found? What does the nucleolus do? What does the cytoskeleton do? Cytosol goes by what other name? What is the function of cytosol? What is the function of lysosomes? Sketch the mitochondria, rough and smooth ...
Eukaryotic Cells and Cell Organelles
... Some organelles do jobs other than making proteins. Mitochondria Mitochondria are bean-shaped organelles that produce chemical energy that is usable by a cell. They have two membranes. The inner membrane has lots of folds that form compartments. Mitochondria also have their own ribosomes and DNA. At ...
... Some organelles do jobs other than making proteins. Mitochondria Mitochondria are bean-shaped organelles that produce chemical energy that is usable by a cell. They have two membranes. The inner membrane has lots of folds that form compartments. Mitochondria also have their own ribosomes and DNA. At ...
Cells - Life Learning Cloud
... • Can you recognise cell structures such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast and vacuole, and describe their functions? • What are the major differences between plant and animal cells? ...
... • Can you recognise cell structures such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast and vacuole, and describe their functions? • What are the major differences between plant and animal cells? ...
7th grade Midterm Review - St. Joseph Hill Academy
... stem cell - unspecialized cell that develops into many different cell types tissue - group of similar types of cells that work together to carry out specific tasks cell membrane - protects the inside of a cell from the environment cell wall - stiff structure outside the cell membrane chloroplast mem ...
... stem cell - unspecialized cell that develops into many different cell types tissue - group of similar types of cells that work together to carry out specific tasks cell membrane - protects the inside of a cell from the environment cell wall - stiff structure outside the cell membrane chloroplast mem ...
Glossary of Vocab Terms
... chromatin the DNA and proteins in the nucleus of a nondividing cell (80) chromosome DNA and protein in a coiled, rod-shaped form that occurs during cell division (81) cilium a short, hairlike organelle that extends from a cell and functions in locomotion or in the movement of substances across the c ...
... chromatin the DNA and proteins in the nucleus of a nondividing cell (80) chromosome DNA and protein in a coiled, rod-shaped form that occurs during cell division (81) cilium a short, hairlike organelle that extends from a cell and functions in locomotion or in the movement of substances across the c ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑