5.2. Protocol for PCR
... Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) separates proteins according to their molecular weight. Note that unpolymerized acrylamide and TEMED are poisonous, try not to inhale and preferably use in fume hood. Materials: ...
... Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) separates proteins according to their molecular weight. Note that unpolymerized acrylamide and TEMED are poisonous, try not to inhale and preferably use in fume hood. Materials: ...
Supplementary Materials: Monoclonal IgA Antibodies for
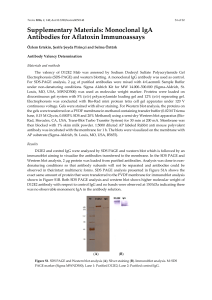
... Electrophoresis (SDS‐PAGE) and western blotting. A monoclonal IgG antibody was used as control. For SDS‐PAGE analysis, 2 μg of purified antibodies were mixed with 4×Laemmli Sample Buffer under non‐denaturing conditions. Sigma Aldrich Kit for MW 14.000–500.000 (Sigma‐Aldrich, ...
... Electrophoresis (SDS‐PAGE) and western blotting. A monoclonal IgG antibody was used as control. For SDS‐PAGE analysis, 2 μg of purified antibodies were mixed with 4×Laemmli Sample Buffer under non‐denaturing conditions. Sigma Aldrich Kit for MW 14.000–500.000 (Sigma‐Aldrich, ...
Guidelines for separating DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) using gel
... separated DNA fragments. However, this compound can alter the biochemical structure of DNA by causing the mass of the fragments to change or the rigidity of the fragments to be altered. Some agarose gel electrophoresis protocols suggest that the ethidium bromide can be added to agarose gel before lo ...
... separated DNA fragments. However, this compound can alter the biochemical structure of DNA by causing the mass of the fragments to change or the rigidity of the fragments to be altered. Some agarose gel electrophoresis protocols suggest that the ethidium bromide can be added to agarose gel before lo ...
A simple and efficient method for the purification
... per ng of DNA in the presence of 0.2 mM dATP at 37°C for 1 hour. The enzyme was deactivated (65°C for 10'), and the reaction mixture was passed through a G-25 (Pharmacia) column prior to precipitation with ethanol. The DNA pellet was resuspended in coupling buffer consisting of 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1 ...
... per ng of DNA in the presence of 0.2 mM dATP at 37°C for 1 hour. The enzyme was deactivated (65°C for 10'), and the reaction mixture was passed through a G-25 (Pharmacia) column prior to precipitation with ethanol. The DNA pellet was resuspended in coupling buffer consisting of 10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1 ...
Protein Extraction Protocol
... 2. From each plant cut up 1 g of fresh plant tissue as fine as you can with a razor blade. Place this into a mortar with approximately 1 ml of cold QB buffer containing protease inhibitor and a pinch of clean sand. Grind until smooth with a pestle. It is very important to grind the tissue well. You ...
... 2. From each plant cut up 1 g of fresh plant tissue as fine as you can with a razor blade. Place this into a mortar with approximately 1 ml of cold QB buffer containing protease inhibitor and a pinch of clean sand. Grind until smooth with a pestle. It is very important to grind the tissue well. You ...
Sbjct = Alu sequence
... of DNA. This quantity of DNA is required for downstream applications such as DNA fingerprinting and DNA sequencing. The in vitro copying of DNA in the laboratory follows the same basic steps that occur in vivo in the cell each time DNA is replicated prior to cell division. However there are some imp ...
... of DNA. This quantity of DNA is required for downstream applications such as DNA fingerprinting and DNA sequencing. The in vitro copying of DNA in the laboratory follows the same basic steps that occur in vivo in the cell each time DNA is replicated prior to cell division. However there are some imp ...
Classification of Amino Acids
... Beads with covalently attached chemical group Binding of proteins with affinity for the chemical group ...
... Beads with covalently attached chemical group Binding of proteins with affinity for the chemical group ...
DNA Sequencing and Gene Analysis
... of the same base in a row) are notoriously tricky to sequence accurately. Using the opposite strand often helps resolve these regions. Also using a different ...
... of the same base in a row) are notoriously tricky to sequence accurately. Using the opposite strand often helps resolve these regions. Also using a different ...
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and/or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving.Proteins are separated by charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for separation of nanoparticles.Gel electrophoresis uses a gel as an anticonvective medium and/or sieving medium during electrophoresis, the movement of a charged particle in an electrical field. Gels suppress the thermal convection caused by application of the electric field, and can also act as a sieving medium, retarding the passage of molecules; gels can also simply serve to maintain the finished separation, so that a post electrophoresis stain can be applied. DNA Gel electrophoresis is usually performed for analytical purposes, often after amplification of DNA via PCR, but may be used as a preparative technique prior to use of other methods such as mass spectrometry, RFLP, PCR, cloning, DNA sequencing, or Southern blotting for further characterization.