Physiology (17%) Sample Test Prep Questions
... bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication, the body’s primary defenses against bacterial and viral infections, and effective treatments of these infections. Summary: A virus, which is the simplest form of a genetic entity, is incapable of metabolic life and r ...
... bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication, the body’s primary defenses against bacterial and viral infections, and effective treatments of these infections. Summary: A virus, which is the simplest form of a genetic entity, is incapable of metabolic life and r ...
what is an infectious disease?
... pathogens are capable of causing a change that disrupts the homeostasis in the body. Any disease caused by the presence of pathogens in the body is called an infectious disease. The main sources of pathogens are soil, contaminated water, and infected animals, including other people ...
... pathogens are capable of causing a change that disrupts the homeostasis in the body. Any disease caused by the presence of pathogens in the body is called an infectious disease. The main sources of pathogens are soil, contaminated water, and infected animals, including other people ...
Ch 19 Packet
... 7. What occurs when viruses get inside of cells? Once inside, the viral genes are expressed. The cell transcribes and translates the viral genetic information into viral capsid proteins. Sometimes the program may cause the cell to make copies of the virus, and in the process the host cell is destroy ...
... 7. What occurs when viruses get inside of cells? Once inside, the viral genes are expressed. The cell transcribes and translates the viral genetic information into viral capsid proteins. Sometimes the program may cause the cell to make copies of the virus, and in the process the host cell is destroy ...
1 Discover the World of Microbes, Bacteria, Archaea - Wiley-VCH
... g is the time required for doubling the number of cells, whereas td is the time required for doubling the cell mass. 2. Describe the characteristic feature of the logarithmic growth phase. The logarithmic growth phase is characterized by a linear increase of the logarithm of the cell number with tim ...
... g is the time required for doubling the number of cells, whereas td is the time required for doubling the cell mass. 2. Describe the characteristic feature of the logarithmic growth phase. The logarithmic growth phase is characterized by a linear increase of the logarithm of the cell number with tim ...
S2 rev pkt 2013(evol - body)
... cheetahs. In the biome, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) results in plants that are small and stunted. The biome has both deciduous and coniferous trees, has cold winters and warm summers, and is home to deer, black bears, squirrels, raccoons and skunk. The biome has dense evergreen forests o ...
... cheetahs. In the biome, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil) results in plants that are small and stunted. The biome has both deciduous and coniferous trees, has cold winters and warm summers, and is home to deer, black bears, squirrels, raccoons and skunk. The biome has dense evergreen forests o ...
Chapter 1
... Algae • Eukaryotes • Cellulose cell walls • Use photosynthesis for energy • Produce molecular oxygen and organic compounds Figure 1.1d ...
... Algae • Eukaryotes • Cellulose cell walls • Use photosynthesis for energy • Produce molecular oxygen and organic compounds Figure 1.1d ...
Classification
... to ID an organism • To use, you read both options, decide which variation is best, and move on to the next step. ...
... to ID an organism • To use, you read both options, decide which variation is best, and move on to the next step. ...
3.1 Diversity of Organisms
... Substances produced by bacteria or fungi [accept microorganisms] to treat infections[kill other bacteria or fungi] Lives on dead organisms An organism living in or on another organism causing it harm. ...
... Substances produced by bacteria or fungi [accept microorganisms] to treat infections[kill other bacteria or fungi] Lives on dead organisms An organism living in or on another organism causing it harm. ...
Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis: subversive
... Anaplasma spp. and Ehrlichia spp. cause several emerging human infectious diseases. Anaplasma phagocytophilum andEhrlichia chaffeensis are transmitted between mammals by blood-sucking ticks and replicate inside mammalian white blood cells and tick salivary-gland and midgut cells. Adaptation to a lif ...
... Anaplasma spp. and Ehrlichia spp. cause several emerging human infectious diseases. Anaplasma phagocytophilum andEhrlichia chaffeensis are transmitted between mammals by blood-sucking ticks and replicate inside mammalian white blood cells and tick salivary-gland and midgut cells. Adaptation to a lif ...
Chapter Notes - schallesbiology
... Escherichia Coli – some strains are harmless, even helpful;- live in our intestines, but strain E. coli 157 is responsible for food poisoning deaths. According to the CDC there are an estimated 73,000 cases of E. Coli infection every year in the United States. The typical symptoms are bloody diarrhe ...
... Escherichia Coli – some strains are harmless, even helpful;- live in our intestines, but strain E. coli 157 is responsible for food poisoning deaths. According to the CDC there are an estimated 73,000 cases of E. Coli infection every year in the United States. The typical symptoms are bloody diarrhe ...
Microbiology
... * He also showed that fermentation - a process used in baking was caused by microorganisms. *Developed vaccinations for Rabies and Chicken cholera. *He developed the process for sterilizing milk and this was ...
... * He also showed that fermentation - a process used in baking was caused by microorganisms. *Developed vaccinations for Rabies and Chicken cholera. *He developed the process for sterilizing milk and this was ...
Six Kingdoms of Living Things Teacher Notes
... Until the 20th century, most biologists considered all living things to be classifiable as either a plant or an animal. But in the 1950s and 1960s, most biologists came to the realization that this system failed to accommodate the fungi, protists, and bacteria. By the 1970s, a system of Five Kingdom ...
... Until the 20th century, most biologists considered all living things to be classifiable as either a plant or an animal. But in the 1950s and 1960s, most biologists came to the realization that this system failed to accommodate the fungi, protists, and bacteria. By the 1970s, a system of Five Kingdom ...
Micro-organisms and humans - questions
... 30 Micro-organisms and humans 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into thei ...
... 30 Micro-organisms and humans 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into thei ...
StudyBlue Guide - Microbiology Study Guides
... The attractions between two different water molecules are called H bonds This would not be found in DNA Uracil Bacteria reproduce by Binary fission Generation time of a bacteria can be as short as 10 minutes A nucleotide does not contain sulphur An example of a nucleotide-containing molecule All the ...
... The attractions between two different water molecules are called H bonds This would not be found in DNA Uracil Bacteria reproduce by Binary fission Generation time of a bacteria can be as short as 10 minutes A nucleotide does not contain sulphur An example of a nucleotide-containing molecule All the ...
10.4 Don`t Bug Me - Texarkana Independent School District
... of 4-6 with a student requiring enrichment in charge. They may send representatives to other groups to clarify transmission within groups, but each group should have to identify the transmitter on their own. Give students about 15-20 minutes to try to identify the cup number that contained the origi ...
... of 4-6 with a student requiring enrichment in charge. They may send representatives to other groups to clarify transmission within groups, but each group should have to identify the transmitter on their own. Give students about 15-20 minutes to try to identify the cup number that contained the origi ...
Slide 1
... They live in a watery environment, in salty oceans, and fresh water or in moist soil. Can be autotroph, heterotroph or switch to both ways if necessary Some of them live as parasites ...
... They live in a watery environment, in salty oceans, and fresh water or in moist soil. Can be autotroph, heterotroph or switch to both ways if necessary Some of them live as parasites ...
Abiotic- a non living thing
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
... bird sees, the bird forever sees as its mother. Habituation- becoming so used to something that you cease to be bothered by it or notice it. Ex. not noticing your ceiling fan anymore or a train that passes by your house Classical conditioning- this is making unrelated things become associated. Pavlo ...
Chapter 1 - Bellarmine University
... microbiologists from those studied by other biologists 2. Explain Carl Woese’s contributions in establishing the three domain system for classifying cellular life 3. Provide an example of the importance to humans of each of the major types of microbes 4. Determine the type of microbe (e.g., bacteriu ...
... microbiologists from those studied by other biologists 2. Explain Carl Woese’s contributions in establishing the three domain system for classifying cellular life 3. Provide an example of the importance to humans of each of the major types of microbes 4. Determine the type of microbe (e.g., bacteriu ...
Systems of classification
... are among those in use today. Top: Aristotle’s system distinguished only between plants and animals on the basis of movement, feeding mechanism, and growth patterns. This system groups prokaryotes, algae, and fungi with the plants, and moving, feeding protozoa with the animals. Center: The increasin ...
... are among those in use today. Top: Aristotle’s system distinguished only between plants and animals on the basis of movement, feeding mechanism, and growth patterns. This system groups prokaryotes, algae, and fungi with the plants, and moving, feeding protozoa with the animals. Center: The increasin ...
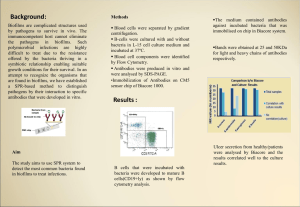
Background: Results
... The medium contained antibodies against incubated bacteria that was immobilised on chip in Biacore system. ...
... The medium contained antibodies against incubated bacteria that was immobilised on chip in Biacore system. ...
a. domain. b. phylum c. species. d. class.
... If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence true, write “TRUE” in the space provided. If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence false, write the correct term or phrase in the space provided. _____ 8. Any species that can’t reproduce will not survive. _____ 9. Organisms in the sam ...
... If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence true, write “TRUE” in the space provided. If the underscored word or phrase makes the sentence false, write the correct term or phrase in the space provided. _____ 8. Any species that can’t reproduce will not survive. _____ 9. Organisms in the sam ...
Unit 4 Review
... Bacteria are how big? ___________________________________________ Bacteria are unicellular organisms that contain what type of cell? ________________________________ Identify the three types of shapes used to describe bacteria. ...
... Bacteria are how big? ___________________________________________ Bacteria are unicellular organisms that contain what type of cell? ________________________________ Identify the three types of shapes used to describe bacteria. ...