LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 8. Sex Pili participate in the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. 9. Rubella virus grows well in chorioallantoic membrane of the embryonated eggs. 10. Animal virus has receptor sites that attach to the attachment sites on the host cell surface. III Complete the following: (5 x 1 = 5) 11. ...
... 8. Sex Pili participate in the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. 9. Rubella virus grows well in chorioallantoic membrane of the embryonated eggs. 10. Animal virus has receptor sites that attach to the attachment sites on the host cell surface. III Complete the following: (5 x 1 = 5) 11. ...
Chicken Pox - Kelsey Trail Health Region
... Chicken Pox is caused by a virus. The chicken pox virus lives in the nose and throat and in blisters on the skin of an infected person. It is spread by direct contact with infected fluids from these areas. The virus can be spread for about 1 - 2 days before a rash appears and up until the blisters a ...
... Chicken Pox is caused by a virus. The chicken pox virus lives in the nose and throat and in blisters on the skin of an infected person. It is spread by direct contact with infected fluids from these areas. The virus can be spread for about 1 - 2 days before a rash appears and up until the blisters a ...
Outbreak! Viruses in Our Water Assessment
... B. The UV light destroys the entire virus body so nothing is visible. C. The UV light does not completely destroy viruses. D. The UV light destroys the genetic material so replication cannot happen. ______ 8. How do most viruses get into water supplies? A. Diarrhea and vomit are flushed down the toi ...
... B. The UV light destroys the entire virus body so nothing is visible. C. The UV light does not completely destroy viruses. D. The UV light destroys the genetic material so replication cannot happen. ______ 8. How do most viruses get into water supplies? A. Diarrhea and vomit are flushed down the toi ...
Bacteria Wanted Poster Research Project
... 4. Most common victims it preys upon. 5. Where it is most likely to be found. 6. Most common injury done to the victim. 7. Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. 8. Number of victims. 9. Most effective weapons against the germ. Can it be prevented or treated? 10. Any ...
... 4. Most common victims it preys upon. 5. Where it is most likely to be found. 6. Most common injury done to the victim. 7. Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. 8. Number of victims. 9. Most effective weapons against the germ. Can it be prevented or treated? 10. Any ...
Size and Shape of Viruses
... DNA: Yes they do have their own Grow and develops: Only in host Viruses are parasites that can only perform certain characteristics in host cells. Host: The cell that the virus attaches and uses their DNA and resources. ...
... DNA: Yes they do have their own Grow and develops: Only in host Viruses are parasites that can only perform certain characteristics in host cells. Host: The cell that the virus attaches and uses their DNA and resources. ...
Virus
... • Monopartite genome • Transmitted by leafhopper vectors to monocotyledonous plants • H-Maize, Sugarcane, wheat, Bajra, Chickpea, Millets, Bean ...
... • Monopartite genome • Transmitted by leafhopper vectors to monocotyledonous plants • H-Maize, Sugarcane, wheat, Bajra, Chickpea, Millets, Bean ...
VIROIDS, PRIONS A virus is a small infectious agent that can
... early expression of virus genes (either directly by translation, if virus contains "+" RNA, or indirectly after transription and then translation) replication of virus nucleic acid synthesis of new virion components packaging and assembly of new virions exit from cell Measurement of viral growth • M ...
... early expression of virus genes (either directly by translation, if virus contains "+" RNA, or indirectly after transription and then translation) replication of virus nucleic acid synthesis of new virion components packaging and assembly of new virions exit from cell Measurement of viral growth • M ...
Virus Structure
... Modifications at the ends of virus genomes • covalently linked protein at the 5 end. In at least some viruses this is a vestige of a primer that was used for initiation of genome synthesis • Some genome RNAs have one or both of the modifications that occur in eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs): a ...
... Modifications at the ends of virus genomes • covalently linked protein at the 5 end. In at least some viruses this is a vestige of a primer that was used for initiation of genome synthesis • Some genome RNAs have one or both of the modifications that occur in eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs): a ...
File
... 5. So many viruses are made inside the host cell that the cell bursts (lysis) 6. The new viruses leave the host cell and go on to infect new cells. ...
... 5. So many viruses are made inside the host cell that the cell bursts (lysis) 6. The new viruses leave the host cell and go on to infect new cells. ...
Immune Responses To Infectious Diseases Chpt.17
... Recognize Bacterial Molecules • TLR-4 (Recognizes LPS, gram negative bacteria) • TLR-2 (Recognizes PGN, gram positive bacteria) • TLR-3,7,9 (viral nucleic acids) • Viruses Induce Production of Interferons (IFN-, IFN- and IFN) • Interferons produce an anti-viral state ...
... Recognize Bacterial Molecules • TLR-4 (Recognizes LPS, gram negative bacteria) • TLR-2 (Recognizes PGN, gram positive bacteria) • TLR-3,7,9 (viral nucleic acids) • Viruses Induce Production of Interferons (IFN-, IFN- and IFN) • Interferons produce an anti-viral state ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. Viruses are similar to bacteria in that they are small, have some kind of genetic material, can be infectious, and can evolve. But viruses are much smaller than bacteria, and they cannot reproduce independently or respond to stimuli. Most biologists do not consider viruses to be alive. 2. An aver ...
... 1. Viruses are similar to bacteria in that they are small, have some kind of genetic material, can be infectious, and can evolve. But viruses are much smaller than bacteria, and they cannot reproduce independently or respond to stimuli. Most biologists do not consider viruses to be alive. 2. An aver ...
virus
... Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nucleocapsid composed of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein capsid that may be icosahedral, helical, or complex in structure. ...
... Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nucleocapsid composed of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein capsid that may be icosahedral, helical, or complex in structure. ...
VIRUSES - Piscataway Township Schools
... • Virus: small, nonliving particle that invades and then multiplies inside a living cell. – Do not use energy to grow or to respond to their surroundings – Cannot make food, take in food, or produce wastes ...
... • Virus: small, nonliving particle that invades and then multiplies inside a living cell. – Do not use energy to grow or to respond to their surroundings – Cannot make food, take in food, or produce wastes ...
Micro Notes
... Some viruses only infect a particular type of tissue or cell within a single species; for example the human cold virus infects only cells of the _upper respiratory tract______; HIV binds to receptors on certain _white blood cells_____. C. Viral Replication A virus can infect a host cell and use it ...
... Some viruses only infect a particular type of tissue or cell within a single species; for example the human cold virus infects only cells of the _upper respiratory tract______; HIV binds to receptors on certain _white blood cells_____. C. Viral Replication A virus can infect a host cell and use it ...
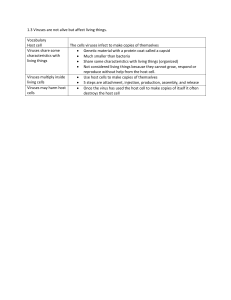
1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell
... 1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell Viruses share some characteristics with living things ...
... 1.3 Viruses are not alive but affect living things. Vocabulary Host cell Viruses share some characteristics with living things ...
File - Mr. SR Brandt
... copies of viral genes that along with viral proteins are assembled into new viruses, which burst from the host cell, killing it. ...
... copies of viral genes that along with viral proteins are assembled into new viruses, which burst from the host cell, killing it. ...
Kingdom: Viruses
... •The proteins on the outside of the virus allow it to attach to proteins on our cell membranes. Once attached, the virus is able to release its RNA into our cells to take control of ribosomes and make copies of itself. ...
... •The proteins on the outside of the virus allow it to attach to proteins on our cell membranes. Once attached, the virus is able to release its RNA into our cells to take control of ribosomes and make copies of itself. ...
Virusesand Prions - Pandem-Sim
... organisms. However, they lack cell structure and they cannot reproduce outside a host cell. These two are characteristics that scientists use to define life. Even though viruses have a seemingly simple structure, they come in a variety of shapes and can be quite distinctive in appearance. For exampl ...
... organisms. However, they lack cell structure and they cannot reproduce outside a host cell. These two are characteristics that scientists use to define life. Even though viruses have a seemingly simple structure, they come in a variety of shapes and can be quite distinctive in appearance. For exampl ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to viruses
... Virus causes changes in cellular gene expression. Uncontrolled cell multiplication and ...
... Virus causes changes in cellular gene expression. Uncontrolled cell multiplication and ...
Instructions for Animal Virus
... Zometool Animal Virus Project—thanks to Dr. Steve Yoshinaga, concept and copywriting; Dr. Brenda Yoshinaga and Dr. Marion Freistadt, editing; Dr. Scott Vorthmann, vZome software used for renderings; Anni Wildung and Tara Brouwer, graphic design; Paul Hildebrandt, project management, etc. Please send ...
... Zometool Animal Virus Project—thanks to Dr. Steve Yoshinaga, concept and copywriting; Dr. Brenda Yoshinaga and Dr. Marion Freistadt, editing; Dr. Scott Vorthmann, vZome software used for renderings; Anni Wildung and Tara Brouwer, graphic design; Paul Hildebrandt, project management, etc. Please send ...
Hospitality and Tourism Travel and Tourism Management Multiple Choice Science Assessment Problems
... (G) analyze security measures to protect the guests, customers, and staff and to limit liability. Biology. (4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells ...
... (G) analyze security measures to protect the guests, customers, and staff and to limit liability. Biology. (4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells ...
Preventable Feline Diseases
... common cause of cancer in cats, it may cause various blood disorders and it may lead to a state of immune deficiency that hinders the cat’s ability to protect itself against other infections. The virus is shed in very high quantities in saliva and nasal secretions, but also in urine, feces and milk ...
... common cause of cancer in cats, it may cause various blood disorders and it may lead to a state of immune deficiency that hinders the cat’s ability to protect itself against other infections. The virus is shed in very high quantities in saliva and nasal secretions, but also in urine, feces and milk ...
Viruses
... 2. Penetration (injection) of viral DNA or RNA 3. Virus reprograms host to copy viral DNA and make viral proteins 4. New viruses assemble and mature 5. Cell lyses (bursts) and releases the new viruses to attack other cells 6. Results in death of the host cell ...
... 2. Penetration (injection) of viral DNA or RNA 3. Virus reprograms host to copy viral DNA and make viral proteins 4. New viruses assemble and mature 5. Cell lyses (bursts) and releases the new viruses to attack other cells 6. Results in death of the host cell ...
Virus quantification

Virus quantification involves counting the number of viruses in a specific volume to determine the virus concentration. It is utilized in both research and development (R&D) in commercial and academic laboratories as well as production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable. For example, the production of viral vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually adapt and monitor the process in order to optimize production yields and respond to ever changing demands and applications. Examples of specific instances where known viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization and adaptation of methods to cell culture. This page discusses various techniques currently used to quantify viruses in liquid samples. These methods are separated into two categories, traditional vs. modern methods. Traditional methods are industry-standard methods that have been used for decades but are generally slow and labor-intensive. Modern methods are relatively new commercially available products and kits that greatly reduce quantification time. This is not meant to be an exhaustive review of all potential methods, but rather a representative cross-section of traditional methods and new, commercially available methods. While other published methods may exist for virus quantification, non-commercial methods are not discussed here.