Module 6 Exam Review 1. Compared to eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic
... 32. Organisms that commonly live in or on the body and are usually not pathogenic are part of the body’s ___ ___. normal flora 33. Pathogenicity is the organism’s ability to ________________. cause disease 34. Virulence would be described as _________________________. the severity of disease 35. Hya ...
... 32. Organisms that commonly live in or on the body and are usually not pathogenic are part of the body’s ___ ___. normal flora 33. Pathogenicity is the organism’s ability to ________________. cause disease 34. Virulence would be described as _________________________. the severity of disease 35. Hya ...
Characteristics of pathogenic bacteria
... variety of lifestyles. Some of them are free living, not requiring other organisms for their survival, and existing in everything from the soil and fresh water to extreme environments such as deep ocean volcanic vents and radioactive waste, for example. Some bacteria can be beneficial to other organ ...
... variety of lifestyles. Some of them are free living, not requiring other organisms for their survival, and existing in everything from the soil and fresh water to extreme environments such as deep ocean volcanic vents and radioactive waste, for example. Some bacteria can be beneficial to other organ ...
Abstract Actinobacteria are important members of the soil
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
Nessun titolo diapositiva
... maximun bacterial exposition at the MIPSSZEOMET® = 2107UFC after 20’ aerozolitation at a rate of 0,1 ml/min. resulted in no bacterial leakage/carry over from the filter. This level of exposition far exceeds that normally expected in refrigerators and is actually comparable to the bacterial concentr ...
... maximun bacterial exposition at the MIPSSZEOMET® = 2107UFC after 20’ aerozolitation at a rate of 0,1 ml/min. resulted in no bacterial leakage/carry over from the filter. This level of exposition far exceeds that normally expected in refrigerators and is actually comparable to the bacterial concentr ...
bacteria
... This term is used to describe the lack of a nucleus in a bacterium cell. • microscopic: until they multiple into millions to form a colony which is visible by the human eye • found everywhere: soil, food, plants, animals • require water, food, and a place to live • classified in either the Kingdom E ...
... This term is used to describe the lack of a nucleus in a bacterium cell. • microscopic: until they multiple into millions to form a colony which is visible by the human eye • found everywhere: soil, food, plants, animals • require water, food, and a place to live • classified in either the Kingdom E ...
Notes: Bacteria and Viruses
... A. Characteristics of prokaryotes (bacteria cells) 1. single celled 2. no nucleus 3. smallest and most common organisms 4. microscopic B. How to identify prokaryotes: 1. Shape a. bacillus – rod shaped b. cocci – spherical shaped c. spirilla – spiral shaped 2. Movement (motility) a. Structure that al ...
... A. Characteristics of prokaryotes (bacteria cells) 1. single celled 2. no nucleus 3. smallest and most common organisms 4. microscopic B. How to identify prokaryotes: 1. Shape a. bacillus – rod shaped b. cocci – spherical shaped c. spirilla – spiral shaped 2. Movement (motility) a. Structure that al ...
File
... 20. The optimum pH for the growth of molds and yeast is *c. 5-6 21. During conjunction, the genetic material will be transferred through *c. sex pili 22. Which of these is a type of mutation? *e. Base substitution 23. Gram positive cells have a *b. multiple layer of peptidoglycan that helps to retai ...
... 20. The optimum pH for the growth of molds and yeast is *c. 5-6 21. During conjunction, the genetic material will be transferred through *c. sex pili 22. Which of these is a type of mutation? *e. Base substitution 23. Gram positive cells have a *b. multiple layer of peptidoglycan that helps to retai ...
Bacteria
... the cell membranes of some Gram-negative bacteria, that are poisonous. They are released when the bacteria die. ...
... the cell membranes of some Gram-negative bacteria, that are poisonous. They are released when the bacteria die. ...
Name
... Many bacteria are also able to exchange genetic information by a process called conjugation. During conjugation, a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and genes move from one cell to the other. This transfer of genetic information increases genetic diversity in populations of bacteria. ...
... Many bacteria are also able to exchange genetic information by a process called conjugation. During conjugation, a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and genes move from one cell to the other. This transfer of genetic information increases genetic diversity in populations of bacteria. ...
Bacteria and Germs
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
... – Pathogens – microbes that cause disease • Botulism – improperly canned foods • E. coli – improperly cooked beef • Salmonella – improperly cooked chicken ...
Micro Ch 3 Study Guide
... Know the types of membranous sacs used by eukaryotic cells What types of things have a cell wall The fluid mosaic model is not a representative model of which type of organism What can viruses do outside of a host cell This is the name given to a cytoplasmic membrane that allows some substances in a ...
... Know the types of membranous sacs used by eukaryotic cells What types of things have a cell wall The fluid mosaic model is not a representative model of which type of organism What can viruses do outside of a host cell This is the name given to a cytoplasmic membrane that allows some substances in a ...
WISTR Content Teaching Goals: Microbial Life
... 7. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually or clonally (simple cell division) but have many unique ways of assuring new genetic combinations, including gene sharing between cells. 8. Prokaryotes are extremely diverse metabolically. Prokaryotes can live without oxygen in a variety of ways, can live at temper ...
... 7. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually or clonally (simple cell division) but have many unique ways of assuring new genetic combinations, including gene sharing between cells. 8. Prokaryotes are extremely diverse metabolically. Prokaryotes can live without oxygen in a variety of ways, can live at temper ...
Bacteria
... Pictured to the right is a _____________. There are 3 main components to a __________. They are:________, ________, & _________. They appear in 4 main styles, or structures. They are: ...
... Pictured to the right is a _____________. There are 3 main components to a __________. They are:________, ________, & _________. They appear in 4 main styles, or structures. They are: ...
Life in a different time frame
... It has the ability to react to the reintroduction small amounts of nutrients that results in the almost immediate conversion of dormant back to an actively growing cell ...
... It has the ability to react to the reintroduction small amounts of nutrients that results in the almost immediate conversion of dormant back to an actively growing cell ...
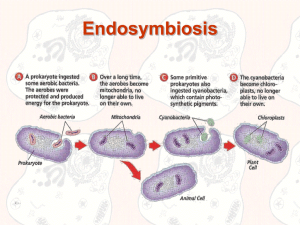
Endosymbiosis - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • New mitochondria and chloroplasts are formed only through a process similar to binary fission. • Much of the internal structure and biochemistry of chloroplasts, for instance the presence of thylakoids and particular chlorophylls, is very similar to that of cyanobacteria. ...
... • New mitochondria and chloroplasts are formed only through a process similar to binary fission. • Much of the internal structure and biochemistry of chloroplasts, for instance the presence of thylakoids and particular chlorophylls, is very similar to that of cyanobacteria. ...
Bacteria in your life HW
... 8. The textbook mentions that many bacteria that produce toxins are able to produce thick walls around their cells. What are these called and why is this a helpful adaptation for the bacteria? ...
... 8. The textbook mentions that many bacteria that produce toxins are able to produce thick walls around their cells. What are these called and why is this a helpful adaptation for the bacteria? ...
Bacteria - LiveText
... 2) exotoxin - secreted by living bacterial cell into surrounding environment (host) - usually Gram-positive ...
... 2) exotoxin - secreted by living bacterial cell into surrounding environment (host) - usually Gram-positive ...
Microbiology Primer
... These are, in fact, incomplete shreds of protein whose origin are unknown. They can insert themselves into the genetic code of healthy cells. ...
... These are, in fact, incomplete shreds of protein whose origin are unknown. They can insert themselves into the genetic code of healthy cells. ...