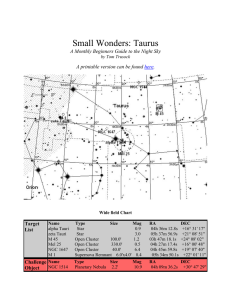
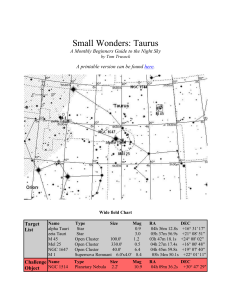
The Magnitude Scale
... are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star Catalogue), and the planet Venus varies in brightness generally from magnitude -4.5 to -3.7. Note that a comet of magnitude 5 will not be a ...
... are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star Catalogue), and the planet Venus varies in brightness generally from magnitude -4.5 to -3.7. Note that a comet of magnitude 5 will not be a ...
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... As to the naked eye sightings of lage numbers of the Pleiades, what may complicate the matter is the debate over the visibility of the nebulosity that runs throughout M45. Some say it's easily visible, others think it's not and what people are actually seeing and taking for nebulosity is the light o ...
... As to the naked eye sightings of lage numbers of the Pleiades, what may complicate the matter is the debate over the visibility of the nebulosity that runs throughout M45. Some say it's easily visible, others think it's not and what people are actually seeing and taking for nebulosity is the light o ...
Warm-Up Monday, July 23, 2012
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
Astronomy 12: Introduction to Astronomy
... c. The separation of the hydrogen envelope to form a planetary nebula. d. The formation of helium by fusing hydrogen together. 4. When a star’s gravitational force pulling inwards and its internal pressure pushing outward are balanced, it is considered to be in what? a. Hydrostatic equilibrium b. Su ...
... c. The separation of the hydrogen envelope to form a planetary nebula. d. The formation of helium by fusing hydrogen together. 4. When a star’s gravitational force pulling inwards and its internal pressure pushing outward are balanced, it is considered to be in what? a. Hydrostatic equilibrium b. Su ...
Celestial Objects
... name. They usually represent mythological gods, people, animals, or objects. An example of a constellation is Orion, the hunter 24. ...
... name. They usually represent mythological gods, people, animals, or objects. An example of a constellation is Orion, the hunter 24. ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive s ...
... massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive s ...
Life Histories Stars
... massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive s ...
... massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of the universe? What’s Going On? In this activity, you can see that the very massive s ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why is that? Large stars, like all stars, form inside giant gaseous nebulae. An example of such a nebula is the Great Nebula in Orion (see photo). Inside nebulae, particle ...
... In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why is that? Large stars, like all stars, form inside giant gaseous nebulae. An example of such a nebula is the Great Nebula in Orion (see photo). Inside nebulae, particle ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... A Star is a “self-luminous” (it is giving off light as opposed to reflecting it) sphere of gas that is undergoing Nuclear Fusion in its center. ...
... A Star is a “self-luminous” (it is giving off light as opposed to reflecting it) sphere of gas that is undergoing Nuclear Fusion in its center. ...
15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda galaxy, have a bulge at the center and spiral arms. The spiral arms are made up of gas, dust, and new stars that have formed. The galaxy in which we live is a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way. The Milky Way consists of about 200 billion stars, including the s ...
... Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda galaxy, have a bulge at the center and spiral arms. The spiral arms are made up of gas, dust, and new stars that have formed. The galaxy in which we live is a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way. The Milky Way consists of about 200 billion stars, including the s ...
RTFS Test - 2017 BCS Cobra
... 30. This DSO belongs to a constellation which is shaped like one or more letters of the alphabet. Name the letter. 31. What does light green area in the model represent (include the element)? 32. What do the purple ...
... 30. This DSO belongs to a constellation which is shaped like one or more letters of the alphabet. Name the letter. 31. What does light green area in the model represent (include the element)? 32. What do the purple ...
Seating Chart for Wednesday PHOTO ID REQUIRED! SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW!
... • So light falls back. • “Schwarzschild radius” or “event horizon” = radius around mass concentration within which light can no longer escape to outside. ...
... • So light falls back. • “Schwarzschild radius” or “event horizon” = radius around mass concentration within which light can no longer escape to outside. ...
Star Show FACILITATOR NOTES
... closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filaments operate at a lower temperature (around 2500°C) which gives a more reddish-orange color ...
... closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filaments operate at a lower temperature (around 2500°C) which gives a more reddish-orange color ...
The First Stars - Amazon Web Services
... Exploding stars In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their ...
... Exploding stars In the century that followed, astronomers measured the masses of many stars, typically by using the orbits in binary systems, and confirmed Eddington’s reasoning. The smaller balls of gas make the planets. The massive stars explode, after exhausting their nuclear fuel, because their ...
30galaxies and the universe
... instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s birth, but instead evolve with the galaxy by trapping an amazingly exact percentage (0.2) of the mass ...
... instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s birth, but instead evolve with the galaxy by trapping an amazingly exact percentage (0.2) of the mass ...
Test 2, November 14, 2016 - Physics@Brock
... Date of Examination: November 14, 2014 Time of Examination: 17:00–17:50 ...
... Date of Examination: November 14, 2014 Time of Examination: 17:00–17:50 ...
eta carinae – nature`s own hadron collider
... ETA CARINAE IS ONE OF THE MOST MASSIVE STARS KNOWN. IT IS AROUND 100 SOLAR MASSES. THE UPPER LIMIT OF STAR SIZE IS THOUGHT TO BE AROUND 150 SOLAR MASSES. BECAUSE OF ITS SIZE, AND THE HIGH ENERGIES PRODUCED BECAUSE OF GRAVITY, IT IS UNSTABLE. ...
... ETA CARINAE IS ONE OF THE MOST MASSIVE STARS KNOWN. IT IS AROUND 100 SOLAR MASSES. THE UPPER LIMIT OF STAR SIZE IS THOUGHT TO BE AROUND 150 SOLAR MASSES. BECAUSE OF ITS SIZE, AND THE HIGH ENERGIES PRODUCED BECAUSE OF GRAVITY, IT IS UNSTABLE. ...
Name - MIT
... Name____________________________________ ID #__________________________ No notes, No books; 1) The planet Mars never passes through which of these constellations as seen from Earth? A) Virgo B) Capricorn C) Leo D) Ursa Minor E) Aquarius 2) Which of these planets takes the shortest time to travel one ...
... Name____________________________________ ID #__________________________ No notes, No books; 1) The planet Mars never passes through which of these constellations as seen from Earth? A) Virgo B) Capricorn C) Leo D) Ursa Minor E) Aquarius 2) Which of these planets takes the shortest time to travel one ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.