Types of Stars http://space.about.com/od/stars/tp/What-Are
... star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to each other. They orbit around a common point, called the center of mass. It is estimated that about half of all the stars in our galaxy are part of a binary system. Visual binaries can be seen as two separate stars through a telescope. ...
... star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to each other. They orbit around a common point, called the center of mass. It is estimated that about half of all the stars in our galaxy are part of a binary system. Visual binaries can be seen as two separate stars through a telescope. ...
Planets and Stars Key Vocabulary: Comparing and Contrasting
... How can technology be used to observe distant objects in the sky? Technological resources, such as telescopes and space probes, are used to observe distant objects in the sky. Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of star ...
... How can technology be used to observe distant objects in the sky? Technological resources, such as telescopes and space probes, are used to observe distant objects in the sky. Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of star ...
Exercise 8
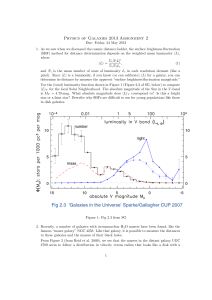
... How accurate were you? Is the criterion or criteria you used a good way to find galaxy distances? ...
... How accurate were you? Is the criterion or criteria you used a good way to find galaxy distances? ...
Stella Finger Prints
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
Astronomy 1020 Exam 4 Review Questions
... 19. What would the mass of a black hole be if its Schwarzschild radius was the same radius as the Sun? 20. What 3 observational characteristics do the best black hole candidates possess? What are the 4 best black hole candidates that have been observed? Of these 4, which is the best stellar black ho ...
... 19. What would the mass of a black hole be if its Schwarzschild radius was the same radius as the Sun? 20. What 3 observational characteristics do the best black hole candidates possess? What are the 4 best black hole candidates that have been observed? Of these 4, which is the best stellar black ho ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... structure of the Milky Way. 1. The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) extends much further than previously thought. The disk of the Milky Way extends further is a clear possibility and is supported by evidence of the newly discovered Outer Arm extension of the Cygnus Arm. 2. With the discovery of the Sagittariu ...
... structure of the Milky Way. 1. The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) extends much further than previously thought. The disk of the Milky Way extends further is a clear possibility and is supported by evidence of the newly discovered Outer Arm extension of the Cygnus Arm. 2. With the discovery of the Sagittariu ...
Lab 2
... 12. Draw the location of the Sun as accurately as possible on figure 3. 13. Two students are discussing their answers to the question “Figure 4 shows the same view of the sky one month later on January 1. Draw the location of the Sun as accurately as possible on figure 4.” Student 1 (Davey): The Sun ...
... 12. Draw the location of the Sun as accurately as possible on figure 3. 13. Two students are discussing their answers to the question “Figure 4 shows the same view of the sky one month later on January 1. Draw the location of the Sun as accurately as possible on figure 4.” Student 1 (Davey): The Sun ...
6 - In the Beginning: Science and Genesis 1-11
... Seven of the eight planets of our solar system follow highly circular orbits, despite the fact that NASA must plan with great precision to put a satellite into a nearly circular orbit and have difficulty keeping it there very long. Modern theories predict our planets should have developed abnormali ...
... Seven of the eight planets of our solar system follow highly circular orbits, despite the fact that NASA must plan with great precision to put a satellite into a nearly circular orbit and have difficulty keeping it there very long. Modern theories predict our planets should have developed abnormali ...
The Stars of Namaqualand
... Saturn is the second largest planet after Jupiter and it has 30 moons. You can find Saturn with the naked eyes. It’s visible 10 month out of the year. Saturn is very far away from the Earth, so you can’t see all of the moons. With a telescope you can see 5 of the moons (Tethys, Dione, Rhea, Titan, I ...
... Saturn is the second largest planet after Jupiter and it has 30 moons. You can find Saturn with the naked eyes. It’s visible 10 month out of the year. Saturn is very far away from the Earth, so you can’t see all of the moons. With a telescope you can see 5 of the moons (Tethys, Dione, Rhea, Titan, I ...
mars, antares, the sting and more
... TO FIND THE SCORPION, LOOK JUST ABOVE THE HORIZON FOR STARS THAT FORM A FISHHOOK SHAPE. IT'S A LITTLE TOUGHER TO SEE THE DISTINCT OUTLINE OF THE CONSTELLATION SINCE THERE ARE TWO VISITING PLANETS AMONG THE NORMAL STARS OF THE SCORPION. BUT BE PATIENT, WE'LL GET TO THOSE SOON ENOUGH. JAMES: IT MAY BE ...
... TO FIND THE SCORPION, LOOK JUST ABOVE THE HORIZON FOR STARS THAT FORM A FISHHOOK SHAPE. IT'S A LITTLE TOUGHER TO SEE THE DISTINCT OUTLINE OF THE CONSTELLATION SINCE THERE ARE TWO VISITING PLANETS AMONG THE NORMAL STARS OF THE SCORPION. BUT BE PATIENT, WE'LL GET TO THOSE SOON ENOUGH. JAMES: IT MAY BE ...
The Kunlun Infrared Sky Survey
... Race is now on to distinguish Einstein vacuum energy from other possible equations of state. Requires accumulation of hundreds of accurate SNIa measurements. SkyMapper (Schmidt et al. 2005) is devoted to this. ...
... Race is now on to distinguish Einstein vacuum energy from other possible equations of state. Requires accumulation of hundreds of accurate SNIa measurements. SkyMapper (Schmidt et al. 2005) is devoted to this. ...
Measuring the Distance to Stars Using Parallax
... The astronomer Friedrich Bessel used the exact method you used to measure the height of the flagpole to find the distance to a nearby star, 61 Cygni, in 1838. This was a monumental achievement that came about due to technological improvements in telescopes that gave humans their first realistic glim ...
... The astronomer Friedrich Bessel used the exact method you used to measure the height of the flagpole to find the distance to a nearby star, 61 Cygni, in 1838. This was a monumental achievement that came about due to technological improvements in telescopes that gave humans their first realistic glim ...
ExoplanetWorksheet
... *There are two ways to plot the data on each axis (linear and logarithmic). For ‘planet mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. ...
... *There are two ways to plot the data on each axis (linear and logarithmic). For ‘planet mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... (b) False. 19. Chandrasekhar’s limit is (a) the maximum radius of a red giant. (b) the radius within which an object must shrink to become a black hole. (c) the maximum mass of a body composed of degenerate matter. (d) the minimum mass of a body composed of degenerate matter. 20. The maximum mass th ...
... (b) False. 19. Chandrasekhar’s limit is (a) the maximum radius of a red giant. (b) the radius within which an object must shrink to become a black hole. (c) the maximum mass of a body composed of degenerate matter. (d) the minimum mass of a body composed of degenerate matter. 20. The maximum mass th ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 1-4
... night sky during summer (in the Southern Hemisphere). It is a constellation that contains two famous deep sky wonders – the Orion Nebula and the Horsehead Nebula, and two supergiant stars – Betelgeuse and Rigel. In the Southern Hemisphere, Orion the Hunter appears to be upside down, as are many cons ...
... night sky during summer (in the Southern Hemisphere). It is a constellation that contains two famous deep sky wonders – the Orion Nebula and the Horsehead Nebula, and two supergiant stars – Betelgeuse and Rigel. In the Southern Hemisphere, Orion the Hunter appears to be upside down, as are many cons ...
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
... stars having larger magnitudes. Don’t confuse the relative magnitude with absolute magnitude. The relative magnitude measures the brightness of a star as it appears in the sky and it depends on the brightness and on the distance; if we put a star at the distance of 10 Parsec (33 year light), its mag ...
Review for Exam I PHYS 1050
... • circumference of circle = 2 x radius • area of circle = r2 • astronomical unit = 1 AU = 150 x 106 km = average distance from Earth to Sun • speed of light = 300,000 km/sec • light year = 1 LY = distance light travels in one year • distance = speed x time ...
... • circumference of circle = 2 x radius • area of circle = r2 • astronomical unit = 1 AU = 150 x 106 km = average distance from Earth to Sun • speed of light = 300,000 km/sec • light year = 1 LY = distance light travels in one year • distance = speed x time ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.