Astronomy 21 – Test 2 – Answers
... cannot see this light with your eyes (unless it is silhouetted against brighter background regions) – how could you “observe” dark clouds nevertheless? What is the astrophysical process that gives rise to that “invisible” light? There are at least two options, you only need to mention one for full c ...
... cannot see this light with your eyes (unless it is silhouetted against brighter background regions) – how could you “observe” dark clouds nevertheless? What is the astrophysical process that gives rise to that “invisible” light? There are at least two options, you only need to mention one for full c ...
April 2016
... after the Big Bang, and the hot radiation from young stars doesn't ionize the majority of the universe until 550 million years have passed. In most directions, this galaxy would be invisible, as the neutral gas would block this light, the same way the light from the center of our galaxy is blocked b ...
... after the Big Bang, and the hot radiation from young stars doesn't ionize the majority of the universe until 550 million years have passed. In most directions, this galaxy would be invisible, as the neutral gas would block this light, the same way the light from the center of our galaxy is blocked b ...
No Slide Title
... community of European astronomers interested in making use of observations in the ultraviolet regime. Such structuring is necessary to ensure that the capability to study the planets and the Universe in this important spectral region is sustained over the next decades. NUVA will bring together inter ...
... community of European astronomers interested in making use of observations in the ultraviolet regime. Such structuring is necessary to ensure that the capability to study the planets and the Universe in this important spectral region is sustained over the next decades. NUVA will bring together inter ...
Folie 1 - univie.ac.at
... representing objects which dominate the ecology of our Universe, and also highly evolved giant stars of lower mass to probe the future development of our Sun. The operation policy will be to observe a few fields over a long time span and possibly some short runs in between, which will assure optimum ...
... representing objects which dominate the ecology of our Universe, and also highly evolved giant stars of lower mass to probe the future development of our Sun. The operation policy will be to observe a few fields over a long time span and possibly some short runs in between, which will assure optimum ...
Return both exam and scantron sheet when you
... 17. The luminosity of quasar X varies with a period of one day and the luminosity of quasar Y varies with the period of one week. Which quasar has the smaller active region? (a) Quasar X. (b) Quasar Y. (c) [No conclusion can be made.] 18. White dwarfs will stop emitting light in a distant future. (a ...
... 17. The luminosity of quasar X varies with a period of one day and the luminosity of quasar Y varies with the period of one week. Which quasar has the smaller active region? (a) Quasar X. (b) Quasar Y. (c) [No conclusion can be made.] 18. White dwarfs will stop emitting light in a distant future. (a ...
Deep O/IR Survey Of Chandra Galactic Bulge Fields
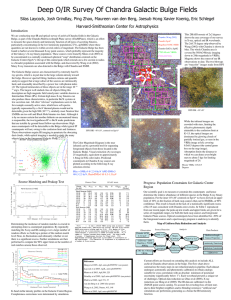
... =0. The typical luminosities of these objects are in the range 10 3133 erg/s. The largest well studied class of objects fitting this description are high magnetic field cataclysmic variables known as Intermediate Polars (IPs). Certain high mass X-ray binaries can also produce these characteristics, ...
... =0. The typical luminosities of these objects are in the range 10 3133 erg/s. The largest well studied class of objects fitting this description are high magnetic field cataclysmic variables known as Intermediate Polars (IPs). Certain high mass X-ray binaries can also produce these characteristics, ...
Supernovae – the biggest bangs since the Big Bang
... (also known as a “Type Ia supernova”). Imagine you made a series of bombs, each with the same amount of the same material. The bombs would all have about the same power, right? The same is true of white dwarf supernovae. If each one is the explosion of 1.4 solar masses of mostly carbon and oxygen ...
... (also known as a “Type Ia supernova”). Imagine you made a series of bombs, each with the same amount of the same material. The bombs would all have about the same power, right? The same is true of white dwarf supernovae. If each one is the explosion of 1.4 solar masses of mostly carbon and oxygen ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... In the first decades of the twentieth century, the work of Edwin Hubble and others led to newer techniques for determining the distances of some of the nebulae20. It turns out that some of these nebulae were far too distant to be within our Milky way. Thus, they were shown to be distinct from and in ...
... In the first decades of the twentieth century, the work of Edwin Hubble and others led to newer techniques for determining the distances of some of the nebulae20. It turns out that some of these nebulae were far too distant to be within our Milky way. Thus, they were shown to be distinct from and in ...
Burgess_final - University of Hertfordshire
... The dwarfs were found in a star forming region named IC 348, which lies almost 1000 light years from the Solar System towards the constellation of Perseus. This cluster is approximately 3 million years old – extremely young compared to our 4.5 billion year old Sun – which makes it a good location in ...
... The dwarfs were found in a star forming region named IC 348, which lies almost 1000 light years from the Solar System towards the constellation of Perseus. This cluster is approximately 3 million years old – extremely young compared to our 4.5 billion year old Sun – which makes it a good location in ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... A. Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. B. Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. C. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
... A. Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. B. Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. C. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
the curious incident of the dog in the night-time
... In the book, Christopher mentions (p.10) the scenario that our Universe will one day collapse after it has reached its maximum expansion radius. In fact, there are three basic scenarios for the future of the Universe: (i) collapsing, as Christopher suggests is like a ball tossed up with moderate spe ...
... In the book, Christopher mentions (p.10) the scenario that our Universe will one day collapse after it has reached its maximum expansion radius. In fact, there are three basic scenarios for the future of the Universe: (i) collapsing, as Christopher suggests is like a ball tossed up with moderate spe ...
Stars and Galaxies
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
... 24. Astronomers use spectrographs to study the ___________________ of stars to identify properties of stars. 25. Spectrographs break ______________________ into its component colors. 26. Dark lines are in the spectrum of a star. 27. The dark lines are caused by _____________________ in the star’s at ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL: 100 marks Section A Please
... explains this observation? (a) It is rotating too slowly. (b) Radioactive elements were never abundant on the Moon. (c) It is too small. (d) The crust is too thin. (e) It does not have water on its surface. ...
... explains this observation? (a) It is rotating too slowly. (b) Radioactive elements were never abundant on the Moon. (c) It is too small. (d) The crust is too thin. (e) It does not have water on its surface. ...
After Dark M S
... both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binary star system. The discovery and origins of these two exploding stars, more than 20 mi ...
... both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binary star system. The discovery and origins of these two exploding stars, more than 20 mi ...
Colonization of the Milky Way The distances between the stars are
... You may object that I have surely left out important considerations. Two obvious ones are: • We’ve emphasized that if rocky planets are needed for life to develop, heavy elements are essential. Perhaps it is only now that these elements are in sufficient abundance, so much more ancient civilizations ...
... You may object that I have surely left out important considerations. Two obvious ones are: • We’ve emphasized that if rocky planets are needed for life to develop, heavy elements are essential. Perhaps it is only now that these elements are in sufficient abundance, so much more ancient civilizations ...
ASTRONOMY 0089: EXAM 1 Class Meets M,W,F, 1:00 PM Feb 12
... d. Only in directions 180 degrees away from the Sun. e. All over. 31. If you are standing at the North Pole which of the following statements is true? a. As the seasons change you are able to see all locations on the celestial sphere. b. At the beginning of Winter the Sun is above the horizon for at ...
... d. Only in directions 180 degrees away from the Sun. e. All over. 31. If you are standing at the North Pole which of the following statements is true? a. As the seasons change you are able to see all locations on the celestial sphere. b. At the beginning of Winter the Sun is above the horizon for at ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... – Same stuff as with eyes and Binoculars, but…. – Now you will be able to see objects up to 100’s of times more faint – Ability to see fine detail (resolution) ...
... – Same stuff as with eyes and Binoculars, but…. – Now you will be able to see objects up to 100’s of times more faint – Ability to see fine detail (resolution) ...
Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies
... The Distribution of Galaxies in Space There are three spirals in this group – the Milky Way, Andromeda, and M33. These and their satellites – about 45 galaxies in all – form the Local Group. Such a group of galaxies, held together by its own gravity, is called a galaxy cluster. ...
... The Distribution of Galaxies in Space There are three spirals in this group – the Milky Way, Andromeda, and M33. These and their satellites – about 45 galaxies in all – form the Local Group. Such a group of galaxies, held together by its own gravity, is called a galaxy cluster. ...
Answer titese questions on a piece of loose leaf paper.
... to measure distances to nearby stars. Qiini: Think about the thumb demo we didin class.) I I . The Hcrczspiung-Russcll diagram shows the relationship between wliai two charaeteiistios of stars? 12- More than 90% of all stars arc cotisiderx;d stars and can be found in a diagonal path aaoss the center ...
... to measure distances to nearby stars. Qiini: Think about the thumb demo we didin class.) I I . The Hcrczspiung-Russcll diagram shows the relationship between wliai two charaeteiistios of stars? 12- More than 90% of all stars arc cotisiderx;d stars and can be found in a diagonal path aaoss the center ...
Build your own Galaxy - McDonald Observatory
... Stars: glitter. The hottest and brightest stars are blue and white. But these stars live short lives — only ten million to a few hundred million years — and spend their whole lives close to where they were born in the spiral arms. Older stars found in the bulge and disk may be yellow, like the Sun, ...
... Stars: glitter. The hottest and brightest stars are blue and white. But these stars live short lives — only ten million to a few hundred million years — and spend their whole lives close to where they were born in the spiral arms. Older stars found in the bulge and disk may be yellow, like the Sun, ...
$doc.title
... interstellar gas that fills the dwarf galaxies in which the supernovae reside, and revealing each galaxy's composition. Once an observed supernova fades a couple of months later, astronomers can directly stud ...
... interstellar gas that fills the dwarf galaxies in which the supernovae reside, and revealing each galaxy's composition. Once an observed supernova fades a couple of months later, astronomers can directly stud ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.