(Real) Time Machine Demonstration Manual
... The radar gun compares the shift in reflected light from a moving object to the original light that first left the radar gun. The difference is recorded in miles per hour. This is similar to what astronomers do when looking at light from stars. ...
... The radar gun compares the shift in reflected light from a moving object to the original light that first left the radar gun. The difference is recorded in miles per hour. This is similar to what astronomers do when looking at light from stars. ...
Is Draco II one of the faintest dwarf galaxies? First study from Keck
... Observations were taken following our usual routine (e.g., Martin et al. 2014) for a total of 3,600s, split into three 1,200s sub-exposures, under good conditions (50% humidity, 0.7′′ seeing). We further observed NeArKrXe calibrations through the slit mask after the science frames at the same locati ...
... Observations were taken following our usual routine (e.g., Martin et al. 2014) for a total of 3,600s, split into three 1,200s sub-exposures, under good conditions (50% humidity, 0.7′′ seeing). We further observed NeArKrXe calibrations through the slit mask after the science frames at the same locati ...
Spectroscopy and Spectrophotometry
... again (perpendicularly) using an echelle gra@ng. The echelle creates a spectrum at high order (m ~ 50). At such high m, we have overlapping of neighboring orders. The CCD image then consists of ~50 ver@cally displaced orders. The spectral range is thus increased by a factor of ~50 from before. ...
... again (perpendicularly) using an echelle gra@ng. The echelle creates a spectrum at high order (m ~ 50). At such high m, we have overlapping of neighboring orders. The CCD image then consists of ~50 ver@cally displaced orders. The spectral range is thus increased by a factor of ~50 from before. ...
Module1: Scale of the Universe
... starlight&is&refracted&by&Earth's&atmosphere&and&causes&the&star&to&appear&blurred.& Determining&the&position&of&a&star,&plus&that&of&several&reference&stars&in&the&same& Bield,&to&a&very&small&fraction&of&this&blurry&dot&is¬&an&easy&task.&& All&stars&in&a&Bield&exhibit¶llax.&& In&practice,&a ...
... starlight&is&refracted&by&Earth's&atmosphere&and&causes&the&star&to&appear&blurred.& Determining&the&position&of&a&star,&plus&that&of&several&reference&stars&in&the&same& Bield,&to&a&very&small&fraction&of&this&blurry&dot&is¬&an&easy&task.&& All&stars&in&a&Bield&exhibit¶llax.&& In&practice,&a ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... We shall use this information later to see how one estimates the star formation history of a galaxy and the universe ...
... We shall use this information later to see how one estimates the star formation history of a galaxy and the universe ...
Big Bang Theory
... “nebulae” and determined that these objects were located far outside the Milky Way. This confirmed that these “nebulae” were in fact other galaxies much like our own Milky Way. In 1912 another American astronomer, Vesto Slipher, analyzed spectrographs of galaxies and measured their redshift. Hubble ...
... “nebulae” and determined that these objects were located far outside the Milky Way. This confirmed that these “nebulae” were in fact other galaxies much like our own Milky Way. In 1912 another American astronomer, Vesto Slipher, analyzed spectrographs of galaxies and measured their redshift. Hubble ...
SMMP_BISANA - Infinity and Beyond
... constellations were not associated with any particular myth, hero, or god. They were instead known simply as the objects or animals which they represented--the Lyre, for instance, or the Ram. By the 5th century B.C., however, most of the constellations had come to be associated with myths, and the C ...
... constellations were not associated with any particular myth, hero, or god. They were instead known simply as the objects or animals which they represented--the Lyre, for instance, or the Ram. By the 5th century B.C., however, most of the constellations had come to be associated with myths, and the C ...
sections 7-8 instructor notes
... The primary opacity source in the atmospheres of B and A-type stars is atomic hydrogen, which makes its presence obvious in the flux distributions of such stars with discrete discontinuities in the stellar continua at λ912Å (the Lyman discontinuity), λ3647Å (the Balmer discontinuity), and λ8206Å (t ...
... The primary opacity source in the atmospheres of B and A-type stars is atomic hydrogen, which makes its presence obvious in the flux distributions of such stars with discrete discontinuities in the stellar continua at λ912Å (the Lyman discontinuity), λ3647Å (the Balmer discontinuity), and λ8206Å (t ...
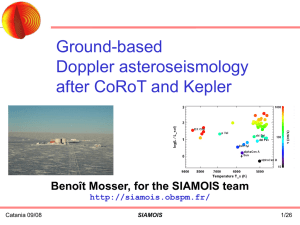
targets - siamois
... What do we need after CoRoT, that Kepler, and hopefully PLATO, will not provide? Doppler velocity (Space-borne observations are photometric) ...
... What do we need after CoRoT, that Kepler, and hopefully PLATO, will not provide? Doppler velocity (Space-borne observations are photometric) ...
Chapter 16 - Astronomy
... formed. When we look at a spiral galaxy, the arms are obvious to us because they are the areas containing the bright stars. 6. One problem with the density wave theory is the question of how the density wave is sustained through the life of the galaxy. Also, observations of the Whirlpool Galaxy show ...
... formed. When we look at a spiral galaxy, the arms are obvious to us because they are the areas containing the bright stars. 6. One problem with the density wave theory is the question of how the density wave is sustained through the life of the galaxy. Also, observations of the Whirlpool Galaxy show ...
Astronomical Facts `n Stuff
... Any optical defect and/or design error which causes any of the processed light to deviate from reaching the focal point, therefore reducing the quality of the image. Aberration of Starlight The apparent displacement of a star's position as a consequence of Earth's motion through space and the finite ...
... Any optical defect and/or design error which causes any of the processed light to deviate from reaching the focal point, therefore reducing the quality of the image. Aberration of Starlight The apparent displacement of a star's position as a consequence of Earth's motion through space and the finite ...
Supernova! Toledo Astronomical Association, February 2009
... In just a few weeks, a supernova can give off as much energy as the sun in it’s entire lifetime RARE On average, only one every 50 years in the entire Milky Way FAST Up to 3% of the speed of light ...
... In just a few weeks, a supernova can give off as much energy as the sun in it’s entire lifetime RARE On average, only one every 50 years in the entire Milky Way FAST Up to 3% of the speed of light ...
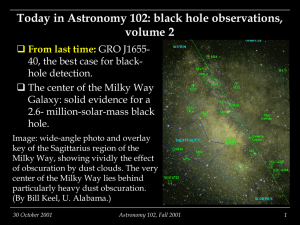
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... Rotational motion and the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A West The center of the Milky Way is obscured by dust; it cannot be seen at visible through longer X-ray wavelengths. It is bright at infrared and radio wavelengths, and hard (shortwavelength) X rays, which are transmitted through th ...
... Rotational motion and the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A West The center of the Milky Way is obscured by dust; it cannot be seen at visible through longer X-ray wavelengths. It is bright at infrared and radio wavelengths, and hard (shortwavelength) X rays, which are transmitted through th ...
The cosmological significance of high
... investigations of its stellar content. The H I mass of the cloud is 2.0 × 107 (d/27 kpc)2 M⊙ , making Complex H one of the most massive HVCs if its distance is more than ∼ 20 kpc. Virtually all similar H I clouds in other galaxy groups are associated with low surface brightness dwarf galaxies. We se ...
... investigations of its stellar content. The H I mass of the cloud is 2.0 × 107 (d/27 kpc)2 M⊙ , making Complex H one of the most massive HVCs if its distance is more than ∼ 20 kpc. Virtually all similar H I clouds in other galaxy groups are associated with low surface brightness dwarf galaxies. We se ...
Distances in Cosmology One of the most basic measurements that
... direction appears to change, by an amount that is inversely proportional to its distance from the viewing points. This is one of the ways we obtain depth perception; looking out with first one eye, then the other, shows that close things appear to move more than distant things. If you know the dista ...
... direction appears to change, by an amount that is inversely proportional to its distance from the viewing points. This is one of the ways we obtain depth perception; looking out with first one eye, then the other, shows that close things appear to move more than distant things. If you know the dista ...
MICROQUASARS
... Particle energy in QSOs and mQSOs are comparable (blazar-microblazar analogy) The kinetic power in mQSOs is equal or larger than the radiated power Electrons in the jets are accelerated up to TeV energies LS 5039: jets are steady, two-sided, seem to have bulk motions of 0.2-0.3c as compact mQSO jets ...
... Particle energy in QSOs and mQSOs are comparable (blazar-microblazar analogy) The kinetic power in mQSOs is equal or larger than the radiated power Electrons in the jets are accelerated up to TeV energies LS 5039: jets are steady, two-sided, seem to have bulk motions of 0.2-0.3c as compact mQSO jets ...
lect3 — 1 Measuring stars: What can be measured?
... smaller (and hence fainter) than Cepheids, and also rarer. Nonetheless, their P-L relation has less uncertainty, so they are often preferred when they can be seen. Finally, an incredibly bright and incredibly useful (for cosmology) standard candle is a particular type of supernova called a Type Ia. ...
... smaller (and hence fainter) than Cepheids, and also rarer. Nonetheless, their P-L relation has less uncertainty, so they are often preferred when they can be seen. Finally, an incredibly bright and incredibly useful (for cosmology) standard candle is a particular type of supernova called a Type Ia. ...
Journey through the cosmos
... It is called the Milky Way because it looks like a giant splash or river of milk across a dark sky. But you probably haven’t seen it look like this, unless you live somewhere a long way away from a town. Until 150 years ago, the Milky Way was the most obvious thing in the night sky. Light pollution ...
... It is called the Milky Way because it looks like a giant splash or river of milk across a dark sky. But you probably haven’t seen it look like this, unless you live somewhere a long way away from a town. Until 150 years ago, the Milky Way was the most obvious thing in the night sky. Light pollution ...
The Cosmic Microwave Background
... density Ωbh2 make the first acoustic peak much larger than the second. The more baryons the more the second peak is relatively suppressed. Baryons constitute about 5% of the critical density today, in agreement with the number derived from studies of light element synthesis in the infant universe. A ...
... density Ωbh2 make the first acoustic peak much larger than the second. The more baryons the more the second peak is relatively suppressed. Baryons constitute about 5% of the critical density today, in agreement with the number derived from studies of light element synthesis in the infant universe. A ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.