* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MICROQUASARS
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Kerr metric wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
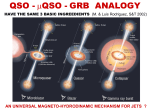
MICROQUASARS Five international workshops VI in Como, Italy (18-22 Sept. 2006) Felix Mirabel European Southern Observatory. Chile on leave from CEA-Saclay. France HIGH ENERGY SOURCES IN THE GALACTIC CENTRE Mirabel, Rodriguez, et al, 1992 Wang et al. ApJ 2002 Chandra Belanger, Goldwurm, Goldoni, ApJ 2003 INTEGRAL Black Hole QUASAR-MICROQUASAR ANALOGY QUASAR MICROQUASAR Mirabel & Rodriguez (Nature 1998) The scales of length and time are proportional to MBH Rsh = 2GMBH/c2 ; DT a MBH Unique system of equations: The maximum color temperature of the accretion disk is: Tcol a (M/ 10M)-1/4 (Shakura & Sunyaev, 1976) Waited era of space astronomy For a given accretion rate: LBol a MBH ; ljet a MBH ; j a MBH-1 ; B a MBH-1/2 (Sams, Eckart, Sunyaev, 96; Rees 04) APPARENT SUPERLUMINAL MOTIONS IN mQSOs AS IN QSOs ? SUPERLUMINAL EJECTION IN A mQSO Mirabel & Rodriguez, 1994 THE PLASMA THAT RADIATES IN THE HARD X-RAYS IS BLOWN IN SUPERLUMINAL JETS l3.6 cm 1 arcsec GRS 1915+105 Vapp > C for a DISTANCE > 8 Kpc VLA SUPERLUMINAL MOTIONS IN THE GALAXY 1) ASYMMETRIES DUE TO RELATIVISTIC ABERRATION IN TWIN JETS 2) mQSOs HAVE SAME BULK LORENTZ FACTORS AS QSOs & BLAZARS 3) JET COLLIMATION @ 30-100 Rsh IN M87 IS CONSISTENT WITH THE BLANDFORD-PAYNE MODEL (Biretta et al., 2004). HADRONIC JETS ? DARK JETS FROM BLACK HOLES Radio (Dubner et al); X-rays: (Brinkmann et al) VLA l20cm SS433/W50 1arcsec 1o = 60 pc • ATOMIC NUCLEI MOVING AT 0.26c • MECHANICAL LUMINOSITY > 1039 erg/sec • NON RADIATIVE JETS = “DARK” JETS • >50% OF THE ENERGY IS NOT RADIATED LARGE-SCALE JETS IN CYGNUS X-1 Gallo, Fender et al. Nature 2005 ring diameter = 5 pc > 50% OF THE RELEASED ENERGY IS NOT RADIATED IS IT A VHE SOURCE ? LARGE-SCALE JETS IN GRS 1915+105 ? Rodriguez & Mirabel (2006) hot spots at ~ 50 pc MOVING X-RAY JETS IN A mQSO mQSOs XTE J1550-564 & H1743-322 Corbel et al. Science 2002, 05 X-rays are produced by synchrotron electrons accelerated to TeV energies ACCRETION–JET CONNECTION DT a MBH 1 hr = 30 yr in SgrA* Mirabel, Dhawan, Rodriguez (1998) GRS 1915+105 - THE ONSET OF THE JET IS AT THE TIME OF A X-RAY “SPIKE” SUDDEN REFILL OF THE INNER DISK & INJECTION INTO THE JETS - SHOCK THROUGH A MILDLY RELATIVISTIC COMPACT JET - COMPACT STEADY JETS Ribo, Dhawan & Mirabel (2005) 2.0 cm GRS 1915+105 Mirabel, Dhawan, et al. 1998 3.6 cm • ~100 AU IN LENGTH PRESENT DURING PLATEAU STATE • SPEED OF THE FLOW < 0.4c (Ribo, Dhawan & Mirabel 2005) • LARGE SCALE JETS ARE SHOCKS PROPAGATING AT ~0.98c THROUGH THE SLOWER MOVING COMPACT JET mQSOs & ULTRALUMINOUS X-RAY SOURCES Microquasars in external galaxies ISOTROPIC BUT MBH > 30 M (Pakull et al. 2002) ANISOTROPIC BUT NOT BEAMED ( King et al 2001) ANISOTROPIC & BEAMED (Mirabel & Rodriguez, 1999; Koerding & Falke 2002) IMBHs DO NOT CONSTITUTE A LARGE FRACTION OF ULXs Fabbiano et al. X-ray (Chandra) Antennae VHE (>100 GeV) FROM g-RAY BINARIES LS 5039 with HESS LSI +61 303 with MAGIC (Aharonian et al. Science 2005) (Albert et al. Science 2006) VHE emission is variable • Both have compact objects with masses M < 4 M • Both are runaway HMXBs formed < 2 x 106 yrs ago LS 5039 WAS EJECTED FROM THE GALACTIC PLANE A VHE (> 100 GEV) SOURCE Paredes, Ribo et al. 2002 Ribo, Paredes et al. 2002 V = 100-140 km/s; e~0.5; Mj = 2000-5000 Km/s M ; Mejected in SN = 5-15 M LSI +61 303 WAS EJECTED FROM A CLUSTER A VHE ( > 100 GEV) SOURCE Mirabel, I. Rodrigues & Lu (A&A, 2004) Massey et al. 1995 IC 1805 V ~ 27 km/s < 2 M were blown away Linear momentum = 430 M km/s, as in runaway neutron stars THE COMPACT OBJECT IN LSI +61 303 WAS FORMED < 2 Myr AGO IN AN ASYMMETRIC SN EXPOLSION MODELS FOR g-RAY BINARIES Mirabel (Science 309, 714, 2006) 1) IC of e- jets on UV photons (Paredes et al. 2002) or hadrons in the jets (Romero et al. 2005) with matter of the stellar wind. Microblazars (Mirabel & Rodriguez,1999) 2) e- from pulsar wind on UV Photons (e.g. PSR B1259-63, Maraschi & Treves, 1981) VHE FROM COMPACT BINARIES • PULSAR WIND MODEL: Power by rotational energy (Dubus, 2006) • • • • • PSR B1259-63, LS 5039 & LSI +61 303 have compact objects with M < 4 MSUN Time variability & x-ray spectrum of LSI +61 303 resemble those of young pulsars LSI +61 303 is a Be star like PSR B1259-63 & all known Be/X-ray binary are NSs But does not satisfactorily fit the GeV & radio wavelength fluxes in LSI & LS 5039 Definitive proof: Detection of pulsations in LS 5039 & LSI +61 303 • MICROQUASAR JET MODELS: Power by accretion (Bosch-Ramon) • • • • • Particle energy in QSOs and mQSOs are comparable (blazar-microblazar analogy) The kinetic power in mQSOs is equal or larger than the radiated power Electrons in the jets are accelerated up to TeV energies LS 5039: jets are steady, two-sided, seem to have bulk motions of 0.2-0.3c as compact mQSO jets, and no radio outbursts have been observed (Paredes et al.) Definitive proof: VHE emission from confirmed BHs (e.g Cyg X-1, V 4641,GRS 1915) RADIO IMAGES WITH HIGHER SENSITIVITY AND RESOLUTION GAMMA-RAY BURSTS OF LONG DURATION MARK THE BIRTH OF BLACK HOLES AT COSMIC DISTANCES • They are detected at large redshifts, up to z = 6.4 • They are exploding massive stars of low metallicity • Associated with SN Ic & super-relativistic jets QSO - mQSO - GRB ANALOGY HAVE THE SAME 3 BASIC INGREEDIENTS (Mirabel & Rodriguez, S&T 2002) no ? no AN UNIVERSAL MAGNETO-HYDRODINAMIC MECHANISM FOR JETS ? SUMMARY Microquasars have provided insight into: • THE PHYSICS OF RELATIVISTIC JETS FROM BH’s • THE CONNECTION BETWEEN ACCRETION & EJECTION Microquasars could provide insight into: • A LARGE FRACTION OF ULXs IN NEARBY GALAXIES • GRBs OF LONG DURATION IN DISTANT GALAXIES • THE PHYSICS IN THE JETS OF DISTANT BLAZARS HOW ARE BLACK HOLE BINARIES FORM ? THERE ARE THEORETICAL MODELS e.g. Fryer & Kalogera ; Woosley & Heger (2002) BUT FEW OBSERVATIONS ! Mirabel & I. Rodrigues (2001-05) used the kinematics of mQSOs to find out: •BIRTH PLACE & NATURE OF THE PROGENITOR STARS •WHETHER THE PROGENITOR STAR ALWAYS EXPLODES AS AN ENERGETIC SUPERNOVAE A BLACK HOLE IN THE GALACTIC HALO XTE J1118+480 MBH~7 M M*=0.1–0.5 M ; l=158o b=+62o ; D=1.9 kpc GALACTOCENTRIC ORBIT FOR THE LAST 230 Myrs Yellow: Sun White: BH binary Orbit typical of globular clusters (Mirabel, Dhawan et al Nature 2001) but Solar abundances in the star imply that the black hole formed in a SN that polluted the donnor (astro-ph by Gonzalez et al. 2006) WAS THE BH FORMED IN THE HALO, THICK DISK OR IN THE GALACTIC THIN DISK BY A VIOLENT NATAL KICK ? A RUNAWAY BLACK HOLE GRO J1655-40 MBH ~ 4 M ORBITS FOR THE LAST 230 Myrs Yellow: Sun A LIKELY FOSSIL OF A GRBs FORMED IN AN HYPER-NOVA (Israelian et al. Nature 2001) White: BH binary Mirabel, Irapuan Rodrigues et al. (A&A 395, 595, 2002) Proper motion with HST + radial velocity from ground RUNAWAY VELOCITY ~120 km/s MOMENTUM = 550 M km/s as in runaway neutron stars LOW-MASS BLACK HOLE FORMED IN A LUMINOUS SUPERNOVA THE GALACTIC TRIP OF SCORPIUS X-1 The best determined XRB path. Parallax and proper motion from Fomalont et al. (Mirabel & I. Rodrigues, 2003) GALACTOCENTRIC ORBIT FOR THE LAST 230 Myrs Yellow: Sun Red: BH binary SCO X-1 FORMED IN A GLOBULAR CLUSTER OR GALACTIC BULGE THE ~10 M BLACK HOLE IN Cyg X-1 WAS BORN IN THE DARK Mirabel & I. Rodrigues, Science (2003) V < 9 +/- 2 km/s < 1 M ejected in SN Otherwise it would have been shot out from the parent association of massive stars MASSIVE STELLAR BH FORM PROMPTLY FORMATION OF THE BH IN GRS 1915+105 Black hole of 14 +/-4 M with a ~1 M donnor (Greiner et al. 2002-3) VLBA astrometry during 7 years: 6.8+/-0.2 mas/yr (Dhawan & M., 2005) Moves in the Galactic plane with Vb = 0 +/- 4 km/sec VBH = (33 to 70) +/- 12 km/s for D = 9 to 12 kpc (Chapuis & Corbel,2004) But dispersion velocity of 6x109 yr old disk population is ~50 km/s THE BH WAS FORMED PROMPTLY IN THE DISK QPOs AND GENERAL RELATIVITY XTE & INDIAN SAT. GRS 1915+105 (Strohmayer) •High frequency QPOs (e.g. 40 & 67 Hz repeat in GRS) •This 3:2 ratio now found in 4 BHXBs (Remillard et al.) Jerome Rodriguez et al. must depend on fundamental properties of black hole nmax = f(MBH, Spin) DETERMINE THE SPIN OF BLACK HOLES THE BLACK HOLE SPIN & DISK TEMPERATURE SUGGEST THAT JETS MAY BE POWERED BY THE BLACK HOLE SPIN SUMMARY Microquasars have provided insight into: • THE PHYSICS OF RELATIVISTIC JETS FROM BH’s • THE CONNECTION BETWEEN ACCRETION & EJECTION • THE FORMATION OF STELLAR-MASS BLACK HOLES Microquasars could provide insight into: • A LARGE FRACTION OF ULXs IN NEARBY GALAXIES • GRBs OF LONG DURATION IN DISTANT GALAXIES BLACK HOLE ASTROPHYSICS IS TODAY IN AN ANALOGOUS SITUATION AS WAS STELLAR ASTRONOMY IN THE FIRST HALF OF LAST CENTURY, WHEN THE HR DIAGRAM WAS CONSTRUCTED FOR FIRST TIME IF THE EMPIRICAL CORRELATIONS X-ray/radio/mass Gallo et al. 2004 QPOs/mass Abramovics, 2005 Noise-spectrum/mass Uttley et al. 2004 BECOME MORE ROBUST, INDEPENDENTLY OF THE MODELS, THE MASS AND SPIN OF BLACK HOLES WILL BE DETERMINED THE BLACK HOLE FUNDAMENTAL PLANE Merloni et al. Falke, Koerding et al. SUPERLUMINAL MOTIONS IN QSOs & AGN •OBSERVED IN > 30 QSOs & AGN •IN RADIO & OPTICAL WAVES • PROPER MOTION SEEN IN YEARS •Vapp UP TO 30c in blazars •One sided because of Doppler boosting •WHAT IS THE NATURE ? “PLASMONS” OR SHOCKS ?