Preliminary Talk Abstract Book - MoCA
... Clusters of galaxies are the most massive virialised cosmic structures. The diversity of their environmental conditions, from the dense cores to the sparse outskirts, allows them to be used as observational laboratories for the study of the environmental drivers of galaxy evolution. Furthermore, the ...
... Clusters of galaxies are the most massive virialised cosmic structures. The diversity of their environmental conditions, from the dense cores to the sparse outskirts, allows them to be used as observational laboratories for the study of the environmental drivers of galaxy evolution. Furthermore, the ...
Surface reflectance properties of distant Solar system bodies
... of possible faint objects found on long-exposure frames taken with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Cochran et al. (1995) found that many of the possible objects identified were not just noise, but were likely to be Halley-sized (i.e. ~ 10 kIn) KBOs (although no one object could be confirmed as bei ...
... of possible faint objects found on long-exposure frames taken with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), Cochran et al. (1995) found that many of the possible objects identified were not just noise, but were likely to be Halley-sized (i.e. ~ 10 kIn) KBOs (although no one object could be confirmed as bei ...
Scientific Justification
... Upper Sco targets. Objects in Taurus are scheduled to be observed as part of large maps in existing GTO programs and we will include these data in our analysis when they become available. Because most of the sources in Taurus have known L-band magnitudes, IRAC observations in this region are not as ...
... Upper Sco targets. Objects in Taurus are scheduled to be observed as part of large maps in existing GTO programs and we will include these data in our analysis when they become available. Because most of the sources in Taurus have known L-band magnitudes, IRAC observations in this region are not as ...
A novel and sensitive method for measuring very weak magnetic
... Context. Searches for magnetic fields in white dwarfs have clarified both the frequency of occurrence and the global structure of the fields found down to field strengths of the order of 500 kG. Below this level, the situation is still very unclear. Aims. We are engaged in a project to find and stud ...
... Context. Searches for magnetic fields in white dwarfs have clarified both the frequency of occurrence and the global structure of the fields found down to field strengths of the order of 500 kG. Below this level, the situation is still very unclear. Aims. We are engaged in a project to find and stud ...
Slide 1
... position, decides whether the burst merits a spacecraft slew and, if so, sends the position to the spacecraft. In order to study bursts with a variety of intensities, durations, and temporal structures, the BAT must have a large dynamic range and trigger capabilities. The BAT uses a twodimensional c ...
... position, decides whether the burst merits a spacecraft slew and, if so, sends the position to the spacecraft. In order to study bursts with a variety of intensities, durations, and temporal structures, the BAT must have a large dynamic range and trigger capabilities. The BAT uses a twodimensional c ...
A search for debris disks in the Herschel
... within the main sequence locus (see Fig. 2). Within this sample we expect considerable contamination from dust obscured QSOs or unresolved galaxies whose optical colours are reddened into the main sequence locus (Ivezić et al. 2002). Indeed, the sample have a median r-band magnitude of 19.8, fainte ...
... within the main sequence locus (see Fig. 2). Within this sample we expect considerable contamination from dust obscured QSOs or unresolved galaxies whose optical colours are reddened into the main sequence locus (Ivezić et al. 2002). Indeed, the sample have a median r-band magnitude of 19.8, fainte ...
Ch 33) Astrophysics and Cosmology
... This Hubble eXtreme Deep Field (XDF) photograph is of a very small part of the sky. It includes what may be the most distant galaxies observable by us (small red and green squares, and shown enlarged in the corners), with z L 8.8 and 11.9, that already existed when the universe was about 0.4 billion ...
... This Hubble eXtreme Deep Field (XDF) photograph is of a very small part of the sky. It includes what may be the most distant galaxies observable by us (small red and green squares, and shown enlarged in the corners), with z L 8.8 and 11.9, that already existed when the universe was about 0.4 billion ...
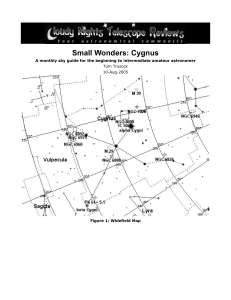
Small Wonders: Cygnus
... Three degrees almost directly east of Deneb, we come across one of the most photographed nebulae in the night sky. The North American Nebula is spectacular in long exposure photographs, and unlike many objects in the sky clearly resembles its namesake. Until recently tho, its been considered a chall ...
... Three degrees almost directly east of Deneb, we come across one of the most photographed nebulae in the night sky. The North American Nebula is spectacular in long exposure photographs, and unlike many objects in the sky clearly resembles its namesake. Until recently tho, its been considered a chall ...
night watch - Warren Astronomical Society
... small as it seemed to be from direct measurement of the size of the disk-much smaller than the giant planets just inside it-its density would be impossibly high. This density would be many times greater than that of any other object in the solar system. To resolve this difficulty, we must be as cert ...
... small as it seemed to be from direct measurement of the size of the disk-much smaller than the giant planets just inside it-its density would be impossibly high. This density would be many times greater than that of any other object in the solar system. To resolve this difficulty, we must be as cert ...
ppt
... • Every output class needs substantial representation in the training set. • Overlap between classes should be minimized. • Classifier accuracy can be improved with additional information (i.e., flux in different bandpass), but not always! ...
... • Every output class needs substantial representation in the training set. • Overlap between classes should be minimized. • Classifier accuracy can be improved with additional information (i.e., flux in different bandpass), but not always! ...
A New Science Strategy for Space Astronomy and Astrophysics
... next decade,1 prepared by a committee under the leadership of John Bahcall. Like previous decadal studies in this field, the report identified in priority order the most important scientific programs and projects for both groundand space-based research. It recommended a single large initiative for s ...
... next decade,1 prepared by a committee under the leadership of John Bahcall. Like previous decadal studies in this field, the report identified in priority order the most important scientific programs and projects for both groundand space-based research. It recommended a single large initiative for s ...
T3-Cosmic Star Formation History
... through N-body numerical simulations of increasing resolution and size (e.g., Davis et al. 1985; Dubinski & Carlberg 1991; Moore et al. 1999; Springel et al. 2005, 2008; Diemand et al. 2008; Stadel et al. 2009; Klypin et al. 2011). However, the same does not hold for the baryons. Several complex pro ...
... through N-body numerical simulations of increasing resolution and size (e.g., Davis et al. 1985; Dubinski & Carlberg 1991; Moore et al. 1999; Springel et al. 2005, 2008; Diemand et al. 2008; Stadel et al. 2009; Klypin et al. 2011). However, the same does not hold for the baryons. Several complex pro ...
Why do we Still Believe in Newton`s Law? Facts, Myths and Methods
... was enthusiastically accepted after the verification of light deflection in 1919 and the explanation of the anomalous advance of the perihelion of mercury known since 1859. From the 1960s until today, general relativity (GR) has undergone an impressive series of confirmations I will briefly review b ...
... was enthusiastically accepted after the verification of light deflection in 1919 and the explanation of the anomalous advance of the perihelion of mercury known since 1859. From the 1960s until today, general relativity (GR) has undergone an impressive series of confirmations I will briefly review b ...
Document
... You need a reference point source (star) for the wavefront measurement. The reference star must be within the isoplanatic angle, of about 10-30 arcseconds If there is no bright (mag ~ 14-15) nearby star then you must use an artificial star or „laser guide star“. All laser guide AO systems use a sodi ...
... You need a reference point source (star) for the wavefront measurement. The reference star must be within the isoplanatic angle, of about 10-30 arcseconds If there is no bright (mag ~ 14-15) nearby star then you must use an artificial star or „laser guide star“. All laser guide AO systems use a sodi ...
Chapter 16
... formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative model, several separate clouds of gas merge to form than Galaxy rather than one. High-velocity atomic hydrogen clouds have been observed since 1963; t ...
... formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative model, several separate clouds of gas merge to form than Galaxy rather than one. High-velocity atomic hydrogen clouds have been observed since 1963; t ...
doc - Eu-Hou
... instrument, limited time slots are available. Applicants can expect to receive a response within a week after submission of a request which will be sent to the email address given in the application. If the request can be accommodated, the response will contain the date and time of the measurements, ...
... instrument, limited time slots are available. Applicants can expect to receive a response within a week after submission of a request which will be sent to the email address given in the application. If the request can be accommodated, the response will contain the date and time of the measurements, ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.