Close Double Stars from Video
... We now strongly encourage observation with relatively inexpensive video equipment to better quantify the observations, and obtain at least approximate photometric information using specially-developed software for analyzing video records, esp. Limovie from Japan and Tangra from Australia We encourag ...
... We now strongly encourage observation with relatively inexpensive video equipment to better quantify the observations, and obtain at least approximate photometric information using specially-developed software for analyzing video records, esp. Limovie from Japan and Tangra from Australia We encourag ...
The formation of disc galaxies in high-resolution moving
... that a crucial requirement for the current generation of cosmological simulations of galaxy formation is that their numerical models should be sufficiently well posed to yield results approximately invariant with numerical resolution, at least over a reasonable range where crucial physics remains su ...
... that a crucial requirement for the current generation of cosmological simulations of galaxy formation is that their numerical models should be sufficiently well posed to yield results approximately invariant with numerical resolution, at least over a reasonable range where crucial physics remains su ...
attached file
... Cosmological Principle) it can be shown that the corresponding distortion of space-time (due to the gravitational effects of this matter) can only have one of three forms, as shown schematically in the picture at left. It can be "positively" curved like the surface of a ball and finite in extent; it ...
... Cosmological Principle) it can be shown that the corresponding distortion of space-time (due to the gravitational effects of this matter) can only have one of three forms, as shown schematically in the picture at left. It can be "positively" curved like the surface of a ball and finite in extent; it ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... A. Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. B. Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. C. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. © 2005 Pearson Education Inc., publishing a ...
... A. Because no galaxies exist at such a great distance. B. Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. C. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. © 2005 Pearson Education Inc., publishing a ...
Summer 2004 ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Professor: ER Capriotti Sample Questions
... D. gone into space E. rocks 72. Rocks on the Moon have been shown to have ages A. between 10 and 20 billion years. B. between 6 and 8 million years. C. of 3.5 billion years with no range in age. D. They have not been dated. E. between 2.5 and 4.6 billion years. 73. Most lunar craters were apparently ...
... D. gone into space E. rocks 72. Rocks on the Moon have been shown to have ages A. between 10 and 20 billion years. B. between 6 and 8 million years. C. of 3.5 billion years with no range in age. D. They have not been dated. E. between 2.5 and 4.6 billion years. 73. Most lunar craters were apparently ...
12 The Milky Way - Journigan-wiki
... which these stars orbit has a mass of 4 million solar masses, yet nothing is seen there. Therefore, many astronomers almost inescapably conclude that a massive black hole lies at the heart of our galaxy. This evidence is perhaps the best yet that black holes actually exist. ...
... which these stars orbit has a mass of 4 million solar masses, yet nothing is seen there. Therefore, many astronomers almost inescapably conclude that a massive black hole lies at the heart of our galaxy. This evidence is perhaps the best yet that black holes actually exist. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars: Supernovae in Starbursts by Jason Kezwer
... The brightening event is dimmer in the H and J bands, appearing to be affected by extinction. Interpreting this as a supernova-related event we estimate the extinction in the nuclear regions of Arp 220 to lie between 2.01 ≤ AK ≤ 3.40 or 17.95 ≤ AV ≤ 30.36 in the optical, in agreement with several ot ...
... The brightening event is dimmer in the H and J bands, appearing to be affected by extinction. Interpreting this as a supernova-related event we estimate the extinction in the nuclear regions of Arp 220 to lie between 2.01 ≤ AK ≤ 3.40 or 17.95 ≤ AV ≤ 30.36 in the optical, in agreement with several ot ...
Can TMT Image Habitable Planets ?
... Habitable planets can be imaged on ELTs (physics and nature are on our side) ELTs can operate at ~1e-5/1e-6 raw contrast and photon-noise limited detection limit → characterization (spectroscopy) of 1e-8 habitable planets accessible around dozens of nearby stars, mainly near-IR/visible Ideal targets ...
... Habitable planets can be imaged on ELTs (physics and nature are on our side) ELTs can operate at ~1e-5/1e-6 raw contrast and photon-noise limited detection limit → characterization (spectroscopy) of 1e-8 habitable planets accessible around dozens of nearby stars, mainly near-IR/visible Ideal targets ...
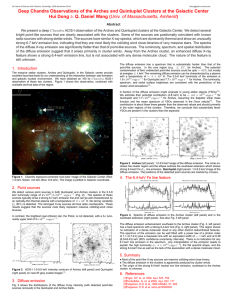
Deep Chandra Observations of the Arches and Quintuplet Clusters at... Hui Dong Q. Daniel Wang ( &
... The diffuse emission enhancement southeast to the Arches cluster (Fig. 3, left panel) has a hard spectrum with a strong 6.4-keV line (Fig. 4, right panel). This region shows no indication of a dense molecular cloud or any other distinct radio/infrared features. The spectrum of the emission can be we ...
... The diffuse emission enhancement southeast to the Arches cluster (Fig. 3, left panel) has a hard spectrum with a strong 6.4-keV line (Fig. 4, right panel). This region shows no indication of a dense molecular cloud or any other distinct radio/infrared features. The spectrum of the emission can be we ...
Document
... • 13.2 GeV photon detected 16.5 sec after trigger – Conservative lower limit on the quantum gravity mass (assuming linear energy scaling): MQG> (1.50 +/- 0.20) x 1018 ...
... • 13.2 GeV photon detected 16.5 sec after trigger – Conservative lower limit on the quantum gravity mass (assuming linear energy scaling): MQG> (1.50 +/- 0.20) x 1018 ...
November - Hawaiian Astronomical Society
... DUNES, DEBRIS. For the time being, the scientists on these teams are the only ones with access to the Herschel data. But in January, all the data these teams are working on will suddenly be released to the public. So they are all under pressure to finish their work by then. The team whose meeting I ...
... DUNES, DEBRIS. For the time being, the scientists on these teams are the only ones with access to the Herschel data. But in January, all the data these teams are working on will suddenly be released to the public. So they are all under pressure to finish their work by then. The team whose meeting I ...
Unravelling the Origin and Evolution of Our Galaxy
... than our Sun. These are all within a distance of about 100 light-years. The planets detectable by this method are rather massive, comparable to Jupiter (which has about 300 times the mass of Earth). The systems have some surprising properties: two thirds of these giant planets are orbiting their hos ...
... than our Sun. These are all within a distance of about 100 light-years. The planets detectable by this method are rather massive, comparable to Jupiter (which has about 300 times the mass of Earth). The systems have some surprising properties: two thirds of these giant planets are orbiting their hos ...
Science Grade 08 Unit 11 Exemplar Lesson 02: Classifying Stars
... 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continue to answer questions. Monitor students’ answers for accuracy as they complete the questions. 7. Divide the class into groups of four, and distribute card sets from Handout: Star Life Cycles to each group. 8 ...
... 7–9 with students. Instruct students to watch for underlined words or phrases as they continue to answer questions. Monitor students’ answers for accuracy as they complete the questions. 7. Divide the class into groups of four, and distribute card sets from Handout: Star Life Cycles to each group. 8 ...
HOPS 383: An Outbursting Class 0 Protostar in Orion
... HOPS team created a grid of 3040 model SEDs with parameters appropriate for protostars, first described by Ali et al. (2010), and updated by E. Furlan et al. (in preparation). We found the best fit by minimizing R, which measures the logarithmic deviation of the models from the observations in units ...
... HOPS team created a grid of 3040 model SEDs with parameters appropriate for protostars, first described by Ali et al. (2010), and updated by E. Furlan et al. (in preparation). We found the best fit by minimizing R, which measures the logarithmic deviation of the models from the observations in units ...
The\^ G Infrared Search for Extraterrestrial Civilizations with Large
... In AGENT parameters, Annis sought galaxies with 0.75 < α < 1 (although his sensitivity near 1 was necessarily limited by the fact that the galaxies were required to have a measured optical rotation curve to be included in his sample, creating a selection bias against the highest-α galaxies). We can ...
... In AGENT parameters, Annis sought galaxies with 0.75 < α < 1 (although his sensitivity near 1 was necessarily limited by the fact that the galaxies were required to have a measured optical rotation curve to be included in his sample, creating a selection bias against the highest-α galaxies). We can ...
View the sky`s greatest nebula
... point, we’re looking along the galaxy’s rim. Toward Scorpius is the central part of the Milky Way. Rather than seeing a field of blazing stars, our view is obscured by huge clouds of dust and gas. In the winter, we see the sky opposite the stellar traffic jam found toward the galaxy’s center. The wi ...
... point, we’re looking along the galaxy’s rim. Toward Scorpius is the central part of the Milky Way. Rather than seeing a field of blazing stars, our view is obscured by huge clouds of dust and gas. In the winter, we see the sky opposite the stellar traffic jam found toward the galaxy’s center. The wi ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.