Long Ago and Far Away
... galaxy’s actual distance to the distance you worked out in Part II#3, estimate the angular size of this galaxy if it were observed at a distance corresponding to 5 billion years after the Big Bang. (The small angle formula breaks down for large cosmological distances, but just assume it works approx ...
... galaxy’s actual distance to the distance you worked out in Part II#3, estimate the angular size of this galaxy if it were observed at a distance corresponding to 5 billion years after the Big Bang. (The small angle formula breaks down for large cosmological distances, but just assume it works approx ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
... Today, the highest-mass stars top out at about 100 solar masses (Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in our Milky Way galaxy, is about 90). But recent cosmological simulations suggest the possibility that in the early universe truly gargantuan stars could exist. So Chen began exploring this w ...
Integrated Science Concepts COS 2010 2011
... Gravitational force (weight) can be calculated from mass, but all other forces will only be quantified through force diagrams. Friction and normal forces are introduced conceptually at this level. Friction is a force between two surfaces that opposes sliding. Equations of static and kinetic friction ...
... Gravitational force (weight) can be calculated from mass, but all other forces will only be quantified through force diagrams. Friction and normal forces are introduced conceptually at this level. Friction is a force between two surfaces that opposes sliding. Equations of static and kinetic friction ...
A Sun-Centered Universe - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... relative to another point, equally offset from center called the equant It is difficult to know whether Ptolemy believed the universe actually worked this way, or was this simply a model that gave fairly accurate predictions. D-7 ...
... relative to another point, equally offset from center called the equant It is difficult to know whether Ptolemy believed the universe actually worked this way, or was this simply a model that gave fairly accurate predictions. D-7 ...
Lec12
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
Multiple Choice, continued Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... that light travels through space in 1 year. Because the speed of light through space is about 300,000 km/ s, light travels approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers in one year. Even after astronomers figured out that stars were far from Earth, the nature of the universe was hard to understand. Some as ...
... that light travels through space in 1 year. Because the speed of light through space is about 300,000 km/ s, light travels approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers in one year. Even after astronomers figured out that stars were far from Earth, the nature of the universe was hard to understand. Some as ...
Lecture 22 - Cosmic distance scale
... as 1000 pc. • How to find distance to objects farther than 1000 pc? ...
... as 1000 pc. • How to find distance to objects farther than 1000 pc? ...
a MS Word version.
... 9. These same measurements have also revealed other parameters which describe our universe. For instance, what do these measurements tell us about the make-up of our universe? i.e.: What percentages of the matter-energy density of the universe are made up of normal (baryonic) matter, dark matter, a ...
... 9. These same measurements have also revealed other parameters which describe our universe. For instance, what do these measurements tell us about the make-up of our universe? i.e.: What percentages of the matter-energy density of the universe are made up of normal (baryonic) matter, dark matter, a ...
Eternal inflation and its implications
... it never disappears, and in fact the total volume of the false vacuum, once inflation starts, continues to grow exponentially with time, ad infinitum. Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of an eternally inflating universe. The top bar indicates a region of false vacuum. The evolution of this region i ...
... it never disappears, and in fact the total volume of the false vacuum, once inflation starts, continues to grow exponentially with time, ad infinitum. Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of an eternally inflating universe. The top bar indicates a region of false vacuum. The evolution of this region i ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... 7.2 Clusters of Galaxies Clusters are systems a few Mpc across, typically containing at least 50-100 luminous galaxies within the central 1 Mpc Clusters are gravitationally bound Clusters are filled with hot X-ray gas Only ~20% of galaxies live in clusters, most live in groups or in the “fi ...
... 7.2 Clusters of Galaxies Clusters are systems a few Mpc across, typically containing at least 50-100 luminous galaxies within the central 1 Mpc Clusters are gravitationally bound Clusters are filled with hot X-ray gas Only ~20% of galaxies live in clusters, most live in groups or in the “fi ...
The Attractive Universe Theory
... attraction of two masses will depend on the fact how the straight line connecting these masses is oriented with respect to the system of fixed stars. Thus the observation of gravitation anisotropy could open up a new astronomical method. ...
... attraction of two masses will depend on the fact how the straight line connecting these masses is oriented with respect to the system of fixed stars. Thus the observation of gravitation anisotropy could open up a new astronomical method. ...
astronomy advisory panel strategy
... parameters and more emphasis on detailed studies of galaxy formation, the intergalactic medium and the distribution of various forms of matter: stellar, gas, non-baryonic....... An essential target of cosmology will be to test the current belief that around 99% of the matter in the Universe is dark, ...
... parameters and more emphasis on detailed studies of galaxy formation, the intergalactic medium and the distribution of various forms of matter: stellar, gas, non-baryonic....... An essential target of cosmology will be to test the current belief that around 99% of the matter in the Universe is dark, ...
Lecture Notes
... Since the completion of the basic Standard Model, many efforts have been made to address these problems, through the development of ‘Grand Unified Theories’ (GUTs; electroweak+strong) and ‘Theories of Everything’ (TOEs; GUT+gravity). For the purposes of this course, the crucial fact to keep in mind ...
... Since the completion of the basic Standard Model, many efforts have been made to address these problems, through the development of ‘Grand Unified Theories’ (GUTs; electroweak+strong) and ‘Theories of Everything’ (TOEs; GUT+gravity). For the purposes of this course, the crucial fact to keep in mind ...
z - STScI
... • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
... • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
Earth_Universe04
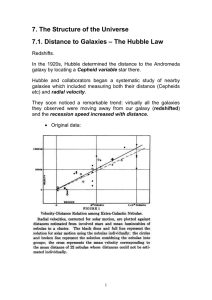
... • Most galaxies exhibit a red Doppler shift • Far galaxies • Exhibit the greatest shift • Greater velocity • Discovered in 1929 by Edwin Hubble • Hubble's Law – the recessional speed of galaxies is proportional to their distance • Accounts for red shifts ...
... • Most galaxies exhibit a red Doppler shift • Far galaxies • Exhibit the greatest shift • Greater velocity • Discovered in 1929 by Edwin Hubble • Hubble's Law – the recessional speed of galaxies is proportional to their distance • Accounts for red shifts ...
Chapter 1 - Chabot College
... Galaxy A great island of stars in space, all held together by gravity and orbiting a ...
... Galaxy A great island of stars in space, all held together by gravity and orbiting a ...
Dark Matter -24-------------------------------~-----------R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C
... visible through radiation in radio and other wavelengths; it contributes so little to the mass of the galaxy, however, that it may be neglected in accounting for the total mass. To a very good approximation, the visible galaxy is a rotating circular two-dimensional distribution of stars. The surface ...
... visible through radiation in radio and other wavelengths; it contributes so little to the mass of the galaxy, however, that it may be neglected in accounting for the total mass. To a very good approximation, the visible galaxy is a rotating circular two-dimensional distribution of stars. The surface ...
1. setting the scene 2. the cosmic dark ages and the first stars
... vicinity. When many such stars had formed, each surrounded by a bubble of ionised hydrogen, a stage was reached when the bubbles merged, and essentially all of intergalactic gas was ionised once again. This was the epoch of ‘reionisation’ (see Figure 2). However by this time (t ∼ 600 million years), ...
... vicinity. When many such stars had formed, each surrounded by a bubble of ionised hydrogen, a stage was reached when the bubbles merged, and essentially all of intergalactic gas was ionised once again. This was the epoch of ‘reionisation’ (see Figure 2). However by this time (t ∼ 600 million years), ...
Lecture 39
... Stars are classified based on their color (and spectral absorption lines), which is in turn related to their surface temperature. On a plot of luminosity versus wavelength of their principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is i ...
... Stars are classified based on their color (and spectral absorption lines), which is in turn related to their surface temperature. On a plot of luminosity versus wavelength of their principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is i ...
chap8 (WP)
... 1. An opera singer on a train is singing high C (f = 512 s-1 ) when the train passes by an observer stationary on the ground. What frequency does the observer hear if the train is traveling at 140 km/hr (a) towards and (b) away from the observer? (Use 342 m/s for the speed of sound in air) 2. A trai ...
... 1. An opera singer on a train is singing high C (f = 512 s-1 ) when the train passes by an observer stationary on the ground. What frequency does the observer hear if the train is traveling at 140 km/hr (a) towards and (b) away from the observer? (Use 342 m/s for the speed of sound in air) 2. A trai ...
Star and Earth Chemistry Lecture Notes (PDF
... Big bang occurred 13-14×109 y ago resulted in a Universe of radiation and elementary particles. Light elements created 3 min after Big Bang. First stars appear 200 million years later. Heavier elements formed >109 y after big bang in stars made during birth and death of generations of stars then sca ...
... Big bang occurred 13-14×109 y ago resulted in a Universe of radiation and elementary particles. Light elements created 3 min after Big Bang. First stars appear 200 million years later. Heavier elements formed >109 y after big bang in stars made during birth and death of generations of stars then sca ...
Information Equation of State
... overwritten in computer systems and subsequently used to predict the future limits to shrinking computer circuit size [2-9]. Shannon information entropy of a computer memory device, log2NL, is just the number of bits needed to distinguish between the NL information bearing degrees of freedom used fo ...
... overwritten in computer systems and subsequently used to predict the future limits to shrinking computer circuit size [2-9]. Shannon information entropy of a computer memory device, log2NL, is just the number of bits needed to distinguish between the NL information bearing degrees of freedom used fo ...
4550-15Lecture33
... principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is inversely related to the fourth power of temperature, this correlation means that hot stars give off more energy than cooler stars. Mass is also related to temperature for main seque ...
... principal emissions (color), called, most stars fall along an array defining the “main sequence”. Since wavelength is inversely related to the fourth power of temperature, this correlation means that hot stars give off more energy than cooler stars. Mass is also related to temperature for main seque ...
1-Syllabus-Intro
... -- The hour before class is usually a bad time except for very brief matters. -- I will usually be in class at least 5 minutes before lecture and can stay afterwards for several minutes. These are good times to take care of most questions. For routine questions about course material, please ask a TA ...
... -- The hour before class is usually a bad time except for very brief matters. -- I will usually be in class at least 5 minutes before lecture and can stay afterwards for several minutes. These are good times to take care of most questions. For routine questions about course material, please ask a TA ...
Word
... The Big Bang theory of the Universe states that the Universe was created in a massive explosion from a point when space, time and matter were created. This event is thought to have occurred about 14 billion years ago. As the Universe expanded and cooled, first nucleons, then nuclei, atoms, molecules ...
... The Big Bang theory of the Universe states that the Universe was created in a massive explosion from a point when space, time and matter were created. This event is thought to have occurred about 14 billion years ago. As the Universe expanded and cooled, first nucleons, then nuclei, atoms, molecules ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.