FREE Sample Here
... were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on observations of the expansion rate, the Big Bang must have occurred about 14 bi ...
... were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on observations of the expansion rate, the Big Bang must have occurred about 14 bi ...
Study Guide Presentation
... How can spectra of elements be used to determine the composition of stars and galaxies? How can spectra of elements be used to determine how fast galaxies are moving away from us? Spectra: Label the three types of spectrum and what causes it: ...
... How can spectra of elements be used to determine the composition of stars and galaxies? How can spectra of elements be used to determine how fast galaxies are moving away from us? Spectra: Label the three types of spectrum and what causes it: ...
Four Big Questions With Pretty Good Answers
... An object without mass would not know how to move. It would not know, from one moment to the next, where in space it was supposed to be. It would be, in a very strong sense, unphysical. Also, in Newton’s law of gravity, the mass of an object governs the strength of the force it exerts. One cannot bu ...
... An object without mass would not know how to move. It would not know, from one moment to the next, where in space it was supposed to be. It would be, in a very strong sense, unphysical. Also, in Newton’s law of gravity, the mass of an object governs the strength of the force it exerts. One cannot bu ...
Scientific Evidence for A
... and for days and years; and let them be for lights in the expanse of the heavens to give light on the earth”; and it was so. And God made the two great lights, the greater light to govern the day, and the lesser light to govern the night; He made the stars also. And God placed them in the expanse of ...
... and for days and years; and let them be for lights in the expanse of the heavens to give light on the earth”; and it was so. And God made the two great lights, the greater light to govern the day, and the lesser light to govern the night; He made the stars also. And God placed them in the expanse of ...
Ellipticity, Its Origin and Progression in Comoving Galaxies
... universe, contrary to Academia’s long-held view, is not expanding. Furthermore, the new-cosmology argument includes incontrovertible proof that our Cosmos is intrinsically cellularly structured, contrary to the view of mere phenomenological cellularity. A remarkable 2009 paper [6] entitled, “The Sto ...
... universe, contrary to Academia’s long-held view, is not expanding. Furthermore, the new-cosmology argument includes incontrovertible proof that our Cosmos is intrinsically cellularly structured, contrary to the view of mere phenomenological cellularity. A remarkable 2009 paper [6] entitled, “The Sto ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... Constellations - A group of stars in a recognizable pattern that appear to be near each other in space. Nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas and plasma. It is the first stage of a star's cycle but it can also refer to the remains of a dying star (planetary nebula). Originally nebula ...
... Constellations - A group of stars in a recognizable pattern that appear to be near each other in space. Nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas and plasma. It is the first stage of a star's cycle but it can also refer to the remains of a dying star (planetary nebula). Originally nebula ...
of the Sun
... PHOTON ERA - energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - visible light, X rays, radio waves and ultraviolet rays. Energy transforms into matter: •quarks •protons and neutrons •helium, deuterium and lithium • The Universe was dominated by energy. • The density of energy was so great that matte ...
... PHOTON ERA - energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - visible light, X rays, radio waves and ultraviolet rays. Energy transforms into matter: •quarks •protons and neutrons •helium, deuterium and lithium • The Universe was dominated by energy. • The density of energy was so great that matte ...
Galaxies - senwiki
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
... that nothing, not even light, can escape. -Why? Black holes have extremely strong gravitational pulls. They can pull in stars and accumulate the mass of the stars. -Where are black holes located? Astronomers believe that each galaxy contains at least one supermassive black hole at its centre. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... 25.3 The Universe The Big Bang The Big Crunch? • The future of the universe follows two possible paths: 1. The universe will expand forever. 2. The outward expansion will stop and gravitational contraction will follow. • The view currently favored by most scientists is an expanding universe with ...
... 25.3 The Universe The Big Bang The Big Crunch? • The future of the universe follows two possible paths: 1. The universe will expand forever. 2. The outward expansion will stop and gravitational contraction will follow. • The view currently favored by most scientists is an expanding universe with ...
The Big Bang
... • The universe had a specific beginning (night sky is dark; Hubble’s Law; approximate age = 1/H0) • The universe is expanding (Hubble’s Law) • The universe has evolved/changed over time • Initially, the universe was extremely hot, dense, and opaque • Cosmic objects (such as stars) should have a chem ...
... • The universe had a specific beginning (night sky is dark; Hubble’s Law; approximate age = 1/H0) • The universe is expanding (Hubble’s Law) • The universe has evolved/changed over time • Initially, the universe was extremely hot, dense, and opaque • Cosmic objects (such as stars) should have a chem ...
Where Does Helium Come from?
... After the Plank Era, or between 10−43 and 10−35 s, we know that the universe, which had already expanded and cooled dramatically (but still a very hot ...
... After the Plank Era, or between 10−43 and 10−35 s, we know that the universe, which had already expanded and cooled dramatically (but still a very hot ...
Studying the Universe Studying the Universe
... The simplest optical telescope has two lenses. One lens, called the objective lens, collects light and forms an image at the back of the telescope. The bigger the objective lens, the more light the telescope can gather. The second lens is located in the eyepiece of the telescope. This lens magnifies ...
... The simplest optical telescope has two lenses. One lens, called the objective lens, collects light and forms an image at the back of the telescope. The bigger the objective lens, the more light the telescope can gather. The second lens is located in the eyepiece of the telescope. This lens magnifies ...
9. Fascinating observations. But how much is well understood?
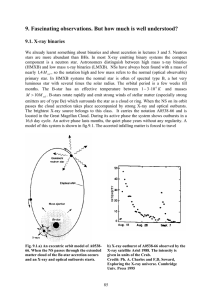
... look for systems at the upper right. There are 2 kinds of data points, black filled circles and red squares. The first belong to the class of Soft Gamma Repeters (SGR). They are transient sources which undergo repeted bursting of subsecond duration. Sometimes they exhibit luminous superflares lastin ...
... look for systems at the upper right. There are 2 kinds of data points, black filled circles and red squares. The first belong to the class of Soft Gamma Repeters (SGR). They are transient sources which undergo repeted bursting of subsecond duration. Sometimes they exhibit luminous superflares lastin ...
nuclear fusion
... emission of e+ (or e-) and a (anti-)neutrino transition of a p or n from a higher to a lower energy level with emission of a ...
... emission of e+ (or e-) and a (anti-)neutrino transition of a p or n from a higher to a lower energy level with emission of a ...
Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe
... Example: • This photo shows the Andromeda Galaxy as it ...
... Example: • This photo shows the Andromeda Galaxy as it ...
Lecture2.2014_v4 - UCO/Lick Observatory
... Example: • This photo shows the Andromeda Galaxy as it ...
... Example: • This photo shows the Andromeda Galaxy as it ...
Gravitational Waves – detectors, sources & science
... • Most galaxies harbour a supermassive black hole in their centre which is surrounded by a cluster of stars. • Encounters between stars in the cluster can put compact objects onto orbits that pass close enough to the black hole to be captured. Emission of GWs drives inspiral into the BH. • Waveforms ...
... • Most galaxies harbour a supermassive black hole in their centre which is surrounded by a cluster of stars. • Encounters between stars in the cluster can put compact objects onto orbits that pass close enough to the black hole to be captured. Emission of GWs drives inspiral into the BH. • Waveforms ...
life
... Number of communicating civilisations = rate of formation of suitable stars x fraction of these stars with planets x number of Earth-like planets per system x fraction of such planets which develop life x fraction of life-bearing planets evolving intelligence x fraction of intelligent specie ...
... Number of communicating civilisations = rate of formation of suitable stars x fraction of these stars with planets x number of Earth-like planets per system x fraction of such planets which develop life x fraction of life-bearing planets evolving intelligence x fraction of intelligent specie ...
absolute brightness: The apparent brightness a star would have if it
... eccentricity: A measure of the flatness of an ellipse, equal to the distance between the two foci divided by the length of the major axis. eclipse: Event during which one body passes in front of another, so that the light from the occulted body is blocked. eclipsing binary: Rare binary-star system t ...
... eccentricity: A measure of the flatness of an ellipse, equal to the distance between the two foci divided by the length of the major axis. eclipse: Event during which one body passes in front of another, so that the light from the occulted body is blocked. eclipsing binary: Rare binary-star system t ...
absolute brightness: The apparent brightness a star would have if it
... eccentricity: A measure of the flatness of an ellipse, equal to the distance between the two foci divided by the length of the major axis. eclipse: Event during which one body passes in front of another, so that the light from the occulted body is blocked. eclipsing binary: Rare binary-star system t ...
... eccentricity: A measure of the flatness of an ellipse, equal to the distance between the two foci divided by the length of the major axis. eclipse: Event during which one body passes in front of another, so that the light from the occulted body is blocked. eclipsing binary: Rare binary-star system t ...
Historical overview of Cosmology
... Beyond the solar system 2) The star distribution in the milky way is asymmetric, with respect to the Earth, but is rather symmetric with respect to a point in the constellation of Sagittarius (Shapley, 1915) The Sun is not at the center of the Galaxy ...
... Beyond the solar system 2) The star distribution in the milky way is asymmetric, with respect to the Earth, but is rather symmetric with respect to a point in the constellation of Sagittarius (Shapley, 1915) The Sun is not at the center of the Galaxy ...
File
... But when I think how infinitely little is all that I have done I cannot feel pride; I only see the great kindness of my scientific comrades, and of all my friends in crediting me for so much. One word characterises the most strenuous of the efforts for the advancement of science that I have made per ...
... But when I think how infinitely little is all that I have done I cannot feel pride; I only see the great kindness of my scientific comrades, and of all my friends in crediting me for so much. One word characterises the most strenuous of the efforts for the advancement of science that I have made per ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.