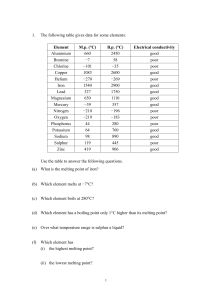
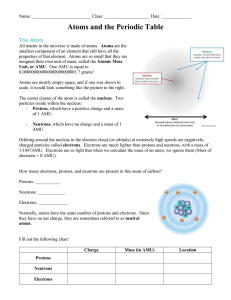
Unit 1: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... atoms gain or lose electrons. Since the # of electrons no longer equals the # of protons, these atoms must be charged. A charged atom is called an ion. Cations are positively charged ions – they have lost electrons (and now have more protons than electrons) Anions are negatively charged ions – they ...
... atoms gain or lose electrons. Since the # of electrons no longer equals the # of protons, these atoms must be charged. A charged atom is called an ion. Cations are positively charged ions – they have lost electrons (and now have more protons than electrons) Anions are negatively charged ions – they ...
Column A
... levels are present. Electrons fill the energy levels in order (2-8-8-18) b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of an atom? 8 d. How can the electron arrangement/configuration be determined for a neutra ...
... levels are present. Electrons fill the energy levels in order (2-8-8-18) b. How many electrons can be found in the first energy level of an atom? 2 c. How many electrons can be found in the second energy level of an atom? 8 d. How can the electron arrangement/configuration be determined for a neutra ...
Answers
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
Review for Exam 1
... CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know The difference between ionic and covalent bonds Define cations and anions Predict cation/anion charge using the octet rule or group number Familiar with metals with multiple potential charges (do not need to memorize) Determine ionic compound formulas from th ...
... CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know The difference between ionic and covalent bonds Define cations and anions Predict cation/anion charge using the octet rule or group number Familiar with metals with multiple potential charges (do not need to memorize) Determine ionic compound formulas from th ...
Note 1.1 Chemistry of Life
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
... Atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of the atom. It determines the particular atom identity. (Periodic Table) Atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are not found within the nucleus and do not contribute to the ...
Atomic Size - ThinkChemistry
... The purpose of this activity is to examine how atomic size changes on going down a column in the periodic table and also on going across a row. Going Down a Group (column): The size of an atom increases going down a group. This is because on going down the group from one element to the next, an elec ...
... The purpose of this activity is to examine how atomic size changes on going down a column in the periodic table and also on going across a row. Going Down a Group (column): The size of an atom increases going down a group. This is because on going down the group from one element to the next, an elec ...
CHEM_Review - Kenston Local Schools
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
... Counting Atoms The formula for a compound indicates the elements that make up the compound and the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These numbers of atoms are indicated by the use of small numbers called subscripts. Sometimes groups of atoms act as a single atom. Such a grou ...
What are Valence Electrons
... • Valence electrons are electrons that have the highest en______ ergy level and are held most loosely ber of • The num______ valence electrons in an atom of an element determines its perties and the pro________ ways it can bond with other atoms ...
... • Valence electrons are electrons that have the highest en______ ergy level and are held most loosely ber of • The num______ valence electrons in an atom of an element determines its perties and the pro________ ways it can bond with other atoms ...
Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt
... Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substa ...
... Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substa ...
Atom - WCHS Physical Science
... • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number to the element's identity. ...
... • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number to the element's identity. ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
Atoms and Isotopes
... They are atoms of the same element that have different Number of Neutrons but must have the same number of Protons. ...
... They are atoms of the same element that have different Number of Neutrons but must have the same number of Protons. ...
lecture slides of chap8
... has three more protons than the electrons. According to the question that it has five electrons in the 3d subshell, and thus the total electrons in valence shells for its atomic type will be 8. Note that the transition metals (with d electrons) losing its s electrons prior to its d electrons and thu ...
... has three more protons than the electrons. According to the question that it has five electrons in the 3d subshell, and thus the total electrons in valence shells for its atomic type will be 8. Note that the transition metals (with d electrons) losing its s electrons prior to its d electrons and thu ...
Notes: Structure of matter
... # of neutrons = _________ State of matter = _______________ Valence number = ________________ ...
... # of neutrons = _________ State of matter = _______________ Valence number = ________________ ...
Chapter 4.3: How Atoms Differ
... Radioactive atoms undergo _____________ that can alter their ___________ through __________ reactions. ...
... Radioactive atoms undergo _____________ that can alter their ___________ through __________ reactions. ...
AHSGE Review
... Groups are together because the elements in them have similar properties and react in the same manner. Across periods (left to right), atomic radius (size) decreases, ionization energy (ease of losing an electron) increases, and electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) increases. ...
... Groups are together because the elements in them have similar properties and react in the same manner. Across periods (left to right), atomic radius (size) decreases, ionization energy (ease of losing an electron) increases, and electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) increases. ...
UNIT 5 - ATOMIC THEORY: THE NUCLEAR MODEL OF THE ATOM
... A) If the electron is stationary, the atom should disappear because the electron would be electrostatically drawn in to the nucleus. B) If the electron orbits the nucleus, it will have to change direction a lot. A change in direction means acceleration, which involves the use of energy. If this is s ...
... A) If the electron is stationary, the atom should disappear because the electron would be electrostatically drawn in to the nucleus. B) If the electron orbits the nucleus, it will have to change direction a lot. A change in direction means acceleration, which involves the use of energy. If this is s ...
Structure of the atom
... carbon? Iron? (see periodic table, p.768) What is an isotope? (p. 321) ...
... carbon? Iron? (see periodic table, p.768) What is an isotope? (p. 321) ...
2Unit 9M.1_atomic_structure6912_Answer
... centre of the atom which is called the nucleus. The size of the nucleus is very small in comparison with the overall size of the atom. If we make a hydrogen atom the size of a football, then its nucleus would be the size of a pinhead. Electrons move around the nucleus somewhat like planets orbit aro ...
... centre of the atom which is called the nucleus. The size of the nucleus is very small in comparison with the overall size of the atom. If we make a hydrogen atom the size of a football, then its nucleus would be the size of a pinhead. Electrons move around the nucleus somewhat like planets orbit aro ...
atom - sandymessana
... electrons outer shell of electrons are called valence electrons the number of electrons in the outer shell = valence # Need to have a neutral overall charge ---if an atom has gained or lost e- in order to become stable, it will bond with another atom(s) that have an opposite charge in order to be ne ...
... electrons outer shell of electrons are called valence electrons the number of electrons in the outer shell = valence # Need to have a neutral overall charge ---if an atom has gained or lost e- in order to become stable, it will bond with another atom(s) that have an opposite charge in order to be ne ...
Instructional Objectives 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in any atom. • Distinguish among atoms, ions, and isotopes. 3.3 Isotopes and Atomic Masses • Describe isotopes of an element how they affect physical and chemical properties. • Describe how an ...
... 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in any atom. • Distinguish among atoms, ions, and isotopes. 3.3 Isotopes and Atomic Masses • Describe isotopes of an element how they affect physical and chemical properties. • Describe how an ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... Use the following data table on the isotopes of element “X” to answer Questions A&B listed below: ...
... Use the following data table on the isotopes of element “X” to answer Questions A&B listed below: ...