Atomic Structure - Madison County Schools
... He was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. In early work he discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, proved that radioactivity involved the nuclear transmutation of one chemical element to another, and also differentiated and named alpha and ...
... He was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. In early work he discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, proved that radioactivity involved the nuclear transmutation of one chemical element to another, and also differentiated and named alpha and ...
Isotopes
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
... left of the chemical symbol, For iron (Fe) we have, for example: 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe. Since the iron has the atomic number zFe = 26, we have 54 - 26 = 28 neutrons in 54Fe, and 30, 31, and 32 neutrons, respectively, in the other three isotopes given. Isotopes come in two basic variants: 1. Rad ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
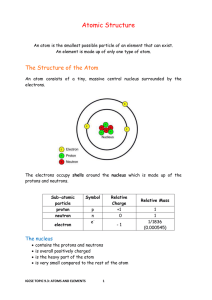
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
Inside the Atom
... Describe the three kinds of particles found in atoms. Where are they located in the atom and what are their charges? In Rutherford’s experiment, why wouldn’t the electrons in the atoms of the gold foil affect the paths of the alpha particles? What is an electron cloud? How many orbitals are there? W ...
... Describe the three kinds of particles found in atoms. Where are they located in the atom and what are their charges? In Rutherford’s experiment, why wouldn’t the electrons in the atoms of the gold foil affect the paths of the alpha particles? What is an electron cloud? How many orbitals are there? W ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... deflected at large angles, thus Thompson’s model could not be correct. Rutherford on YouTube ...
... deflected at large angles, thus Thompson’s model could not be correct. Rutherford on YouTube ...
Physical Science 1st Semester final Review
... 7. Classify the matter below as either a pure substance or a mixture. If you believe that it is a pure substance, write down whether it is an element or a compound. If you believe that it is a mixture, write down whether or not is homogeneous or heterogeneous. a. Table salt (NaCl) ...
... 7. Classify the matter below as either a pure substance or a mixture. If you believe that it is a pure substance, write down whether it is an element or a compound. If you believe that it is a mixture, write down whether or not is homogeneous or heterogeneous. a. Table salt (NaCl) ...
lecture slides of chap8
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
Honors Chemistry Chapter 6 Student Notes
... f block elements are called inner transition elements - they were put into their current position by Glenn Seaborg - the only living person ever to have an element named after himself. ...
... f block elements are called inner transition elements - they were put into their current position by Glenn Seaborg - the only living person ever to have an element named after himself. ...
models_of_the_atom_1
... • Neils Bohr attempted to make a model of an atom to help explain the chemical behavior of atoms and ions • Protons and neutrons are found in a nucleus • Outside the nucleus are electrons in pathways called orbits • Electrons have energy and can move from one orbit to another • The further an electr ...
... • Neils Bohr attempted to make a model of an atom to help explain the chemical behavior of atoms and ions • Protons and neutrons are found in a nucleus • Outside the nucleus are electrons in pathways called orbits • Electrons have energy and can move from one orbit to another • The further an electr ...
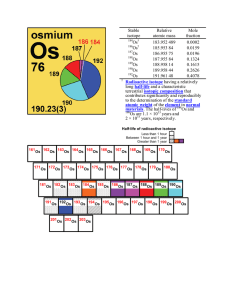
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. beta decay (β-decay) – radioactive decay process resulting in emission of a beta particle of either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric c ...
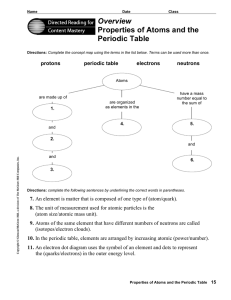
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
Atomic Structure Guided Notes
... 7. Chlorine has 17 protons and 18 neutrons. How many electrons does it have? _________________________ 8. Boron has an atomic number of 5 and a mass number of 11. What does this mean? ____________________ 9. Calcium has an atomic number of 20 and a mass number of 40. What is its electron configurati ...
... 7. Chlorine has 17 protons and 18 neutrons. How many electrons does it have? _________________________ 8. Boron has an atomic number of 5 and a mass number of 11. What does this mean? ____________________ 9. Calcium has an atomic number of 20 and a mass number of 40. What is its electron configurati ...
The Periodic Table
... causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the group, reduces the electronelectron repulsions. A lower electron-nucleus attraction is thus counterbalanced by lower electron-electron repulsion ...
... causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the group, reduces the electronelectron repulsions. A lower electron-nucleus attraction is thus counterbalanced by lower electron-electron repulsion ...
No Slide Title
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... •Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (~1869) independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
... •Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (~1869) independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
File
... 1) All elements consist of atoms that cannot be divided. 2) All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. 3) An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element by a chemical react ...
... 1) All elements consist of atoms that cannot be divided. 2) All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. 3) An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element by a chemical react ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... 6.1 Organizing the Elements and Classifying the Elements Origin of the Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
... 6.1 Organizing the Elements and Classifying the Elements Origin of the Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... elements are called noble, or inert (ie; unreactive) gases. Elements belonging to a certain group all exhibit similar chemical properties. ...
... elements are called noble, or inert (ie; unreactive) gases. Elements belonging to a certain group all exhibit similar chemical properties. ...
Document
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest form of elements. About 100 elements • Hydrogen is an element that accounts for about 90% of total mass of the universe. ...
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest form of elements. About 100 elements • Hydrogen is an element that accounts for about 90% of total mass of the universe. ...
UNIT 5 - ATOMIC THEORY: THE NUCLEAR MODEL OF THE ATOM
... An atom consists of a very small, positively charged nucleus, in which most of the mass of the atom is concentrated, surrounded by the electrons necessary to produce an electrically neutral atom. The Nuclear Model of the Atom At the time, Rutherford only knew about electrons. Electrons circled the p ...
... An atom consists of a very small, positively charged nucleus, in which most of the mass of the atom is concentrated, surrounded by the electrons necessary to produce an electrically neutral atom. The Nuclear Model of the Atom At the time, Rutherford only knew about electrons. Electrons circled the p ...
Isotope Worksheet
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, C (6 protons) + 1 proton ...
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, C (6 protons) + 1 proton ...
Isotope Worksheet
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
... The number of protons in a nucleus determines the identity of the element. For example, any atom having 6 protons will be a "carbon" atom. If we were to add an extra proton to the nucleus, we would have an entirely different element. For example, ! ...
8th-interlude-for-atoms - Epiphany Catholic School
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...