Unit 1 Problem Set
... 12. In the emission spectrum of hydrogen, which electronic transition would produce a line in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum? Show all work. ...
... 12. In the emission spectrum of hydrogen, which electronic transition would produce a line in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum? Show all work. ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... Periodic Table A chart which organizes elements into periods and families to help chemists understand them. Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements ...
... Periodic Table A chart which organizes elements into periods and families to help chemists understand them. Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements ...
Atomic Notation
... -The mass number is the number of protons and neutrons in that element. The number is rounded to the nearest whole number (no decimals in standard notation) -The atomic number is the number of protons -All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons (or atomic number) -The number of el ...
... -The mass number is the number of protons and neutrons in that element. The number is rounded to the nearest whole number (no decimals in standard notation) -The atomic number is the number of protons -All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons (or atomic number) -The number of el ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Chem Basics
... to nonmetals. When metals give and nonmetals receive electrons, they become stable like the noble gases. This electron transfer process forms ionic bonds between metals and nonmetals. On the other hand, covalent bonds form between nonmetals- nonmetals. A nonmetal with 5,6 or 7 valance electrons shar ...
... to nonmetals. When metals give and nonmetals receive electrons, they become stable like the noble gases. This electron transfer process forms ionic bonds between metals and nonmetals. On the other hand, covalent bonds form between nonmetals- nonmetals. A nonmetal with 5,6 or 7 valance electrons shar ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
... Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom? Where are electrons located in an atom? Who was the Greek philosopher responsible for naming the atom? Which two subatomic particles have the greatest mass? An element that is a very reactive gas is most likely a member H of which group ...
rocks and minerals quiz
... The elements of groups 3 through 12 are all metals that do not form alkaline solutions with water. Collectively they are called the transition metals. TRANSITION METALS (Group 3 – 12) The transition metals include: iron, Fe; copper, Cu; nickel, Ni; chromium, Cr; silver, Ag; and gold, Au. THE HALOGEN ...
... The elements of groups 3 through 12 are all metals that do not form alkaline solutions with water. Collectively they are called the transition metals. TRANSITION METALS (Group 3 – 12) The transition metals include: iron, Fe; copper, Cu; nickel, Ni; chromium, Cr; silver, Ag; and gold, Au. THE HALOGEN ...
Early Greek Philosophers determined that atoms are the building
... Halogens Elements in group 17 7 valence electrons Greek “forming salts Very reactive non-metals that easily form compounds with metals. These compounds are known as salts. ...
... Halogens Elements in group 17 7 valence electrons Greek “forming salts Very reactive non-metals that easily form compounds with metals. These compounds are known as salts. ...
Year End Chemistry Review
... 6. Periodic Table, periods and group names 7. Periodic trends: (ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic radius) 8. Atomic number = # of _____ Mass number = # of ________ Isotopes are atoms of the same element, therefore having the same number of __________, but different numb ...
... 6. Periodic Table, periods and group names 7. Periodic trends: (ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic radius) 8. Atomic number = # of _____ Mass number = # of ________ Isotopes are atoms of the same element, therefore having the same number of __________, but different numb ...
Name Date Class Period ______
... K The building block of matter/smallest part of matter. L Pure substances made of only one type of atom. I The heavy center of the atom. ...
... K The building block of matter/smallest part of matter. L Pure substances made of only one type of atom. I The heavy center of the atom. ...
File - 8th Grade Physical Science
... theory that all nature could be understood in terms of the movement of atomos. In ancient times, many elements were known, including C, S, Cu, Ag, Au, Fe, Sn, Sb and Pb. The names of most of these are from the Latin words. ...
... theory that all nature could be understood in terms of the movement of atomos. In ancient times, many elements were known, including C, S, Cu, Ag, Au, Fe, Sn, Sb and Pb. The names of most of these are from the Latin words. ...
File
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
... or share electrons so as to have eight electrons in their outer electron shell. Atoms gain or lose electrons so that they have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. Fo ...
8.2 Families and Periods of the Periodic Table Lesson Objectives
... example, germanium had not been discovered when Mendeleev constructed his table. After gallium, the next known element in Mendeleev’s time was arsenic. Arsenic did not match the chemical characteristics of carbon and silicon. Instead, arsenic matched the chemical characteristics of nitrogen and phos ...
... example, germanium had not been discovered when Mendeleev constructed his table. After gallium, the next known element in Mendeleev’s time was arsenic. Arsenic did not match the chemical characteristics of carbon and silicon. Instead, arsenic matched the chemical characteristics of nitrogen and phos ...
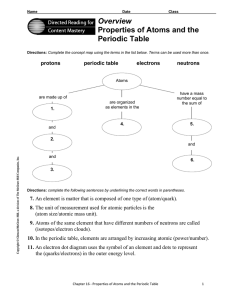
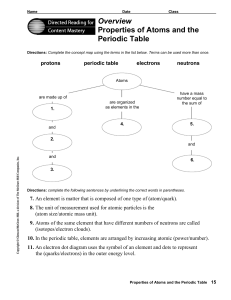
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... number. The mass of the atom is so small that there is a ...
... number. The mass of the atom is so small that there is a ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... atomic theory—states that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms o John Dalton was one of the first scientists to gather evidence for the atomic theory o Dalton’s Atomic Theory: • Each element is composed of atoms • All atoms of a given element are identical • Atoms of different eleme ...
... atomic theory—states that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms o John Dalton was one of the first scientists to gather evidence for the atomic theory o Dalton’s Atomic Theory: • Each element is composed of atoms • All atoms of a given element are identical • Atoms of different eleme ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit), 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
Structure - Mole Cafe
... The number of electrons can be changed when determining the charge of an ion. ...
... The number of electrons can be changed when determining the charge of an ion. ...
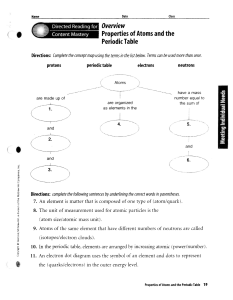
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
... 7. An element is matter that is composed of one type of (atom/quark). 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ...
Chapter Review Answers
... 15. In what ways are protons and neutrons alike? How are they different? Protons and neutrons are alike because they are both located in the nucleus and have the same mass. They are different because protons have a positive charge and neutrons have no charge. 16. Nitrogen-14 and Nitrogen-15 are isot ...
... 15. In what ways are protons and neutrons alike? How are they different? Protons and neutrons are alike because they are both located in the nucleus and have the same mass. They are different because protons have a positive charge and neutrons have no charge. 16. Nitrogen-14 and Nitrogen-15 are isot ...
Chemistry Notes (pg. # 1)
... 2.)Also, the positive charge is very c________ in a small _________. 3.) This experiment disproved the _____ _____ ______. ...
... 2.)Also, the positive charge is very c________ in a small _________. 3.) This experiment disproved the _____ _____ ______. ...