Topic 1 Test - A-Level Chemistry
... Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak. ...
... Write an equation, including state symbols, to show the reaction that occurs when the first ionisation energy of Kr is measured. Sometimes the mass spectrum of Kr has a very small peak with an m/z value of 42. Explain the occurrence of this peak. ...
Electrons
... For example: Na (Sodium), has originally 11 electrons but when an electron is lost it becomes a positive ion. Na+ ...
... For example: Na (Sodium), has originally 11 electrons but when an electron is lost it becomes a positive ion. Na+ ...
Niels bohr
... Here is the light emitted by different elements - Nitrogen, Neon, and Krypton Notice that each element gives off it’s own characteristic color of light ...
... Here is the light emitted by different elements - Nitrogen, Neon, and Krypton Notice that each element gives off it’s own characteristic color of light ...
Chemistry Final - Practice Test I
... Isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers. V. ...
... Isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers. V. ...
20161013082744
... have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers • Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different number of neutrons ...
... have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers • Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers because they have different number of neutrons ...
ChemicalBondingTestAnswers
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
Atoms - ChemistryatBiotech
... How much of a 100g sample of an unstable isotope remains after 25 years if the half life is ...
... How much of a 100g sample of an unstable isotope remains after 25 years if the half life is ...
Chapter Review- Josh and Niels 1. Rutherford`s Atom • Rutherford`s
... two sublevels (two types of orbital’s), the 2s orbital and the three 2p orbital’s; and so on. o 5. The n value is always used to label the orbitals of a given principal level and is followed by the letter that indicates the type of the orbital. For example, the designation 3p means an orbital in lev ...
... two sublevels (two types of orbital’s), the 2s orbital and the three 2p orbital’s; and so on. o 5. The n value is always used to label the orbitals of a given principal level and is followed by the letter that indicates the type of the orbital. For example, the designation 3p means an orbital in lev ...
Learning Targets Chapter 4
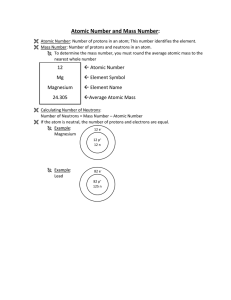
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
... relative mass of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom. I can calculate the number of protons (p+) , neutrons (n0) and electrons (e-) in an atom using the atomic number, mass number and overall charge of the atom or a periodic table provided. I can describe the similarity and di ...
Atoms, Molecules, Compounds, Elements, and Mixtures
... Electrons • Electrons orbit around an atom. In this picture, they are the small yellow bits. • They have a negative charge. • They are lighter than protons or neutrons. • The number of protons=number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
... Electrons • Electrons orbit around an atom. In this picture, they are the small yellow bits. • They have a negative charge. • They are lighter than protons or neutrons. • The number of protons=number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
2/1: Atomic Structure
... • atoms could not be divided • all elements of a given element are the same • different atoms could join to form compounds – Thomson • the plum pudding model • negatively-charged "plums” surrounded by positively-charged "pudding” – Rutherford • atom is made up of a central charge surrounded by a clo ...
... • atoms could not be divided • all elements of a given element are the same • different atoms could join to form compounds – Thomson • the plum pudding model • negatively-charged "plums” surrounded by positively-charged "pudding” – Rutherford • atom is made up of a central charge surrounded by a clo ...
Mid-Term OR Study Guide
... A) Identify the trend for atomic radius as the atomic number increases (moving down the group) or decreases (moving up a group). Be able to explain this trend as we did in class. B) What type of charge will the elements in this group tend to achieve? C) Identify how the atomic radius compares to the ...
... A) Identify the trend for atomic radius as the atomic number increases (moving down the group) or decreases (moving up a group). Be able to explain this trend as we did in class. B) What type of charge will the elements in this group tend to achieve? C) Identify how the atomic radius compares to the ...
November 16-17, 2016 Class Presentation
... •Each column is called a “group” •Each element in a group has the same number of electrons in their outer orbital, also known as “shells”. ...
... •Each column is called a “group” •Each element in a group has the same number of electrons in their outer orbital, also known as “shells”. ...
Elements
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
... Chemical formulas – atoms are indicated by the element symbols; number of each atom is indicated by a subscript – a number that appears to the right of and below the symbol for the element ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
Learning Outcomes for Chemical Reactions and
... • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the ...
... • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the ...
Atomic Structure
... balance and measured everything which lead to the Law of conservation of Mass • He named oxygen which means “acid former” and helped determine that air is a mixture not an element ...
... balance and measured everything which lead to the Law of conservation of Mass • He named oxygen which means “acid former” and helped determine that air is a mixture not an element ...
Atom - WCHS Physical Science
... History of the Periodic Table • Dmitri Mendeleev invented the first periodic table. He arranged it according to increasing atomic mass. • Henry Moseley arranged the modern periodic table. He arranged it according to increasing atomic number. ...
... History of the Periodic Table • Dmitri Mendeleev invented the first periodic table. He arranged it according to increasing atomic mass. • Henry Moseley arranged the modern periodic table. He arranged it according to increasing atomic number. ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.