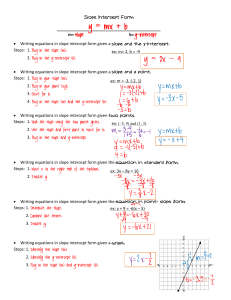
Maxwell equation - Technion moodle
... The system is assumed to be linear the principle of superposition is obeyed. The complex envelopes of the two electric field components of the input and output (transmitted or reflected) waves are related by the weighted superpositions: ...
... The system is assumed to be linear the principle of superposition is obeyed. The complex envelopes of the two electric field components of the input and output (transmitted or reflected) waves are related by the weighted superpositions: ...
DeBroglie Hypothesis
... if the momentum (and energy) is just right (as in the above relation). But this will happen only for specific cases - and those are the specific allowed orbits (rn) and energies (En) that are allowed in the Bohr Theory! ...
... if the momentum (and energy) is just right (as in the above relation). But this will happen only for specific cases - and those are the specific allowed orbits (rn) and energies (En) that are allowed in the Bohr Theory! ...
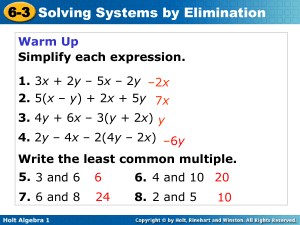
Homework #8 Solutions
... so B = 21 (−4 − A) = − 54 . Thus, a particular solution is y = − 32 x − 54 . 3.5.6. Find a particular solution to the DE 2y00 + 4y0 + 7y = x2 . Solution: In setting up the Method of Undetermined Coefficients, we observe that f ( x ) = x2 corresponds to a triple root r = 0. Since the characteristic e ...
... so B = 21 (−4 − A) = − 54 . Thus, a particular solution is y = − 32 x − 54 . 3.5.6. Find a particular solution to the DE 2y00 + 4y0 + 7y = x2 . Solution: In setting up the Method of Undetermined Coefficients, we observe that f ( x ) = x2 corresponds to a triple root r = 0. Since the characteristic e ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.