CreateSpace Word Templates - WUSD-ALgebra-I-and
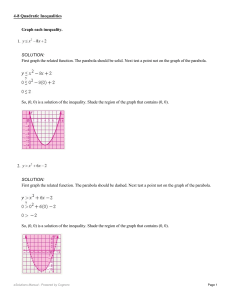
... left hand side of the ordered pairs which would be the top or left side of a table. The vertical axis is the right hand values in the ordered pairs which is the bottom or right hand side of a table. Below is an example of a bar graph created from this data. ...
... left hand side of the ordered pairs which would be the top or left side of a table. The vertical axis is the right hand values in the ordered pairs which is the bottom or right hand side of a table. Below is an example of a bar graph created from this data. ...
Chap1 P1 EM Waves
... By knowing the EM wave’s direction of propagation, given as unit vector ap, is the same as the cross product of Es with unit vector, aE and Hs with unit vector aH : ...
... By knowing the EM wave’s direction of propagation, given as unit vector ap, is the same as the cross product of Es with unit vector, aE and Hs with unit vector aH : ...
S T E L L A R
... radiative processes, and so portions of these notes could be useful for upper-level undergraduates. The text layout uses the tufte-book (https://tufte-latex.github.io/tufte-latex/) LATEX class: the main feature is a large right margin in which the students can take notes; this margin also holds smal ...
... radiative processes, and so portions of these notes could be useful for upper-level undergraduates. The text layout uses the tufte-book (https://tufte-latex.github.io/tufte-latex/) LATEX class: the main feature is a large right margin in which the students can take notes; this margin also holds smal ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.