Section 7.1 - University of South Florida
... you found in Step 3 back into the expression you found in Step 1. The result is the The solution set is {(−6, −3)}. solution(s). They’re preparing us for multiple ...
... you found in Step 3 back into the expression you found in Step 1. The result is the The solution set is {(−6, −3)}. solution(s). They’re preparing us for multiple ...
ppt
... – Look for solutions in the interval 0 ≤ θ < period using the unit circle • Recall the period is 2π for sine, cosine, secant, & cosecant and π for tangent & cotangent • We have seen how to do this when we discussed the circular trigonometric functions in section 4.2 ...
... – Look for solutions in the interval 0 ≤ θ < period using the unit circle • Recall the period is 2π for sine, cosine, secant, & cosecant and π for tangent & cotangent • We have seen how to do this when we discussed the circular trigonometric functions in section 4.2 ...
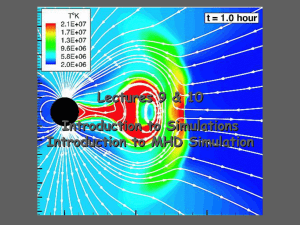
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.