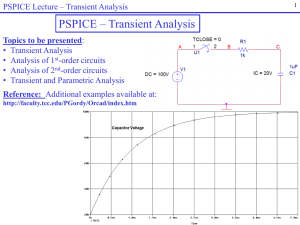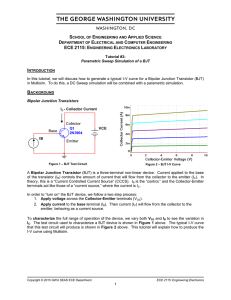
SEQUENCE COMPONENTS AND UNTRANSPOSED
... internal voltage of the motor, and the positive-sequence impedance of the generator, motor, and lines. The negative- and positive-sequence networks contain only sequence impedance. In Figure 9, there is no generated negative- or zero-sequence voltage and no connection between the networks. Therefore ...
... internal voltage of the motor, and the positive-sequence impedance of the generator, motor, and lines. The negative- and positive-sequence networks contain only sequence impedance. In Figure 9, there is no generated negative- or zero-sequence voltage and no connection between the networks. Therefore ...
lecture1423723226
... 1.4.Series connection of coupled circuit ( lecture 2) When inductors are connected together in series so that the magnetic field of one links with the other, the effect of mutual inductance either increases or decreases the total inductance depending upon the amount of magnetic coupling. The effect ...
... 1.4.Series connection of coupled circuit ( lecture 2) When inductors are connected together in series so that the magnetic field of one links with the other, the effect of mutual inductance either increases or decreases the total inductance depending upon the amount of magnetic coupling. The effect ...
Final Report - Senior Design
... This report highlights the advantages of a 3 stage, dual path amplifier as a general topology for successfully implementing our design goals. This topology was originally reported less than a year ago for low-voltage, integrated circuit applications. ...
... This report highlights the advantages of a 3 stage, dual path amplifier as a general topology for successfully implementing our design goals. This topology was originally reported less than a year ago for low-voltage, integrated circuit applications. ...
V - Chi K. Tse
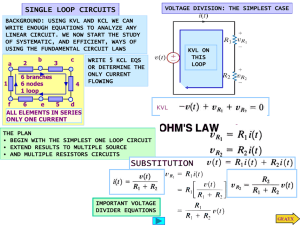
... One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
... One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
R 0
... 1.Superposition theorem can be only applied to calculating voltage and current in linear circuit;It cannot be applied to power(power is source’s quadric function)。It cannot be used in nonlinear circuit,either. 2. Circuit’s structure parameter should be identical when applying it ...
... 1.Superposition theorem can be only applied to calculating voltage and current in linear circuit;It cannot be applied to power(power is source’s quadric function)。It cannot be used in nonlinear circuit,either. 2. Circuit’s structure parameter should be identical when applying it ...
Methods of Analysis - Eastern Mediterranean University Open
... Eastern Mediterranean University ...
... Eastern Mediterranean University ...
reduction of switches and voltage divices in new cascaded h
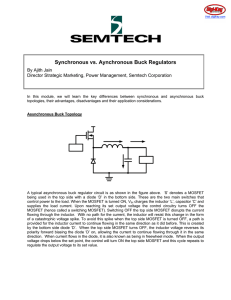
... be obtained. The Cascaded H – Bridge topology are more advantageous compared to above two topologies, because it consists fewer number of components, it is very simple to control. To reduce the number of power supplies and power electronic components, a new topology is proposed in this paper. When c ...
... be obtained. The Cascaded H – Bridge topology are more advantageous compared to above two topologies, because it consists fewer number of components, it is very simple to control. To reduce the number of power supplies and power electronic components, a new topology is proposed in this paper. When c ...
Explicit formulas for the solutions of piecewise linear networks
... the operation of taking the nonnegative part. Furthermore, it will be shown that the nesting of this operator is at most for an -dimensional LCP. The results will then be discussed from the viewpoint of PL electrical networks and their properties. One of the advantages to the approach is that an ana ...
... the operation of taking the nonnegative part. Furthermore, it will be shown that the nesting of this operator is at most for an -dimensional LCP. The results will then be discussed from the viewpoint of PL electrical networks and their properties. One of the advantages to the approach is that an ana ...
Chapter06
... circuit, add the series resistances and combine the parallel resistances. In this diagram, R1 and R2 are in series, and R3 and R4 are in parallel. However, R2 is not in series with the parallel resistances: Resistances in series have the same current, but the current in R2 is equal to the sum of t ...
... circuit, add the series resistances and combine the parallel resistances. In this diagram, R1 and R2 are in series, and R3 and R4 are in parallel. However, R2 is not in series with the parallel resistances: Resistances in series have the same current, but the current in R2 is equal to the sum of t ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.