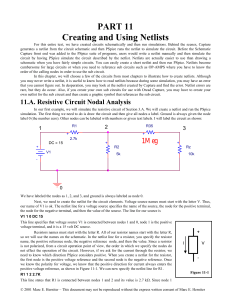
Series-Parallel Circuits
... circuit, add the series resistances and combine the parallel resistances. In this diagram, R1 and R2 are in series, and R3 and R4 are in parallel. However, R2 is not in series with the parallel resistances: Resistances in series have the same current, but the current in R2 is equal to the sum of t ...
... circuit, add the series resistances and combine the parallel resistances. In this diagram, R1 and R2 are in series, and R3 and R4 are in parallel. However, R2 is not in series with the parallel resistances: Resistances in series have the same current, but the current in R2 is equal to the sum of t ...
Lecture11
... The approach will be useful if solving the two circuits is simpler, or more convenient, than solving a circuit with two sources We can have any combination of sources. And we can partition any way we find convenient ...
... The approach will be useful if solving the two circuits is simpler, or more convenient, than solving a circuit with two sources We can have any combination of sources. And we can partition any way we find convenient ...
Assessment of Fault Location in Power Distribution Networks
... Figure 4 illustrates the load blocks connected at bus 1, 2 and 3 of Figure 3. Each load is connected at the low voltage side of a 20/0.4 kV distribution transformer and it is represented by three impedances. A Π of capacitance is also included in parallel at each transformer model in order to simula ...
... Figure 4 illustrates the load blocks connected at bus 1, 2 and 3 of Figure 3. Each load is connected at the low voltage side of a 20/0.4 kV distribution transformer and it is represented by three impedances. A Π of capacitance is also included in parallel at each transformer model in order to simula ...
ppt
... The human cardiovascular system consists of two circuits: pulmonary circulation which carries blood though the lungs, and systemic circulation which carries blood to the organs The organs of the body are connected in parallel in the systemic circuit Simple circuit model*: ...
... The human cardiovascular system consists of two circuits: pulmonary circulation which carries blood though the lungs, and systemic circulation which carries blood to the organs The organs of the body are connected in parallel in the systemic circuit Simple circuit model*: ...
ppt
... ACT: Resistors in parallel Consider a circuit with two resistors R1 and R2 in parallel. Compare I1, the current through R1, to I2, the current through R2: ...
... ACT: Resistors in parallel Consider a circuit with two resistors R1 and R2 in parallel. Compare I1, the current through R1, to I2, the current through R2: ...
Thevenin`s And Norton`s Theorem
... NORTON’S THEOREM: In the Norton circuit, the current source is the short circuit current of the network, that is, the current obtained by shorting the output of the network. The resistance is the resistance seen looking into the network with all sources deactivated. This is the same as RTH. ...
... NORTON’S THEOREM: In the Norton circuit, the current source is the short circuit current of the network, that is, the current obtained by shorting the output of the network. The resistance is the resistance seen looking into the network with all sources deactivated. This is the same as RTH. ...
Document
... ACT: Resistors in parallel Consider a circuit with two resistors R1 and R2 in parallel. Compare I1, the current through R1, to I2, the current through R2: ...
... ACT: Resistors in parallel Consider a circuit with two resistors R1 and R2 in parallel. Compare I1, the current through R1, to I2, the current through R2: ...
w 0
... If Aβ>1, the oscillations will grow in amplitude. We therefore need a nonlinear circuit for gain control to force Aβ to remain equal at the desired value of output amplitude. The function of gain-control mechanism is as follows: To ensure that oscillation will start, Aβ is designed greater tha ...
... If Aβ>1, the oscillations will grow in amplitude. We therefore need a nonlinear circuit for gain control to force Aβ to remain equal at the desired value of output amplitude. The function of gain-control mechanism is as follows: To ensure that oscillation will start, Aβ is designed greater tha ...
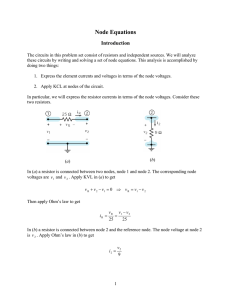
Resistive Network Analysis The Node Voltage Method
... • Apply KVL to each mesh to obtain a set of n equations, one for each mesh. • Branch currents and voltages can be derived from mesh currents. PHY305F - Electronics Laboratory I, Fall Term (K. Strong) ...
... • Apply KVL to each mesh to obtain a set of n equations, one for each mesh. • Branch currents and voltages can be derived from mesh currents. PHY305F - Electronics Laboratory I, Fall Term (K. Strong) ...
Aalborg Universitet A Systematic Method to Synthesize New Transformerless Full-bridge Grid-tied Inverters
... In this section, several examples are provided to show how to use the MN principal to derive a bridge type inverter with minimal leakage currents. In this section, it is assumed that (6) is satisfied. A. M:N=2:2 or 2:3 or 3:2 Fig.6 shows an example of the M1 topology with external diodes. From tab.1 ...
... In this section, several examples are provided to show how to use the MN principal to derive a bridge type inverter with minimal leakage currents. In this section, it is assumed that (6) is satisfied. A. M:N=2:2 or 2:3 or 3:2 Fig.6 shows an example of the M1 topology with external diodes. From tab.1 ...
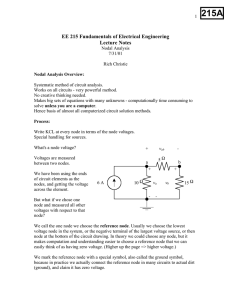
LectNotes3-NodalAnalysis
... Mind you, I would never solve the example circuit by nodal analysis unless someone made me do it. Instead, I would use opportunistic circuit theory, where I would apply a sequence of simple circuit manipulations, involving one or two circuit elements at a time. Specifically, I would : 1. Do a series ...
... Mind you, I would never solve the example circuit by nodal analysis unless someone made me do it. Instead, I would use opportunistic circuit theory, where I would apply a sequence of simple circuit manipulations, involving one or two circuit elements at a time. Specifically, I would : 1. Do a series ...
Additional High Input Low Output Impedance Analog Networks
... configurability gives rise to the possibility of several electronic functions from a single topology, cascadability results in practical utility of analog blocks for designing more complex networks without additional coupling elements in form of buffers [4–6]. The most recent analog circuit topology ...
... configurability gives rise to the possibility of several electronic functions from a single topology, cascadability results in practical utility of analog blocks for designing more complex networks without additional coupling elements in form of buffers [4–6]. The most recent analog circuit topology ...
Chapter 6 Parallel Circuits
... When two equal sources are connected in parallel Each source supplies half the required current ...
... When two equal sources are connected in parallel Each source supplies half the required current ...
Chapter 4 Powerpoint
... – Where labels won’t fit on the device, draw a simple diagram of each device that indicates how each port is used – Use names that are as descriptive as possible – Use established naming conventions Network+ Guide to Networks, 7th Edition ...
... – Where labels won’t fit on the device, draw a simple diagram of each device that indicates how each port is used – Use names that are as descriptive as possible – Use established naming conventions Network+ Guide to Networks, 7th Edition ...
Transactions Briefs HS3-DPG: Hierarchical Simulation for 3-D P/G Network Researchers
... models (SRPMs) to replace some tiers of 3-D P/G network that can also help to mitigate the conflict between data sharing and chip protection. Nevertheless, the key issue is how to build SRPM for each tier. A voltage propagation method for static 3-D P/G network analysis was proposed in [15]. However ...
... models (SRPMs) to replace some tiers of 3-D P/G network that can also help to mitigate the conflict between data sharing and chip protection. Nevertheless, the key issue is how to build SRPM for each tier. A voltage propagation method for static 3-D P/G network analysis was proposed in [15]. However ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.