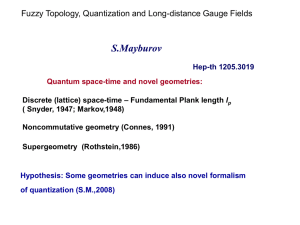
From Gutzwiller Wave Functions to Dynamical Mean
... Since the results of the Gutzwiller approximation describe correlated, paramagnetic fermions with a renormalized kinetic energy one can make contact with Landau’s Fermi liquid theory [32, 30]. In particular, it turns out that the reduction factor q in (15) describes the discontinuity of the momentum ...
... Since the results of the Gutzwiller approximation describe correlated, paramagnetic fermions with a renormalized kinetic energy one can make contact with Landau’s Fermi liquid theory [32, 30]. In particular, it turns out that the reduction factor q in (15) describes the discontinuity of the momentum ...
Kinematics Multiples
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
... This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you look at the graph closely, you will see that the FORCE of spring 2 increases with displacement faster than the force for spring 1. ...
protocol stripping/de-encapsulation
... traverses another network (which also uses MPLS labeling). Such traffic can traverse more than one network. Stripping, or de-encapsulation, removes all MPLS labels from each packet, including single labels, double-stacked, and n-stacked labels. Up to nine MPLS inner most labels can be specified to h ...
... traverses another network (which also uses MPLS labeling). Such traffic can traverse more than one network. Stripping, or de-encapsulation, removes all MPLS labels from each packet, including single labels, double-stacked, and n-stacked labels. Up to nine MPLS inner most labels can be specified to h ...
Energy loss by a fast charged particle moving parallel to a surface
... will be due to the imaginary part of the denominator of the second term in (1I), which is related to the frequency v of collision of the electrons of the medium and to the imaginary part of the above-mentioned denominator, which is proportional to v,. This latter imaginary part will be most importan ...
... will be due to the imaginary part of the denominator of the second term in (1I), which is related to the frequency v of collision of the electrons of the medium and to the imaginary part of the above-mentioned denominator, which is proportional to v,. This latter imaginary part will be most importan ...
Introducing surface tension to spacetime
... Figure 1. Geometry of an arbitrary matter distribution in a small volume of spacetime displaying membrane-like properties Consider the same matter distribution from a relativistic perspective. At the start of most physics problems/experiments, clocks are typically set to zero. At the instant clocks ...
... Figure 1. Geometry of an arbitrary matter distribution in a small volume of spacetime displaying membrane-like properties Consider the same matter distribution from a relativistic perspective. At the start of most physics problems/experiments, clocks are typically set to zero. At the instant clocks ...
Inverted Pendulum
... frequency vs. amplitude length vs. amplitude angle in time (two cases); • inverted pendulum • “inverted” inverted pendulum – for drag determination ...
... frequency vs. amplitude length vs. amplitude angle in time (two cases); • inverted pendulum • “inverted” inverted pendulum – for drag determination ...
Second-Order Linear Differential Equations
... One of the many applications of linear differential equations is describing the motion of an oscillating spring. According to Hooke’s Law, a spring that is stretched (or compressed) y units from its natural length l tends to restore itself to its natural length by a force F that is proportional to y ...
... One of the many applications of linear differential equations is describing the motion of an oscillating spring. According to Hooke’s Law, a spring that is stretched (or compressed) y units from its natural length l tends to restore itself to its natural length by a force F that is proportional to y ...
Quantum Effects in Condensed Matter Systems in Three, Two, and
... Field Theory of Two Point Contact Interferometers of Arbitrary ...
... Field Theory of Two Point Contact Interferometers of Arbitrary ...
Structural Dynamics Introduction
... Before considering how this dynamic equation can be solved let us consider the various terms, or at least some of the components of the terms. The matrix [K ] is the stiffness matrix of the structure, hence, it is completely defined by the structure and should be relatively easy to calculate, either ...
... Before considering how this dynamic equation can be solved let us consider the various terms, or at least some of the components of the terms. The matrix [K ] is the stiffness matrix of the structure, hence, it is completely defined by the structure and should be relatively easy to calculate, either ...
Part2 - Physics 3
... time it takes for a glider released from rest on an inclined 2.00-m-Iong air track to travel various distances. (An air track is a virtually frictionless track.) They tilt the track by putting a 2.0-cm-thick notebook under the legs at one end of the track. They release the glider from the middle of ...
... time it takes for a glider released from rest on an inclined 2.00-m-Iong air track to travel various distances. (An air track is a virtually frictionless track.) They tilt the track by putting a 2.0-cm-thick notebook under the legs at one end of the track. They release the glider from the middle of ...
Document
... A large truck has more momentum than a car moving at the same speed because it has a greater mass. Which is more difficult to slow down? The car or the large truck? ...
... A large truck has more momentum than a car moving at the same speed because it has a greater mass. Which is more difficult to slow down? The car or the large truck? ...
Wave packet
.gif?width=300)
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short ""burst"" or ""envelope"" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation. It is possible to deduce the time evolution of a quantum mechanical system, similar to the process of the Hamiltonian formalism in classical mechanics. The dispersive character of solutions of the Schrödinger equation has played an important role in rejecting Schrödinger's original interpretation, and accepting the Born rule.In the coordinate representation of the wave (such as the Cartesian coordinate system), the position of the physical object's localized probability is specified by the position of the packet solution. Moreover, the narrower the spatial wave packet, and therefore the better localized the position of the wave packet, the larger the spread in the momentum of the wave. This trade-off between spread in position and spread in momentum is a characteristic feature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,and will be illustrated below.